Top 25 Project Management Skills You Need in 2026
Successful project managers blend technical expertise with strong people skills, but these abilities aren’t innate. You can learn and develop project management skills throughout your career.
By the end of this article, you’ll know the essential skills for managing projects in 2026 and how to develop your own leadership abilities.
Key Takeaways
- Project managers combine technical expertise (like budgeting and scheduling) with interpersonal abilities (like communication and leadership) to deliver successful projects.
- Hard skills include planning, risk assessment, and cost management, while soft ones are about team guidance and stakeholder communication.
- Proficiency with modern PM tools like Productive increases workflow efficiency in managing project timelines.
- Understanding methodologies like Agile, Scrum, and traditional Waterfall helps you stay adaptable to different project requirements.
What Are Project Management Skills?
Project management skills are abilities managers need to successfully initiate, plan, execute, monitor, and complete projects within time, budget, and quality standards. In other words, they’re what PMs need to lead their teams to get the job done.
These skills fall into three primary categories: hard (e.g., scheduling and budgeting), soft (e.g., communication), and technical skills (e.g., software proficiency and data analysis).
Mastering this combination improves your ability to deliver successful projects and makes you more valuable to any organization.
Definition and Importance
Project management skills are more than just a professional checklist — they’re what separates successful execution from wasted resources.
Their importance isn’t theoretical. According to PMI’s Job Growth and Talent Gap Report 2021–2031, demand for project management-oriented roles is expected to grow by 2.3 million new positions each year through 2030.
Companies aren’t just hiring project managers — they’re investing heavily in people who can lead initiatives, navigate change, and deliver measurable outcomes.
“Employment in project management-oriented occupations (PMO) is expected to grow by 33 percent through 2027.”
(PMI, Job Growth and Talent Gap Report 2021–2031, page 5)
Without strong project management skills, even the best ideas get lost in missed deadlines, budget overruns, and misaligned teams. With them, organizations can drive innovation, manage risk proactively, and turn strategic goals into reality — even in volatile, fast-moving industries.
Whether you’re leading a major digital transformation or coordinating a small team initiative, mastering these gives you a critical edge: the ability to deliver results consistently, even when everything doesn’t go according to plan.
What Are the Project Management Skill Types?
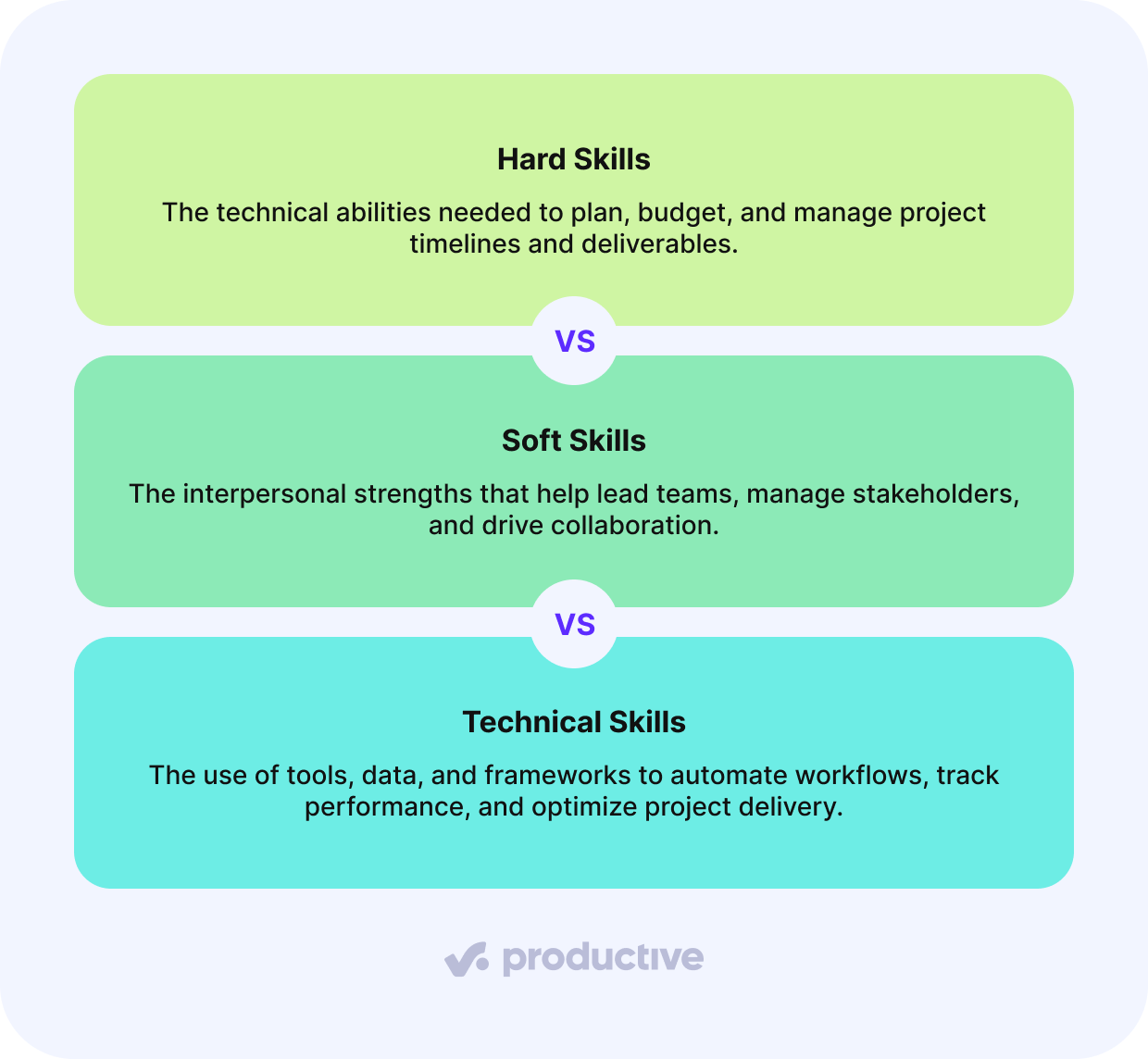
Project management skills can be categorized into three primary types: hard, soft skills, and technical skills, each playing an key role in successful project execution.
Hard skills are concrete, measurable abilities like budgeting, risk management, and forecasting that keep project management effective.
Soft skills, including communication, guidance, and adaptability, complement your technical know-how by enabling you to work well with different interpersonal dynamics.
Technical skills like project scheduling, critical path analysis, and workflow automation provide the specialized knowledge needed to implement complex projects with efficiency.
A successful project manager must possess a blend of strong personality traits like responsibility and commitment to ensure project deliverables meet expectations and deadlines.
Hard Skills
Hard skills include project initiation and planning expertise (understanding methods like Agile project management or Lean), scheduling and control capabilities (using WBS, Gantt charts, and Kanban boards), risk management proficiency, technical tool knowledge (from Productive to Microsoft Project), and data literacy skills that enable automation and process improvement.
