What Is Capacity Management – Guide & Best Practices (2026)
Capacity management is how you make sure you have the right people, time, and budget available for the work you have now, and the work that is coming next.
In this guide, we explain what this discipline means for agencies and service teams, how your capacity plan and process works in practice, and which metrics you need to track.
You will also see capacity and resource planning strategies, examples, and tools you can use to make better decisions about hiring, budgeting, and scheduling.
Key Takeaways
- A solid Capacity plan is essential for optimizing resources in service-providing agencies, including managing teams, their time, and project finances.
- In IT services, this discipline ensures that infrastructure is aligned with business demands to ensure stable and efficient system performance.
- The benefits of managing capacity include balanced resource utilization, increased efficiency, and improved service delivery. Effective strategies for managing capacity enhance operations and contribute to sustained business growth.
- Adopting comprehensive resource planning software, like Productive, enables teams to manage their capacity while integrating it with other key business operations. This supports streamlined daily processes and strategic decision-making based on reliable, real-time data.
Free Capacity Planning Template
Download our template to schedule time for billable vs non-billable tasks, track workloads, and get insights into utilization with preset formulas.

What Is Capacity Management?
Capacity management is the ongoing process of matching your available resources, such as people, time, and budget, to current and future work. The simplest way to describe this discipline for agencies is making sure you can deliver on every project without overloading your team or eroding margins.
When it comes to IT service management specifically, this discipline in IT focuses on infrastructure instead of people. The main processes include monitoring the performance of IT services and systems to ensure that capacity is adjusted to current or future demand.
This article will focus on the general process of planning and using capacity in agencies, but we’ll discuss capacity work in IT in more detail in the later sections. To learn more, check out our IT Capacity Planning Guide.
What Is an Example of Capacity Management?
An example of capacity management is checking next quarter’s projects against the skills and availability of your team before you agree to a new retainer. If you see that senior designers are already close to fully booked, you can move dates, shift work to another office, or hire a freelancer instead of saying yes and hoping it works out.
In Productive, you can see this in a single view, because project budgets, resource planning, and forecasted utilization sit in the same place. That makes it much easier to model a scenario, see the impact on revenue and workload, and then commit to a realistic plan.
Manage capacity with Productive
Capacity Management vs Resource Management
Another part of this discipline that might be confusing is its frequently synonymous terms. One of these is resource management. Certain resources might make a distinction between the two, along the lines of:
- Managing capacity is a strategic process that considers future projects and growth.
- Resource planning is an operational process that deals with day-to-day allocation.
These two can functionally be considered the same, as any process that deals with resource capacity will need to consider both of these practices. Therefore, this article treats these terms as synonymous.
Read more in our guide to project resource management tools for balancing agency resources
Capacity Management vs Capacity Planning
Another popular pair of synonyms is managing capacity vs capacity planning. In this dichotomy, people usually describe the difference as:
- Capacity management concerns handling current and future capacity to ensure availability.
- Resource planning is focused on processes such as forecasting, gap analysis, and day-to-day planning.
As you can see, there’s a lot of similarity between this and the comparison with resource management, though the exact definition of the term changes depending on the source. There are other attempts at differentiation, which define this discipline as the umbrella term and the planning work as the subordinated concept.
In any case, accounting for the slight differences in this terminology is a thankless job. In practice, they will usually be used interchangeably. As with the previous comparison, the two terms will be treated as indistinguishable in this article.
What Are the Benefits of Managing Capacity Well?
The main benefits of managing capacity are more predictable workloads, healthier teams, and more profitable projects. When you review capacity regularly, you can see where people are overloaded or underused, reassign work before problems escalate, and make clearer decisions about which projects to prioritize.
Why Is Managing Capacity Important?
Managing capacity is important because it connects your resources to real client demand, so you can deliver work on time without overspending or burning people out. When you actively manage capacity, you reduce bottlenecks, protect profitability, and make better decisions about hiring, pricing, and which projects to accept.
These benefits reflect in service teams as better project delivery, happier team members, and more predictable profits. It is one of the foundational processes of agency project management.
Effective resource planning ensures that your resources are used efficiently, so there are no gaps that can disrupt the project delivery process.
