What Is Resource Allocation In Project Management?
Resource allocation is a day-to-day project management process of balancing people, budgets, and timelines so projects run smoothly.
This guide is written for managers and project teams that need practical answers.
We’ll cover the resource allocation process in practical steps, which methods and best practices to follow, how to solve common problems, and which tools actually help.
The focus is on ROI and delivery reliability, not academic definitions.
Key Takeaways
- Resource allocation in project management means assigning people, time, and budgets to deliver profitable projects.
- Key factors like scope, timelines, budgets, and skills shape allocation decisions and outcomes.
- Common challenges include overbooking, scope creep, and lack of visibility, all of which have practical fixes.
- The right tools provide visibility, utilization tracking, time tracking, and ROI insights to support better decisions.
What Is Resource Allocation in Project Management?
Resource allocation in project management is the practice of assigning people, time, and budgets to specific projects so that work gets done predictably and profitably. In an agency, this could mean deciding which designer handles a client website while another designer focuses on an internal campaign.
It is about making sure projects move forward without stretching people too thin or leaving gaps in delivery.
For example, imagine an development agency running three projects with overlapping deadlines. Without structured allocation of resources, one developer may be overloaded while another has spare time.
With a clear resource allocation plan, managers can shift work so each project receives the right support, deadlines are met, and client expectations stay intact. If you’d like to learn more about the bigger picture, head over to our resource management guide.
What Does Resource Allocation Do?
Resource allocation gives managers the ability to balance workloads so no one is overloaded, protect staff from burnout, and make sure billable hours are maximized instead of wasted.
In practice, this means knowing when a developer is close to capacity and redirecting work to someone else before deadlines slip. It also means keeping junior and senior team members engaged at the right level so skills are used effectively and clients see value for money.
In short, resource allocation helps teams:
- Balance workloads fairly across projects.
- Prevent burnout by tracking and adjusting assignments.