Soft Skills
Soft skills are about mastering interpersonal dynamics and complementing technical project management skills with essential human-centered capabilities.
These include communication for stakeholder coordination, leadership to guide teams toward objectives, conflict management to resolve disputes, and emotional intelligence to cultivate healthy collaboration.
Throughout the project lifecycle, you’ll need relationship-building abilities, active listening, and negotiation to manage expectations and maintain stakeholder engagement.
Technical Skills
Technical expertise equips you with the tools and methodologies needed to execute projects successfully.
These include proficiency in project scheduling, risk management, budgeting, and various methodologies like Agile and Waterfall. You’ll also need industry-specific knowledge, data analysis capabilities, and strategic planning expertise to align technical solutions with business objectives.
Who Needs Essential Project Management Skills?
Project management skills are a must-have for every employee who needs to efficiently coordinate individual tasks, manage resources, and deliver successful outcomes.
Whether you’re in healthcare, technology, construction, or finance, these skills are universally valuable across all industries and professional roles.
Companies recognize that employees equipped with project management expertise contribute greatly to organizational success, which explains why these competencies often translate into higher earning potential and expanded professional opportunities.
Different Industries and Roles
As we said earlier, these versatile abilities serve professionals in diverse sectors, from construction and IT to healthcare and finance, where they’re expected to coordinate complex initiatives and drive results.
Key industries that require management expertise include:
- Construction and engineering – coordinating architects, engineers, and construction crews.
- IT and technology – overseeing software development and infrastructure initiatives.
- Healthcare – managing compliance issues and system integration.
Beyond dedicated PMs, these abilities benefit team leaders, business analysts, and executives who must efficiently organize resources, manage timelines, and deliver measurable results in super-competitive project environments.
Career Progression Opportunities
These skills will push your career progression forward. They can also help you strategically plan your professional development.
Your journey typically begins with entry-level positions focused on supporting established project managers before advancing to different managerial roles with greater responsibility and autonomy.
| Career Level | Typical Roles | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | Project Assistant, Coordinator | CAPM certification, soft skills |
| Mid-Level | Project Manager, Implementation Manager | PMP certification, leadership experience |
| Senior | Senior PM, Head of Projects | Strategic thinking, multiple project oversight |
| Executive | Director, VP of Project Management | Organizational strategy, industry expertise |
Continuous learning and certification are key ingredients for advancement, while developing specialized knowledge in particular methods or industries can accelerate your career trajectory.
Core Project Management Hard Skills
Project management hard skills revolve around the technical expertise you’ll need to effectively plan and execute projects from start to finish.
You’ll need to be good at project planning and scoping, budgeting and cost management, risk assessment, tracking and reporting progress, and managing time constraints.
These fundamental capabilities will allow you to deliver results on schedule and within budget, regardless of your industry or project type.

1. Project Planning and Scoping
Planning and scoping are blueprints for any project endeavor. When you master these, you’ll be able to establish clear direction, allocate resources effectively, and mitigate potential risks before they happen.
Successful project scoping requires:
- Defining very explicit boundaries and deliverables to prevent scope creep.
- Creating a thorough Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to organize activities logically.
- Documenting stakeholder requirements in a detailed project charter and establishing verification procedures.
Your ability to create concrete project plans and define scope accurately directly impacts project success.
These complementary processes guarantee all team members understand their responsibilities while maintaining alignment with organizational objectives.
2. Budgeting and Cost Management
Scoped work has its cost, that cost is a part of a greater budget and there should be no going overboard. PMs need to establish an accurate budget baseline using various estimation techniques like analogous, parametric, top-down, or bottom-up.
The estimating technique used depends on your project’s specific nature and available historical data.
- Once implemented, use cost control mechanisms like Earned Value Management to track performance against your baseline.
- Regular financial reporting and budget reviews enable you to identify variances early and make necessary adjustments.
- Integrate change control processes to manage scope modifications that impact actual costs.
Remember that successful cost management requires both predictive analytics for forecasting and clear stakeholder communication about financial status.
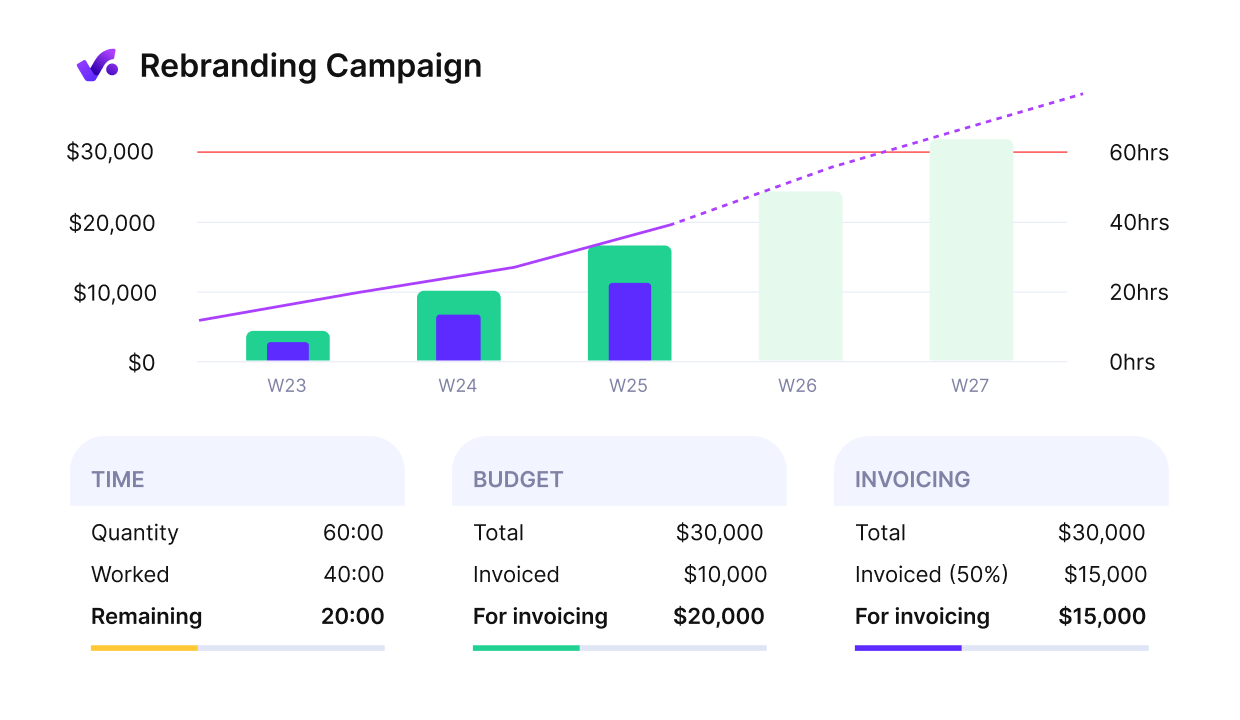
Track project spend and stay on course with Productive’s live budget burn charts.