It also aims to achieve balanced utilization, meaning employees are not overworked or underworked. This can otherwise lead to dissatisfaction, reduced productivity, and even turnover.
A simple example of this discipline in practice is checking next month’s projects against available hours before you agree to a new retainer.
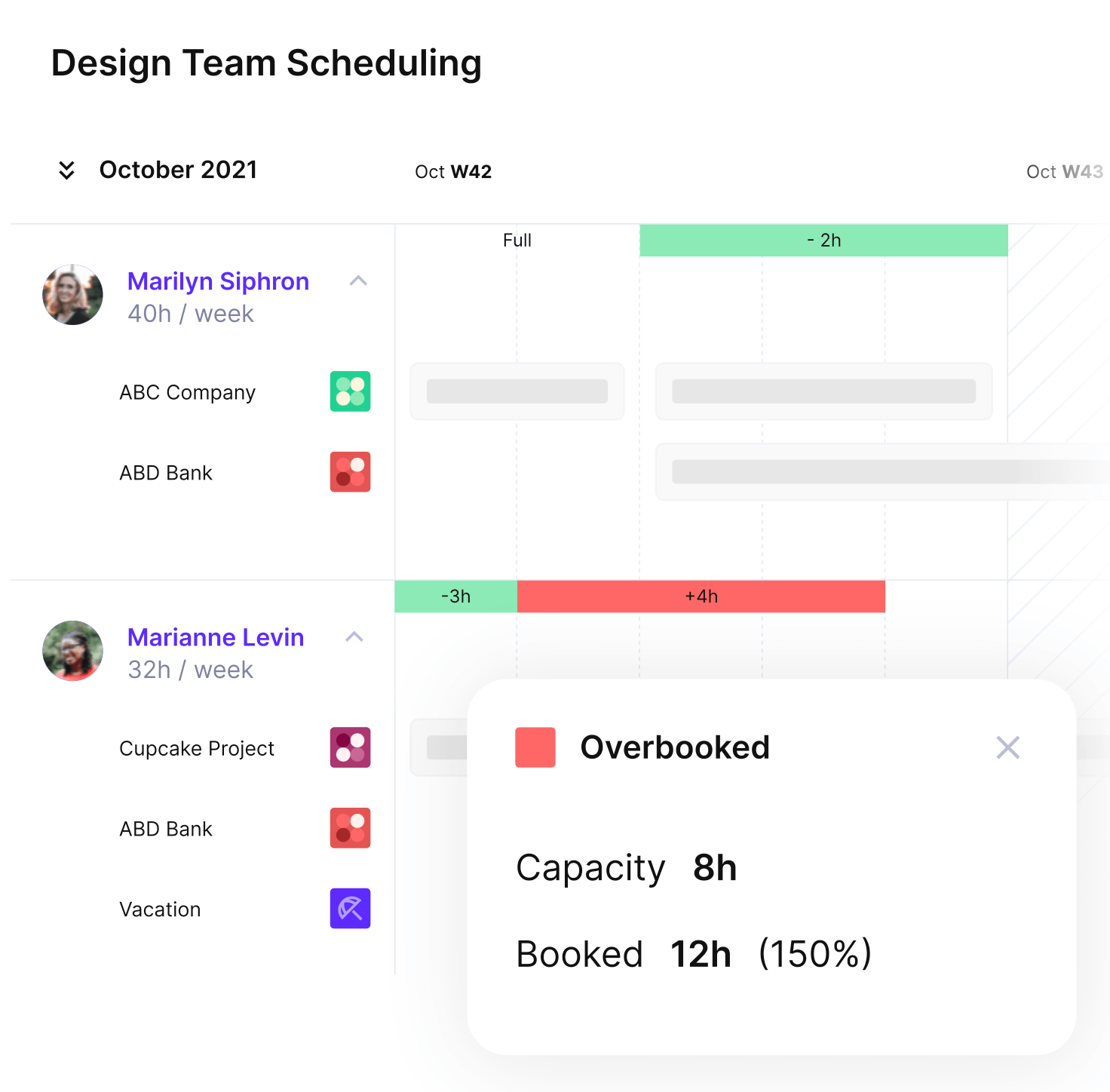
PRODUCTIVE HELPS YOU BALANCE YOUR TEAM’S WORKLOADS
In ITSM, capacity management helps ensure that businesses can meet their SLA compliance, as well as avoid system downtime by anticipating needs and avoiding overload. It provides increased IT system reliability and performance.