- Maximize billable hours while protecting non‑billable time.
- Keep projects profitable by matching skills to the right tasks.
Why Is Resource Allocation Important?
Resource allocation is important because it ensures the right people with the right skills are available at the right time. In agencies that manage several projects at once, this means that timelines stay on track, staff are not overloaded, and deadlines are met without costly overtime.
By matching availability and skills to project needs, teams avoid wasted effort, and managers keep profitability steady. Without a clear approach to allocation, companies risk missed deadlines, overbooked employees, and client dissatisfaction.
Impact on Profitability and Utilization
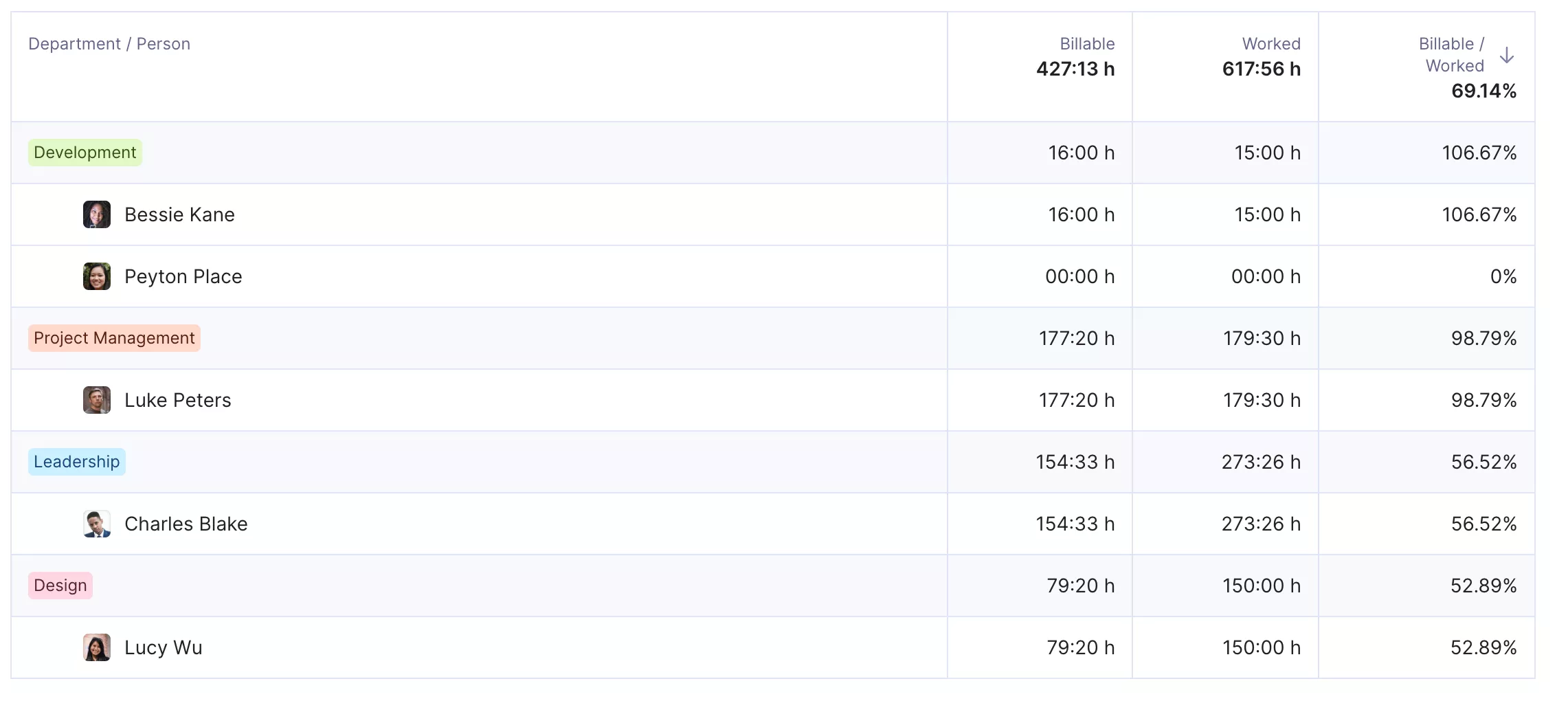
Agencies live or die by how well they use their people’s time. An employee utilization rate of 70% means that out of a 40‑hour week, only 28 hours are billable.
If the average billable rate is $100 per hour, that equals $2,800 in revenue. Increase utilization to 85% and those billable hours climb to 34, bringing revenue to $3,400.
Across a 10‑person team, that difference adds up to $6,000 more each week.
Impact on Client Satisfaction
Effective resource allocation also safeguards client trust. When workloads are balanced and deadlines are realistic, teams deliver on promises without last‑minute crunches. Overbooking often leads to delays, missed project milestones, and frustrated clients.
By aligning availability with project timelines, companies show reliability and consistency. This builds confidence that the work will arrive when expected and at the quality agreed.
For example, an agency that reallocates a designer to avoid overlap ensures both Client A’s campaign and Client B’s website launch on time. That proactive shift prevents disappointment and proves the agency values each client equally.
What Factors Influence Resource Allocation?
The factors that influence resource allocation are project scope, timelines, budgets, and skills, each of which can make or break delivery.
As companies adapt to shifting priorities, these resource constraints interact and create the context in which allocation decisions must be made.
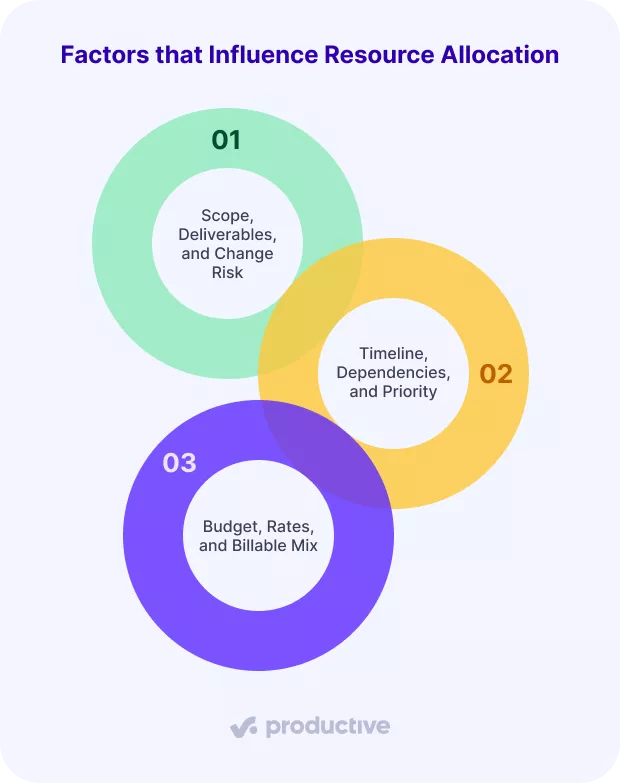
Scope, Deliverables, and Change Risk
Scope defines the amount of work and the deliverables to be produced. If it is unclear or expands mid‑project, resources quickly fall out of sync. Scope creep forces teams to reshuffle, which creates stress and missed deadlines.