3. Risk Management
Risk management is the buffer shield of your project. It safeguards objectives against uncertainty and potential threats throughout the project lifecycle.
When you systematically identify, analyze, and respond to potential risks, you’ll get better at decision-making (also one of the must-have PM skills) and improve project outcomes.
To implement effective risk management, you should:
- Develop a thorough risk register that documents identified risks, their probability, impact, and planned responses.
- Integrate risk analysis with cost, schedule, and quality management processes.
- Maintain a proactive approach by continuously monitoring risks and adapting strategies as project conditions evolve.
Remember that stakeholder engagement is essential—their diverse perspectives will strengthen your risk identification process and response planning.
4. Project Tracking and Reporting
Successful project execution stays successful when you maintain precise oversight and transparent communication using detailed tracking and reporting mechanisms.
Master tools like PPM Express, Microsoft Project, and Productive to effectively monitor task completion, milestones, and resource utilization across departments.
Your reporting arsenal should include status reports, variance analyses, and health assessments that keep stakeholders in the loop and aligned with project goals.
Focus on key PM metrics like task completion rates, budget and schedule variances, earned value, and cost variance to measure progress in actual numbers.
Implement dashboards and Gantt charts to visualize data, while critical path analysis helps identify timeline-critical activities that demand your immediate attention.
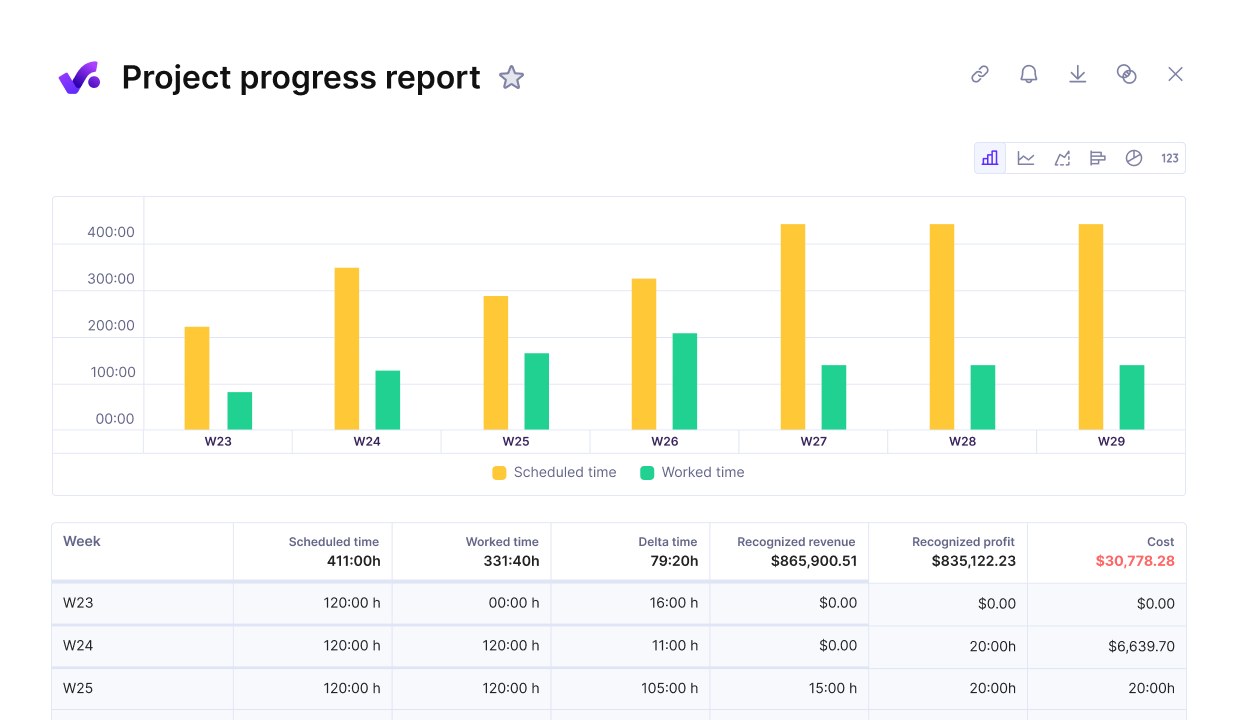
Visualize team performance with detailed progress reports.
5. Time Management
Time management allows you to push through complex timelines while balancing competing priorities. We’ve talked about estimation techniques already. Implementing them guarantees realistic schedules and prevents team burnout.
To be really good at time management, you should:
- Use the 80/20 rule to focus on high-impact activities that deliver the majority of your results.
- Include buffer time into your schedules to accommodate unexpected delays.
- Break large operations into manageable segments and track progress using visual tools like Gantt charts.
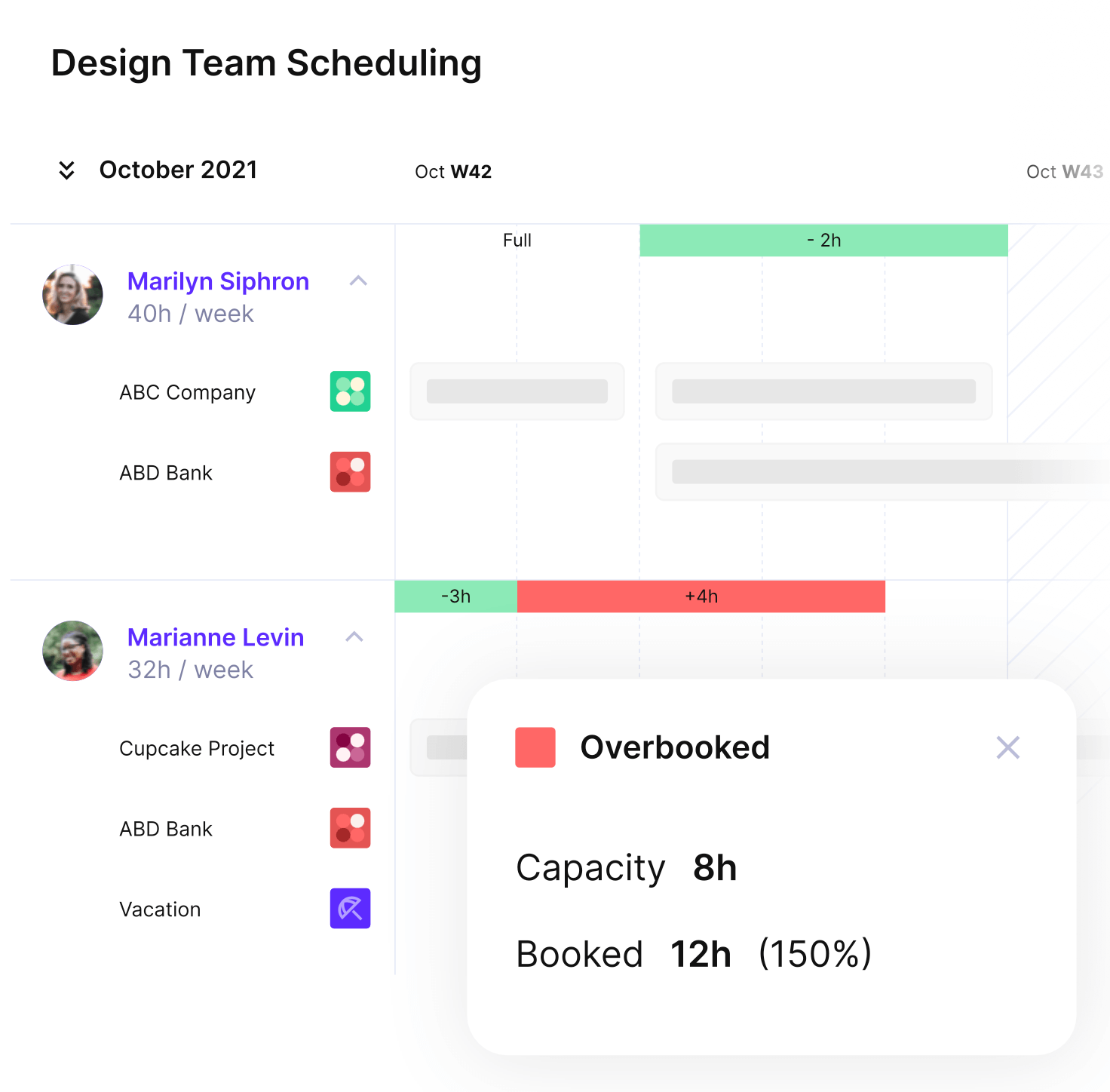
Balance team schedules and avoid overbooking with smart visual planners.