In general, we can summarize enterprise resource planning advantages as:
- Balanced resource utilization
- Increased efficiency
- Improved service delivery
- Enhanced agency operations
What Is a Capacity Management System?
A resource capacity management system is the set of tools, capacity management tools, and processes you use to plan, schedule, and monitor how your people and budgets are used across projects. In many companies, this system is still spread across spreadsheets and disconnected apps.
The aforementioned study by Prosymmetry reports that the vast majority of agencies with a resource management system use a dispersed approach, with only 38% having a centralized platform.
These findings are corroborated by a SoDa & Productive research, which reports that 52% of agencies use disparate tools for their management, with only 14% having an integrated tool that allows for real-time insights.
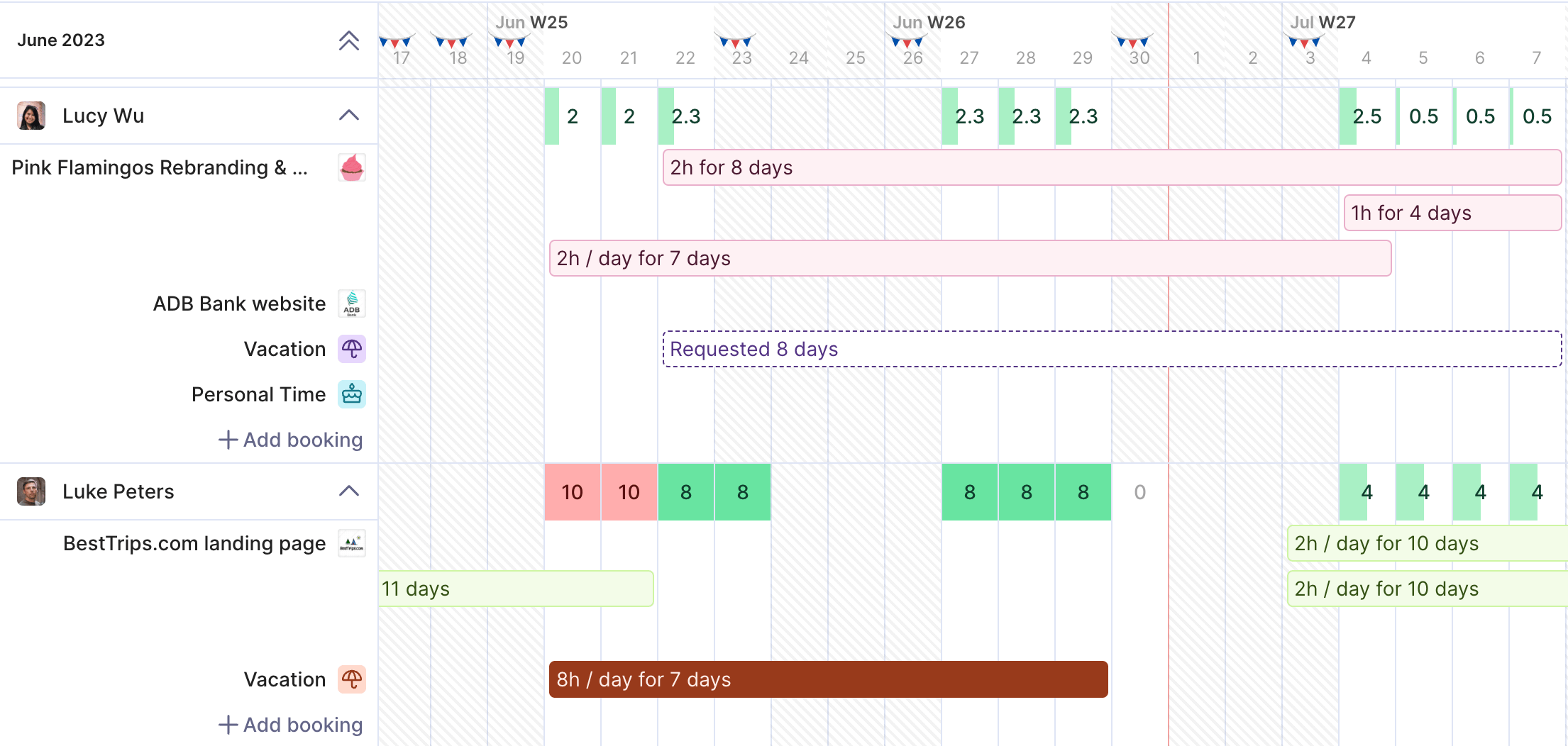
Manage all resources, capacity, workloads and forecasts from Productive.