6. Task Management
While time management focuses on when work happens, task management centers on what work gets done and how. You’ll need to skillfully guide activities through their lifecycle—from ready to verified—while allocating resources and establishing clear priorities based on urgency and importance.
Effective work management requires understanding the interdependencies between activities to maintain workflow integrity. You should implement a structured approach using tools like Kanban boards or Gantt charts while ensuring each task has clear definitions and assigned responsibilities.
Regular status reporting enables better tracking and decision-making.
When you master task management, you’ll increase productivity, improve collaboration, and increase accountability across your team.
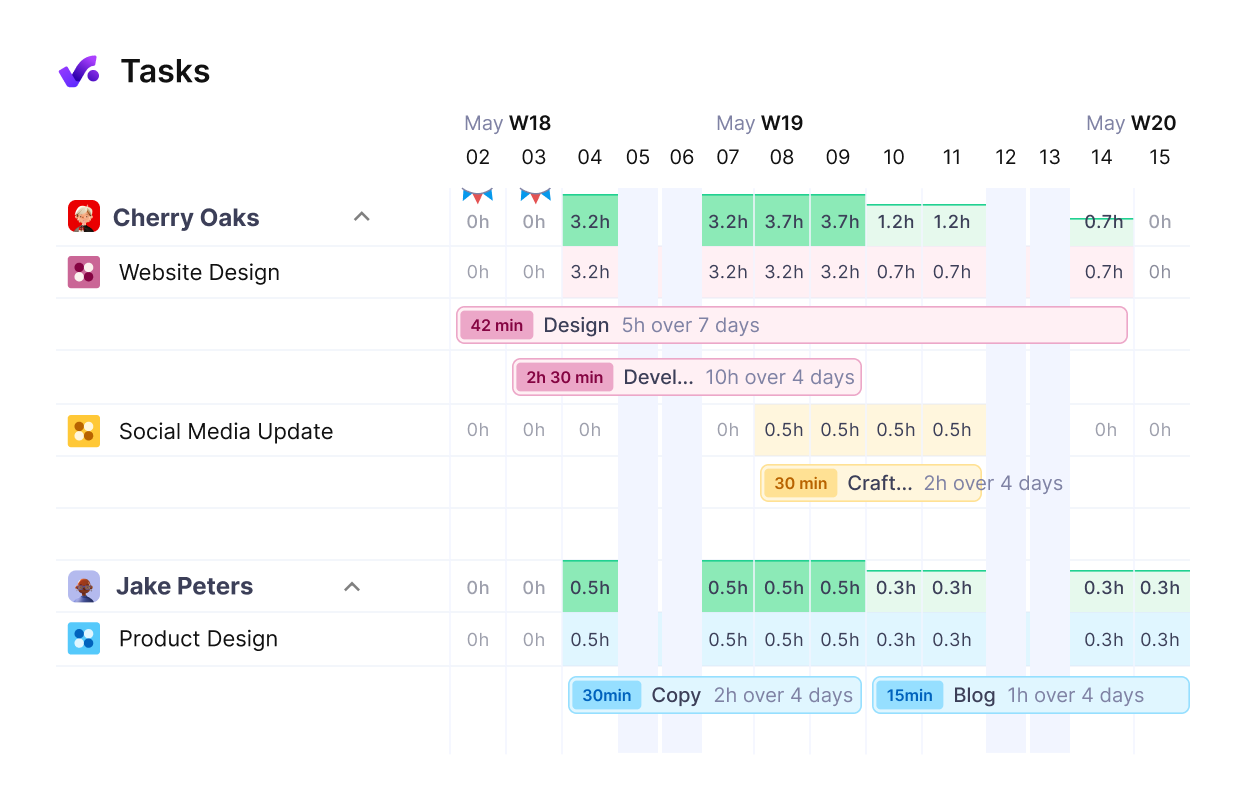
map out tasks, milestones, and deliverables in one visual timeline.
7. Change Management
Steering organizational change demands a distinct set of skills beyond traditional PM techniques. While project management focuses on technical processes and timelines, change management addresses the human factor—how to help teams adapt to and embrace new ways of working.
You’ll need to bridge the gap between outcomes and actual results by managing people’s shifts.
To improve your change management, develop these critical skills:
- Communication to clearly articulate the rationale and benefits of changes.
- Coaching abilities to support stakeholders through shifts.
- Strategic thinking to plan, implement, and reinforce sustainable change.
This people-focused approach reduces resistance, optimizes implementation, and greatly increases your project’s ROI.
Essential Project Management Soft Skills Overview
Soft skills do a lot more than complement technical expertise; one does not go without the other.
You’ll need to demonstrate that you’re a leader by inspiring your team with a clear vision and leading by example, communicating with clarity and empathy, and cultivating genuine collaboration through relationship-building and conflict-resolution techniques.
Additionally, your ability to solve complex problems creatively and adapt to shifting priorities will determine how successfully you rise above the inevitable challenges that arise throughout a project’s lifecycle.