We can generally distinguish types of resource planning and resource management software depending on their comprehensiveness. More specialized resource scheduling software solutions usually provide features that support resource allocation and utilization insights for agencies.
When it comes to integrated solutions, these types of tools combine human resources and financial management with additional collaboration features for project management. A popular example of an all-in-one tool is Productive.
Consider the benefits of comprehensive tools outlined by Brendon Nicholas, the Co-founder of DotDev, an Australian-based product development company:
That was probably the single biggest thing—reducing the amount of tools, platforms, and systems, and using just one. Having a platform that considers everybody’s salaries, the operating expenses of the whole business, and feeding that into project budgets and looking at the internal time vs. client time gives us a much more real-time and accurate view of the profitability of actual, specific projects.
Read the full story of DotDev’s growth of 50% YoY for the past three years.
What Are the Best Practices of Managing Capacity?
The best practices of managing capacity in agencies focus on a simple process you can repeat every week. The core strategies are identifying imbalances, optimizing allocation, and forecasting future demand so you always know whether you can take on more work.

Best Practice 1: Manage excess capacity before it becomes a problem
Excess capacity can happen for various reasons. The volatile nature of client projects may result in sudden spikes of intensive work, with similarly unexpected periods of low utilization. Though it can be difficult to prevent uneven customer demand, there are some common strategies to manage it.
These strategies include:
- Employing a flexible workforce with freelancers or contractors
- Diversifying services to cater to various market segments
- Investing in training during periods of low demand to maintain competitiveness
- Pushing for more retainer projects to ensure more predictable revenue
In Productive, you can see upcoming bookings and unassigned time in your resource plan, which makes it easier to redirect idle capacity to training, internal projects, or sales work instead of letting it go to waste.
Bonus Advice: How can agencies use their capacity more efficiently?
Agencies can use their capacity more efficiently by combining flexible staffing, diversified services, and proactive training with clear visibility into skills and workloads. When you can see who is available, what work is coming up, and where gaps appear, it becomes easier to move people between projects instead of leaving capacity idle.
All of these strategies have their own particular benefits and downsides. What can be managed more easily is underutilization caused by weak internal resource management.
Ensuring that you have a full understanding of your workforce – their skills, abilities, and workloads – can help you get the most out of your agency’s resources. Advanced resource management software can help you achieve these goals.
Best Practice 2: Spot capacity constraints before they affect delivery
On the flip side of excess resources are capacity constraints. These can occur for various reasons, one of which can be overcommitment to client projects without regard to actual resource availability. Another reason can be a poorly implemented lag strategy, where you add people only when demand has already exceeded availability.
The consequences can be significant, as it usually leads to overburdening your employees, causing burnout, reduced efficiency, and decreased quality of deliverables.
With Productive’s scheduling and budgeting views, you can see when a role or person is overbooked and adjust timelines, staffing, or scope before bottlenecks hit your projects.
Identifying resource gaps in time is essential for uninterrupted operations. During project initiation and planning, consider historical data on similar projects to predict where bottlenecks may occur. Techniques such as workflow analysis and capacity requirement planning can support this process.
Best Practice 3: Optimize allocation with clear utilization targets
Alongside managing resource gaps and excess capacity, another key step in optimizing your allocation on a daily basis is monitoring utilization.
Utilization is one of the key metrics, as it shows how efficient and effective your workforce planning is. It is the ratio of billable hours worked or client tasks delivered against total hours worked. Industry benchmarks recommend utilization of around 70 to 90%, though this depends on the seniority and position of each employee.
In general, you should balance billable and non-billable tasks. Non-billable work such as pitching for new projects or expanding your employees’ skill sets can also be crucial to improving performance and growth.
In Productive, utilization reports connect time entries, budgets, and roles, so you can see which teams are overbooked or underused and adjust assignments to hit your targets without overscheduling people.
Learn more about managing your utilization in crisis times:
Best Practice 4: Forecast future demand with real project and sales data
When it comes to demand and resource forecasting, this process is key for both current and upcoming client engagements. Forecasting for ongoing projects can help you see the actual state of your project financials. For example, you can check your profit margins to determine whether you are overcommitting to a client to your detriment.
We ended up terminating contracts with two of our oldest clients after only a few months of using Productive. We thought that we were at least at zero with them, or that we had some small earnings, but it turned out that we were losing money because the money they paid us did not cover salaries, fixed overhead per hour, and variable overhead per hour.
For future client engagements, forecasting metrics such as utilization can help you decide if you have enough capacity to meet client demand. The main challenge of forecasting is dealing with uncertainties such as sudden changes in market trends. However, having a firm grasp on your availability can help reduce the risk of underutilization or overextension of resources.
Productive’s budgeting and forecasting features let you project revenue, margins, and workload from your current pipeline and booked projects, so you can see sooner if you need to hire, slow down sales, or adjust pricing.
How Can You Measure the Success of Your Capacity planning?
You measure the success of your capacity efforts by tracking clear KPIs and reviewing them regularly. To be able to react in time to internal or external changes, you need to continuously monitor the processes discussed above and run regular review sessions to identify and respond to potential areas for improvement.
One of these key metrics is utilization, but there are more ways to gauge whether your initiatives are successful. This is often called return on investment or ROI.
The main challenges include collecting relevant data and accessing it in time. Using modern capacity planning software makes this easier by bringing your data into one place.
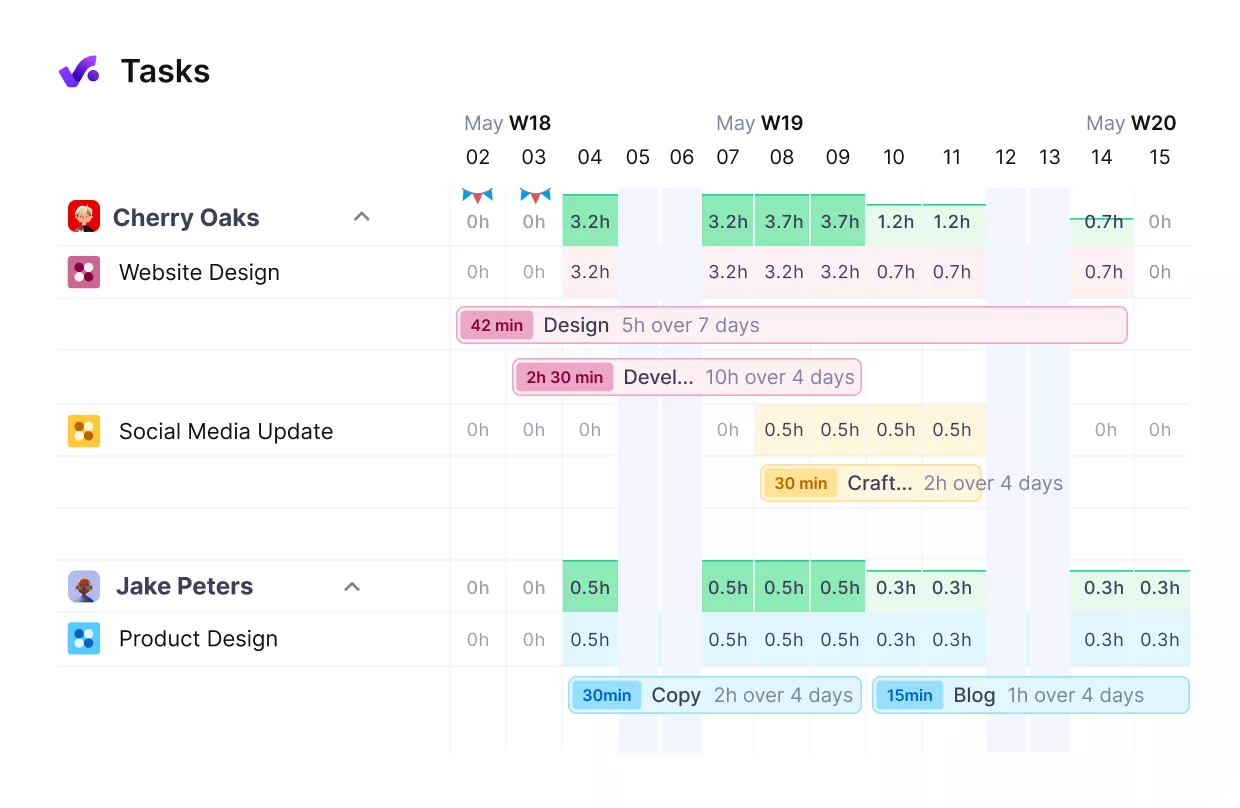
Get real-time overview of your team’s workloads.