1. Leadership
Genuine leadership is the heart of successful project management. It’s a multifaceted ability that goes above authority or position. Effective leaders balance vision-setting with team empowerment.
They adapt their approach as circumstances evolve while maintaining strategic alignment with organizational objectives.
To be a better leader, focus on developing:
- Emotional intelligence – understanding your team’s motivations and managing interpersonal dynamics.
- Situational awareness – flex your leading style based on project conditions and team needs.
- Decision-making proficiency – make informed choices quickly while maintaining integrity.
Your leading style directly impacts team morale, efficiency, and stakeholder relations—ultimately determining whether your project merely concludes or genuinely succeeds.
2. Communication
As a project manager, you’ll spend approximately 90% of your time engaging in communication-related activities, from hosting meetings to drafting thorough reports.
Your ability to adapt your communication style—whether through active listening, clear written documentation, or confident verbal delivery—directly influences stakeholder alignment and team morale.
Developing a robust communication plan that outlines channels, schedules, and responsibilities is key here.
Remember to have two-way dialogues, encourage feedback, and document key discussions to maintain transparency throughout your project’s lifecycle.
Use Productive’s AI features for faster documentation and clearer team communication.
3. Collaboration
Successful project management extends beyond individual communication to the broader dynamic of healthy collaboration among team members. Effective collaboration requires building trust and establishing shared approaches toward mutual objectives, enabling teams to innovate and execute projects more efficiently.
To foster collaborative environments, focus on:
- Active listening – Maintain engagement during interactions to guarantee thorough understanding with each stakeholder.
- Co-creation opportunities – Develop spaces where all contributions are valued and encouraged.
- Transparent communication – Implement open information exchange protocols that minimize misunderstandings.
When team members understand the context-specific nature of collaboration and align their priorities accordingly, projects benefit from diverse perspectives and coordinated efforts.
This leads to better results despite inevitable resource constraints.
4. Problem Solving
Effective problem solving consists of: accurate identification, systematic analysis, and decisive implementation of solutions.
You’ll benefit from developing expertise in recognizing potential issues before they escalate, clearly defining problems, and investigating root causes rather than symptoms.
- When tackling specific challenges, use data-driven approaches alongside creative thinking techniques like mind mapping and brainstorming.
- Structured frameworks such as Kepner-Tregoe can guide your decision-making process.
Remember that strong problem-solving capabilities directly impact your project’s efficiency, team morale, and stakeholder satisfaction while minimizing risks and optimizing resources.
Continuous learning and diverse perspectives will make your problem-solving toolkit sharper.
5. Adaptability
Adaptability helps project management professionals to go beyond uncertainty and thrive when inevitable changes happen.
To cultivate this must-have skill, you’ll need to embrace iterative work processes and maintain open communication channels with every project stakeholder.
Three key approaches to enhance your adaptability:
- Implement agile methodologies like Scrum that inherently support flexibility.
- Establish regular feedback loops to capture evolving requirements.
- Develop cross-functional teams that can quickly pivot when challenges arise.
The most successful managers recognize that adaptability isn’t just reacting to change—it’s anticipating it through continuous learning and proactive risk assessment.
6. Critical Thinking
While facing the complex project challenges, your ability to think critically separates mediocre management from exceptional guidance.
Critical thinking is an objective analysis of information to form sound judgments—enables you to make evidence-based conclusions that keep projects on track.
To become a great critical thinker, practice the five whys method (ask the question “why” five times) to uncover the root causes of problems, challenge your assumptions, and consider alternative perspectives before acting.
When you approach challenges with analytical rigor and open-mindedness, you’ll naturally improve risk management and prevent recurring issues. Your curiosity-driven mindset and reflective practice will lead to greater project success.
7. Conflict Resolution
Interpersonal friction is completely normal in any work environment, but it needs to be handled and put in place. Effective conflict resolution transforms potential disruptions into opportunities for innovation and team growth.
If and when tensions arise, employ these proven techniques:
- Active listening – Focus completely on understanding others’ perspectives before formulating your response.
- Problem-focused approach – Address the root cause rather than assigning blame, keeping discussions centered on solutions.
- Timely intervention – Identify conflict indicators early through observation of team dynamics and communication patterns.
8. Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are the human element that transforms technical competence into exceptional guidance. These capabilities enable you to communicate goals clearly while cultivating an environment where stakeholders feel heard and valued.
Your emotional intelligence helps you navigate team dynamics, building cohesive teams where members collaborate effectively despite diverse backgrounds. When people develop strong interpersonal connections, they create teams that consistently outperform expectations and adapt to changing circumstances.
“Ineffective communications is the primary contributor to project failure one-third of the time and has a negative impact on project success more than half the time.”
— PMI, Pulse of the Profession: The High Cost of Low Performance (2013)
This report underscores why your ability to negotiate, resolve conflicts, and engage stakeholders meaningfully determines delivery success more than any technical expertise alone.
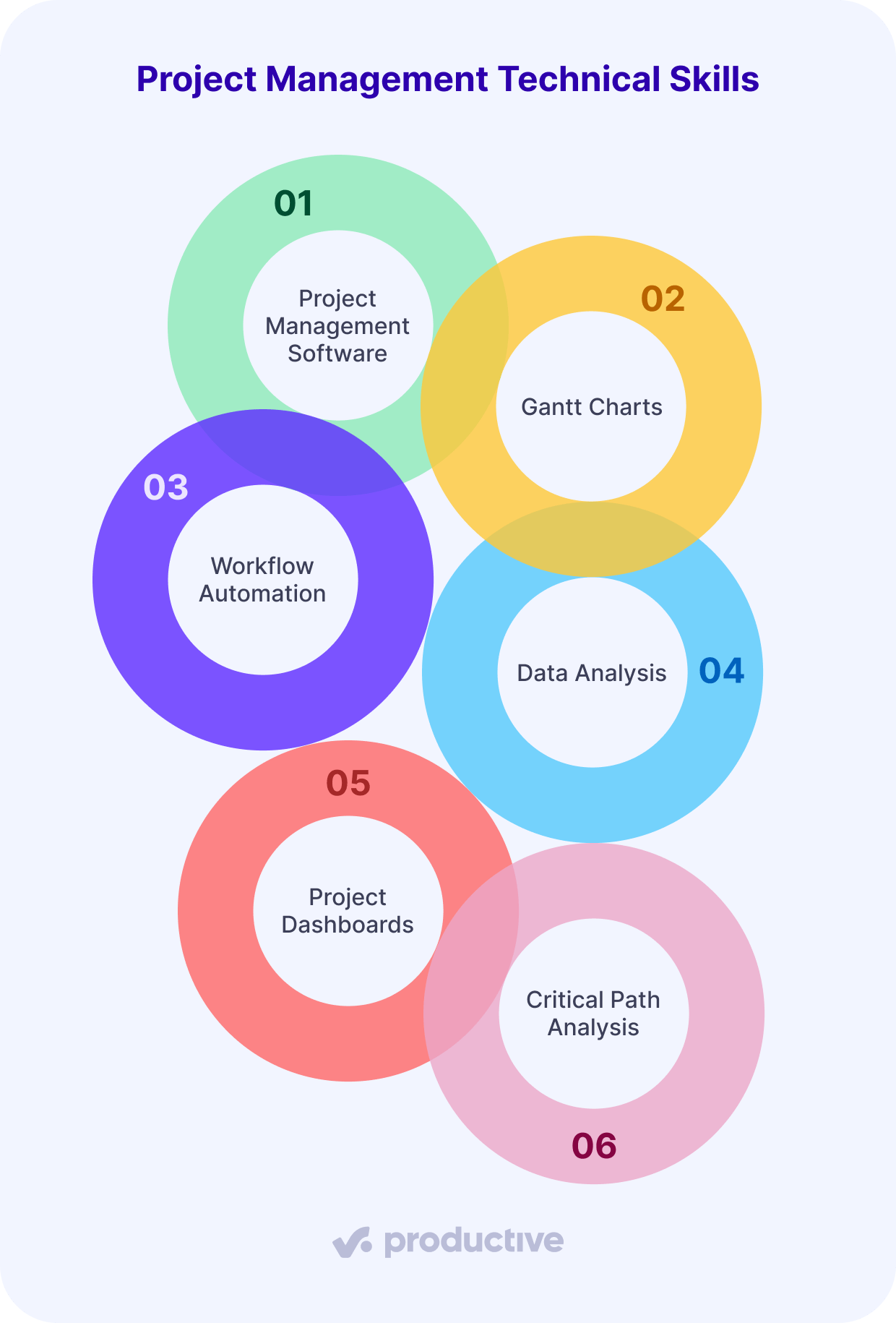
Project Management Technical Skills Overview
Technical project management expertise help you turn complex plans into real results. They’re about knowing how to organize projects efficiently, keep everyone on track, and spot problems before they grow.
You’ll need to get comfortable using Gantt charts to map out timelines, dashboards to monitor real-time progress, and workflow automation to cut down on repetitive operations.
Mastering these tools means you spend less time chasing updates—and more time actually moving forward.
At the center of it all is modern PM software like Productive. It pulls everything into one place: task tracking, budgets, schedules, and team communication. If you want to keep projects running smoothly and make smarter conclusions faster, sharpening your technical PM skills is non-negotiable.
In the sections below, we’ll dissect the mentioned technical skills to give you a clear understanding of what you need to master.
1. How You Use Project Management Software
Modern project management requires modern software tools, which make successful execution go a whole lot smoother.
When using these platforms, you’ll need proficiency in several key technical skills:
- Project management methodology knowledge for selecting appropriate tools (Agile, Scrum, Kanban).
- Data analysis capabilities to interpret metrics and make informed conclusions.
- Integration expertise to connect various systems into a cohesive workflow.
Your selection of software—whether it’s Productive for versatility, Jira for Agile frameworks, or specialized industry solutions—should align with your team’s needs. The right tool will enhance collaboration, improve productivity, and provide real-time dashboards for monitoring progress.
Before you make the final choice of the tool you’ll use, maybe you should check out our detailed guide on choosing the right PM software.
Manage projects smarter with Productive
2. Gantt Charts
Visual powerhouses in project scheduling like Gantt charts are one of the most essential tools you’ll master as a PM. You’ll use them to display tasks along a timeline with horizontal bars indicating duration and diamonds marking key milestones.
When implementing Gantt charts, you’re able to clearly visualize dependencies between activities, allocate resources efficiently, and identify potential bottlenecks. They’re invaluable for tracking progress against your baseline project plan and communicating status to every stakeholder.
Whether you’re managing construction projects or software development, Gantt charts help you apply the Critical Path Method to prioritize activities and guarantee you’re delivering projects on schedule.
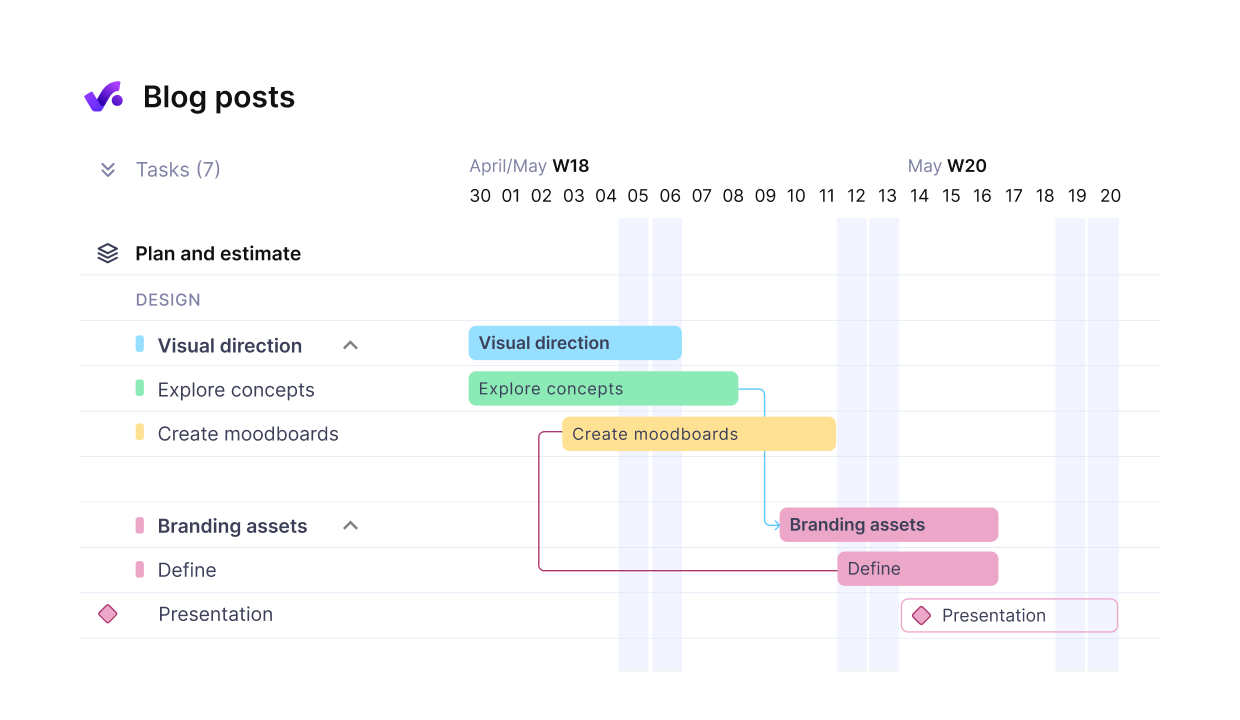
Manage timelines by mapping out tasks, milestones, and deliverables in one visual chart.