Which Capacity Metrics Should You Track?
The main capacity metrics you should track include a mix of utilization, time accuracy, and financial indicators:
- Utilization Rate: Measures the percentage of capacity actually used out of the total available. It’s calculated by dividing billable hours by the total available capacity, i.e., working hours. In Productive, you can get forecasted utilization rates to guide your business strategies.
- Estimated vs Actual Time by Business Unit: Compares the projected time frames set for tasks or projects against the actual time taken to complete them within each business unit. This helps identify discrepancies in resource scheduling, enabling agencies to refine their forecasting and capacity management across different departments.
- Budget Burn: Measures the rate at which an organization or project consumes its allocated budget over a specific period. Productive allows you to set up automated warnings, where you can input thresholds for billable hours delivered to stay in touch with your agency’s progress. You can also forecast your budget burn to get actionable insights into project financials.
And yes, there’s a capacity planning metrics guide that will teach you how to track and optimize your KPIs.
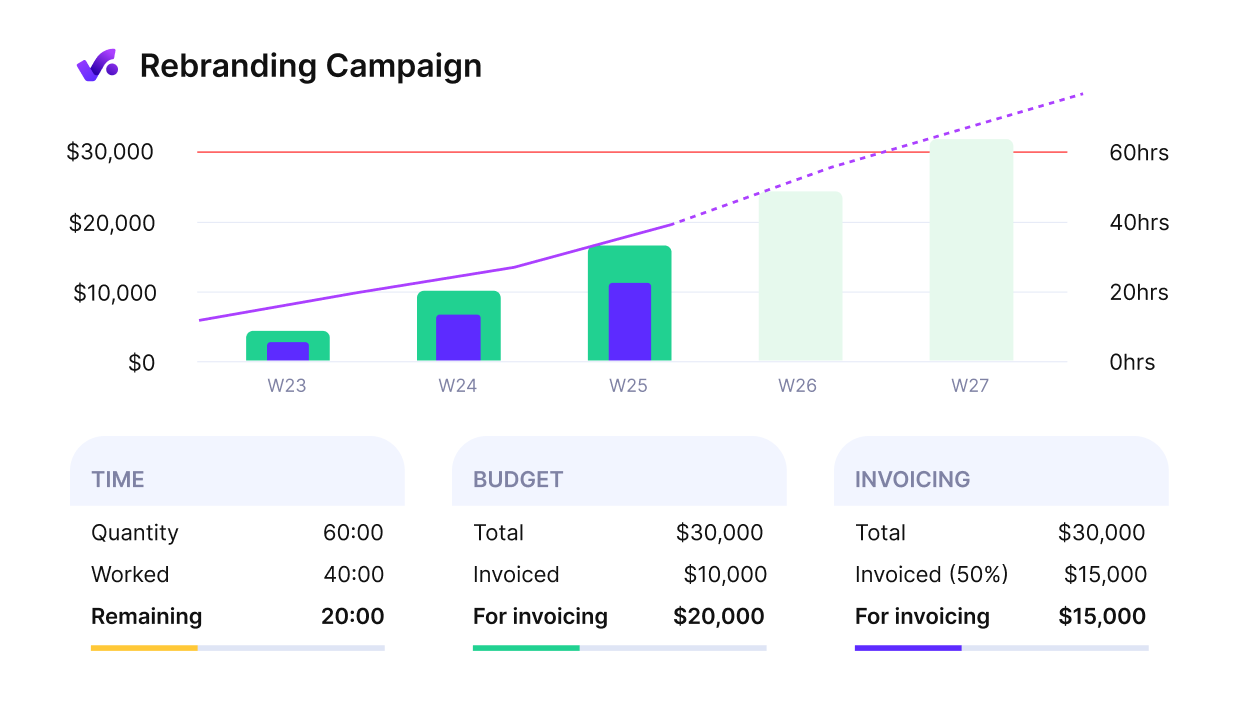
Get early warnings of budget overruns.