3. Workflow Automation
While Gantt charts offer powerful visual representations of timelines, workflow automation is the next level of efficiency—letting you work smarter, not harder.
When you automate repetitive activities, you’ll reduce errors, save time, and allow your team to focus on strategic initiatives.
To implement successful workflow automation in your projects, you should:
- Identify processes that can be automated, such as approval workflows or task assignments.
- Document your current state before mapping out your ideal future workflow.
- Select appropriate tools that integrate with your existing systems, like Productive or dedicated BPM software.
The results are tangible: streamlined processes, improved stakeholder engagement, and data-driven insights that enhance decision-making across departments.
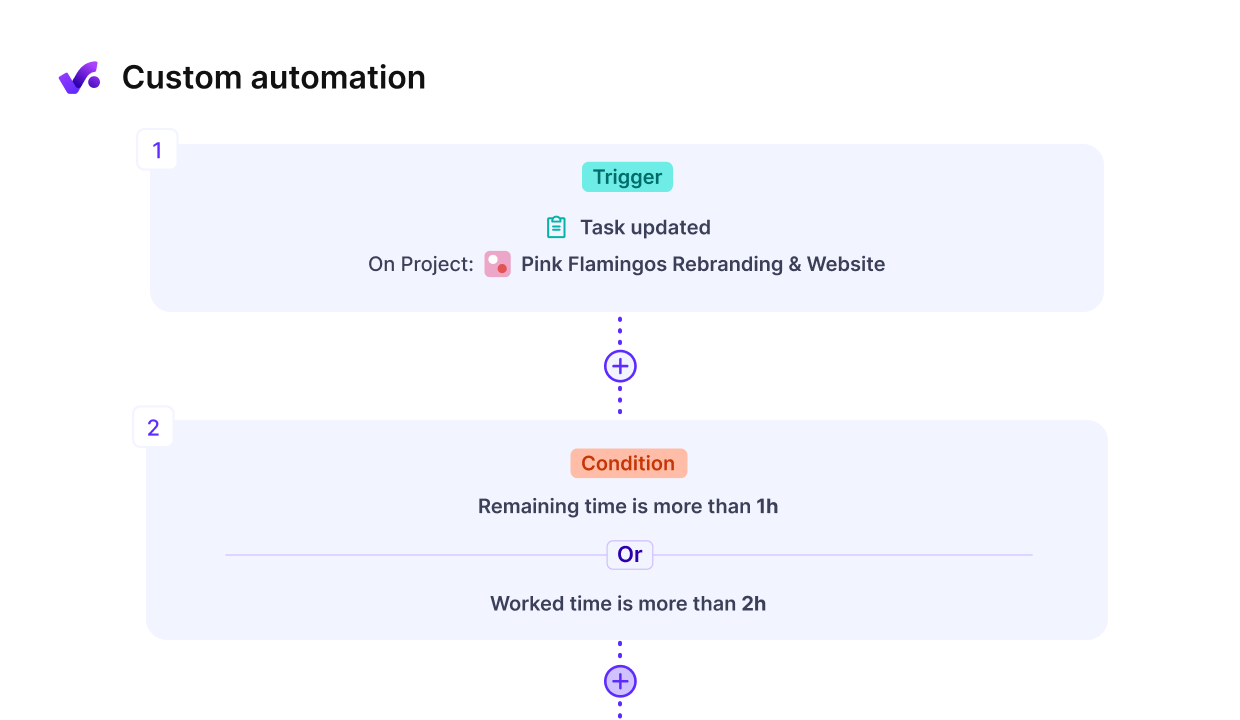
Use Productive’s workflow automations to cut down manual updates and repetitive tasks.
4. Data Analysis
Data analysis transforms raw information into actionable insights that back strategic decisions. You’ll need to master various technical skills to effectively analyze project data and identify patterns that inform your next steps.
| Analysis Type | Tools | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Descriptive | Tableau, Excel, Productive | Historical performance tracking |
| Predictive | Python, R | Risk assessment, forecasting |
| Prescriptive | SQL, SPSS | Resource optimization, decision support |
5. Project Dashboards
Powerful and intuitive dashboards visualize complex data into actionable insights at a glance. They enable data-driven decision-making and enhance stakeholder communication by visualizing project metrics in real time.
To implement effective dashboards, you’ll need to:
- Select appropriate software that integrates with your existing systems and offers customization options.
- Design for clarity, ensuring complex information is presented in an easily digestible format.
- Incorporate interactive visualizations and automated data updates to maintain relevance.
Your technical proficiency with these tools will determine how effectively you can monitor health, analyze performance trends, and communicate progress to steering committee members.
6. Critical Path Analysis
Critical Path Analysis (CPA) is a must-know method of technical project management. With it, you can scientifically determine which activities directly impact your project’s duration. When you identify the critical path, you’ll distinguish between activities that can float and those that mustn’t be delayed.
There’s a detailed guide on critical paths on our blog. You’re welcome.
| CPA Component | Purpose | Project Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Task Listing | Identify all activities | Creates thorough scope |
| Sequencing | Establish dependencies | Reveals workflow logic |
| Duration Estimation | Assign timeframes | Determines project length |
| Path Identification | Locate zero-float tasks | Highlights critical activities |
| Resource Allocation | Optimize team deployment | Maximizes efficiency |
What Tools and Methods Project Managers Need to Know?
Project managers need to know how to properly implement and use project management software, as well as the right methods like Agile —including Scrum, Kanban, or hybrid approaches.
Getting hands-on with tools like Productive or Microsoft Project makes it easier to streamline workflows, keep teams aligned, and spot issues early.
But tools alone aren’t enough. Knowing how to apply different PM methods—like Scrum for fast-moving projects, Kanban for managing flow, or hybrid models that mix both helps your team adapt when things change (and they always do).
You’ll also want to understand when to stick to traditional frameworks like Waterfall for structured, predictable projects or use Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) when resources are tight and timing is critical.
1. Mastery of Modern Project Management Tools
Effective project managers must familiarize themselves with an expanding arsenal of tools and methodologies designed to enhance efficiency and get better outcomes.
Modern tools have AI capabilities and traditional visualization techniques to create thorough management solutions. The key features that you need to master include the following:
- AI-powered automation systems that streamline repetitive activities and enhance decision-making processes.
- Hybrid methodology platforms that blend Waterfall structure with Agile flexibility.
- Visual management interfaces like Kanban boards and Gantt charts that visualize workflows and dependency tracking.
These tools are the crossroads of technology and methodology. They create opportunities for efficiency in project execution.
2. Agile Management
While traditional project management sticks to linear processes, Agile methodology embraces iterative development cycles and adaptability.
There are several frameworks within the Agile ecosystem, including Scrum with its defined sprints and roles, Kanban’s visualization of workflow, and Extreme Programming’s focus on technical excellence.