What Is Capacity Management in IT?
Capacity management in IT is a critical discipline within IT service management. It ensures that an organization’s IT infrastructure and other technological resources can meet current and future demands.
It involves processes such as monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing the use of IT resources to ensure efficient operation and prevent performance bottlenecks.
The main steps of the process include:
- Business Capacity Management: Ensuring the future business requirements for IT services are considered, planned, and implemented in a timely fashion.
- Service Capacity Management: Monitoring, analyzing, and managing the performance of IT services, such as web, hosting, cloud computing, or online transaction processing.
- Component Capacity Management: Managing the capacity of individual IT components, including servers, storage devices, operating systems, and various virtual resources.
The benefits of Capacity and performance management in IT include improved system performance, cost-effective processes, and enhanced user satisfaction.
IT Capacity Planning KPIs
- Performance vs. Capacity: Tracks the relationship between system performance and capacity, helping identify when additional resources are needed to maintain optimal performance levels.
- Forecast Accuracy: Compares predicted resource requirements with actual usage to gauge the accuracy of capacity forecasts, which is essential for improving future planning efforts.
- Service Availability: Monitors the availability of IT services, ensuring that capacity issues do not cause downtime or service interruptions. This KPI is essential for maintaining high service levels and user satisfaction.
Should You Integrate Capacity Work With Other IT Services?
Absolutely. Integrating capacity planning with other IT services, such as incident management, change management, and business continuity planning, ensures that capacity considerations are embedded in the lifecycle of IT services.
This helps keep overall service delivery stable and effective and increases operational efficiency. It also enables proactive identification of capacity-related issues and ensures that this function is aligned with the organization’s strategic goals.
See and Manage Your Capacity in Real-Time
Get a clear picture of who is available, who is overloaded, and where you have hidden capacity. Productive connects projects, time, and budgets so you can manage capacity with real data.
How Should You Manage Your Capacity Planning Process?
You should manage your capacity planning process in a way that keeps resource allocation aligned with strategic goals and overall business priorities.
Whether you’re dealing with an agency environment or IT services, the goal is the same: support sustainable, continuous growth without burning out your team members or eroding margins.
If you’re having thoughts about upgrading your capacity game, while fixing bottlenecks and improving visibility, booking a demo is the smartest way of getting started.
FAQ
What are the 3 components of capacity management?
The three main components or steps in the capacity management process include planning or forecasting future resource requirements; performance management or monitoring of current resources and their allocation; and capacity analysis for understanding and improving your processes.
What are the 5 capacity management strategies?
Capacity management strategies deal with balancing resources effectively to ensure that your supply meets market demand. These include identifying excess capacity, managing constraints in current capacity or capacity gaps, performance management, resource optimization, and forecasting future needs.
How does managing capacity support business growth?
Good planning and management of capacity is one of the basic disciplines for supporting effective business processes. It ensures that your resources are balanced across various projects or initiatives, promoting efficiency and helping you control costs. It also aims to mitigate risks with forecasting, as well as support change management in case of unexpected internal or external factors, so you can grow without losing control of delivery quality or margins.
What is the role of a capacity manager?
The role of a capacity manager is to make sure that resources are well-matched to meet current and future demand. This includes monitoring allocation, measuring performance through key performance indicators (KPIs), identifying disruptions and reallocating capacity, and forecasting upcoming demand.
Connect With Agency Peers
Access agency-related Slack channels, exchange business insights, and join in on members-only live sessions.