To implement Agile effectively, you’ll need specific tools like Jira or Productive for sprint planning, Kanban boards for tracking progress, and collaboration platforms like Slack.
Despite offering benefits like rapid delivery and increased customer satisfaction, Agile requires stakeholder commitment and can present predictability challenges.
3. Project Management Frameworks
Project management frameworks guide your plans, execution, and help you complete your projects from start to finish. These frameworks provide adaptable approaches to meet different needs, while methodologies offer specific procedures within them.
When selecting a framework, consider:
- Project complexity – Waterfall suits well-defined requirements, while Agile frameworks like Scrum excel with evolving specifications.
- Team dynamics – Kanban visualizes workflow and limits work-in-progress for efficiency.
- Stakeholder involvement – PRINCE2 emphasizes governance for projects requiring strict control.
Each framework utilizes specific tools—Gantt charts for Waterfall, Kanban boards for visualizing workflow, and work breakdown structures across various approaches.
How To Develop Skills for Project Management?
The best way to develop project management skills is to combine learning and active repetition in managing projects.
Learning costs nothing. Start investing your time in getting recognized certifications like PMP or PRINCE2. Expand your professional network and cultivate mentorship relationships and industry forums. You’ll benefit from diverse perspectives.
But don’t stop there. Real growth happens when you get your hands dirty: leading projects, dealing with shifting deadlines, managing tough conversations, and figuring out how to course-correct when plans fall apart.
Learning from real-world experience, not just textbooks, is how you sharpen your instincts, not just your resume.
Training and Certification
Acquiring formal training and certifications is one of the most effective pathways to developing your skills.
There are numerous opportunities for learning, from introductory courses like Google’s Project Management Fundamentals to advanced certifications such as PRINCE2 and PMI-ACP.
To maximize your professional development:
- Start with foundational courses that align with your career trajectory, whether through platforms like Coursera or directly from the PMI.
- Supplement formal education with mentorship programs and hands-on experience.
- Consider specialized certifications that reflect your industry’s methodologies—whether agile, Waterfall, or hybrid approaches.
These structured learning paths provide both theoretical knowledge and practical tools essential for success.
Practical Experience
Hands-on experience remains the best approach to develop your project management skills, regardless of formal training or certifications.
You’ll cultivate essential experience through direct application in workplace settings, volunteer opportunities, or side projects.
| Experience Type | Benefits | Development Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Work Projects | Real stakeholder interactions | Communication & risk management |
| Volunteering | Low-pressure skill building | Guidance & team cohesion |
| Side Ventures | Autonomy to experiment | Planning & execution methodologies |
Seek leading roles within your current organization, even without the formal PM title. Join the PMI community to connect with mentors who can provide guidance.
Remember, most PM proficiency comes from implementing theoretical knowledge, receiving feedback, and adapting your approach accordingly.
Continuous Learning Approaches
Long-term success depends on adopting continuous learning strategies that evolve with industry demands. You need to cultivate a positive growth mindset that views challenges as opportunities rather than obstacles.
You should enhance your knowledge base:
- Pursue professional certifications like PMP to identify and address gaps in the required skills.
- Participate in industry conferences, events, and webinars to gain insights from thought leaders.
- Apply new methodologies in controlled simulations before implementing them in actual projects.
Regular self-reflection and documentation of lessons learned will solidify your understanding while contributing to your team’s collective knowledge repository.
Mentorship and Networking
Mentorship and networking are the best go-to approaches for professional development that complement your technical knowledge.
Structured mentorship relationships will help you develop essential leader qualities like emotional intelligence, excellent communication skills, and adaptability—capabilities that extend beyond technical expertise.
Effective mentorship programs feature clear objectives, thoughtful mentor-mentee matching, and formal frameworks with scheduled touchpoints. You’ll benefit from learning from seasoned professionals.
Meanwhile, networking through professional communities, conferences, and peer learning groups creates valuable connections that enhance career opportunities.
Both approaches greatly increase engagement and make your job more satisfying while accelerating your career trajectory.
Career Impact and Future Outlook
As you build your management expertise, you’re positioning yourself better in a rapidly evolving workforce where these skills are increasingly valued across industries.
Your proficiency in methodologies like Agile and Scrum, combined with essential soft skills, will make you an invaluable asset amid the projected shortage of 25 million management professionals by 2030.
The expansion of project management beyond traditional sectors into finance, healthcare, and technology offers you diverse career pathways with significant earning potential, especially when supported by certifications like PMP.
Rising Demand For Project Management Leaders
The need for strong management skills isn’t slowing down — it’s accelerating.
According to PMI’s Talent Gap Report, by 2030, the world will need 25 million more professionals to keep up with demand. That means 2.3 million new project-related jobs open every year across industries like tech, finance, construction, and healthcare.
Companies aren’t just hiring project management roles — they’re investing in skill-building, too.
PMI’s Pulse of the Profession 2023 found that organizations prioritizing personal skills like being a great leader, communicator, and strategic thinker have a 71% success rate, compared to only 52% for companies that don’t.
In other words, if you can lead a team, juggle deadlines, manage risks, and deliver results, you’re already ahead of the curve.
The reality is simple:
- Projects are getting more complex.
- Companies need people who can solve problem and lead.
- Those with strong project management skills are going to be in high demand for years to come.
Whether you’re managing a small creative initiative or coordinating a global product launch, mastering project management skills is no longer optional — it’s your competitive advantage.
What Are the Emerging Trends in Project Management Leading Roles?
The emerging trends in project management leadership revolve around AI integration, cloud computing, and data analytics. These technologies are transforming how projects are executed and monitored, creating unprecedented efficiency.
| PM Trend | Impact | Required Skills |
|---|---|---|
| AI Integration | Automated forecasting, risk assessment | Machine learning literacy |
| Hybrid Work | Flexible, decentralized teams | Virtual collaboration proficiency |
| Sustainability | ESG-focused delivery | Carbon footprint analysis |
| Blockchain | Decentralized management of tasks | Smart contract knowledge |
The fusion of agile and traditional methodologies continues to evolve, requiring your adaptability to shifting frameworks. Embracing these emerging technologies isn’t optional—it’s essential for a long and successful career.
Final Takeaway
You’ve seen how essential project management skills combine technical expertise with strong interpersonal abilities. Develop these to position yourself ahead of the competitive job market.
Whether you’re pursuing formal certification or learning through practical experience, your investment in these key skills will pay out throughout your career.
Since organizations increasingly prioritize efficient delivery, getting better in these areas will become an invaluable professional asset.
You should work had and smart, so using the right tech stack (PM tools) will make a huge difference in how you deliver projects.
Do yourself a huge favor and book a short 30-minute demo to learn how Productive helps you manage projects better with more success.
Level Up Your Project Management Skills with Productive
Manage tasks, track budgets, automate workflows, and lead your projects with confidence — all from one tool.