A clear project scope, combined with a structured change request process, helps managers protect capacity and keep projects realistic.
Timeline, Dependencies, and Priority
Timelines and dependencies often drive allocation decisions. If tasks are tightly linked on the schedule, managers must assign the right people at the right time to avoid bottlenecks. Critical path activities require special attention because delays here ripple through the entire project.
Companies use prioritization rules to decide which projects or clients come first when conflicts arise. Tools like Productive make these dependencies visible in real time, so resource managers can adjust allocations before small delays become major setbacks.
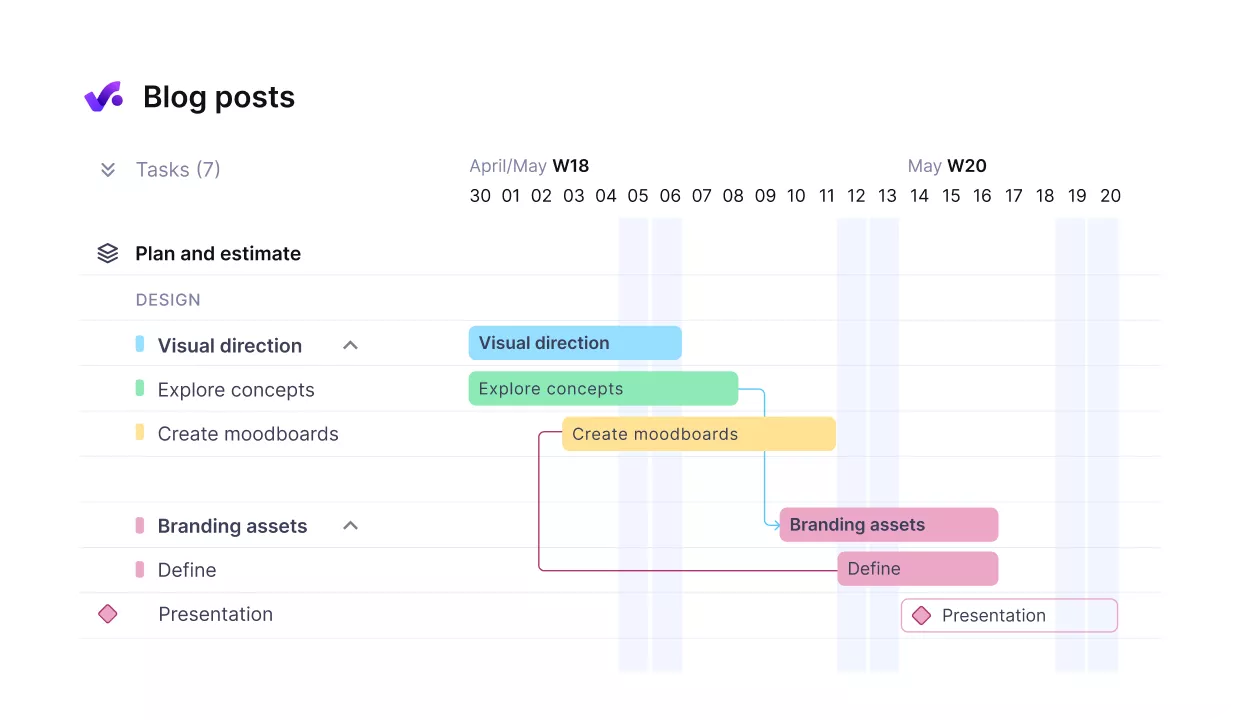
Visualize timelines, dependencies, and workflows.
Budget, Rates, and Billable Mix
Financial resources also shape allocation. Projects with tight budgets require careful matching of junior and senior staff to stay profitable. The ratio of billable to non‑billable hours directly impacts margins, so resource managers must keep an eye on who is doing what.
Tracking actual costs against budget helps keep financial performance predictable. Platforms like Productive support this by connecting budgets, billable hours, and staff rates in one place, so managers see profitability forecasts before problems arise.
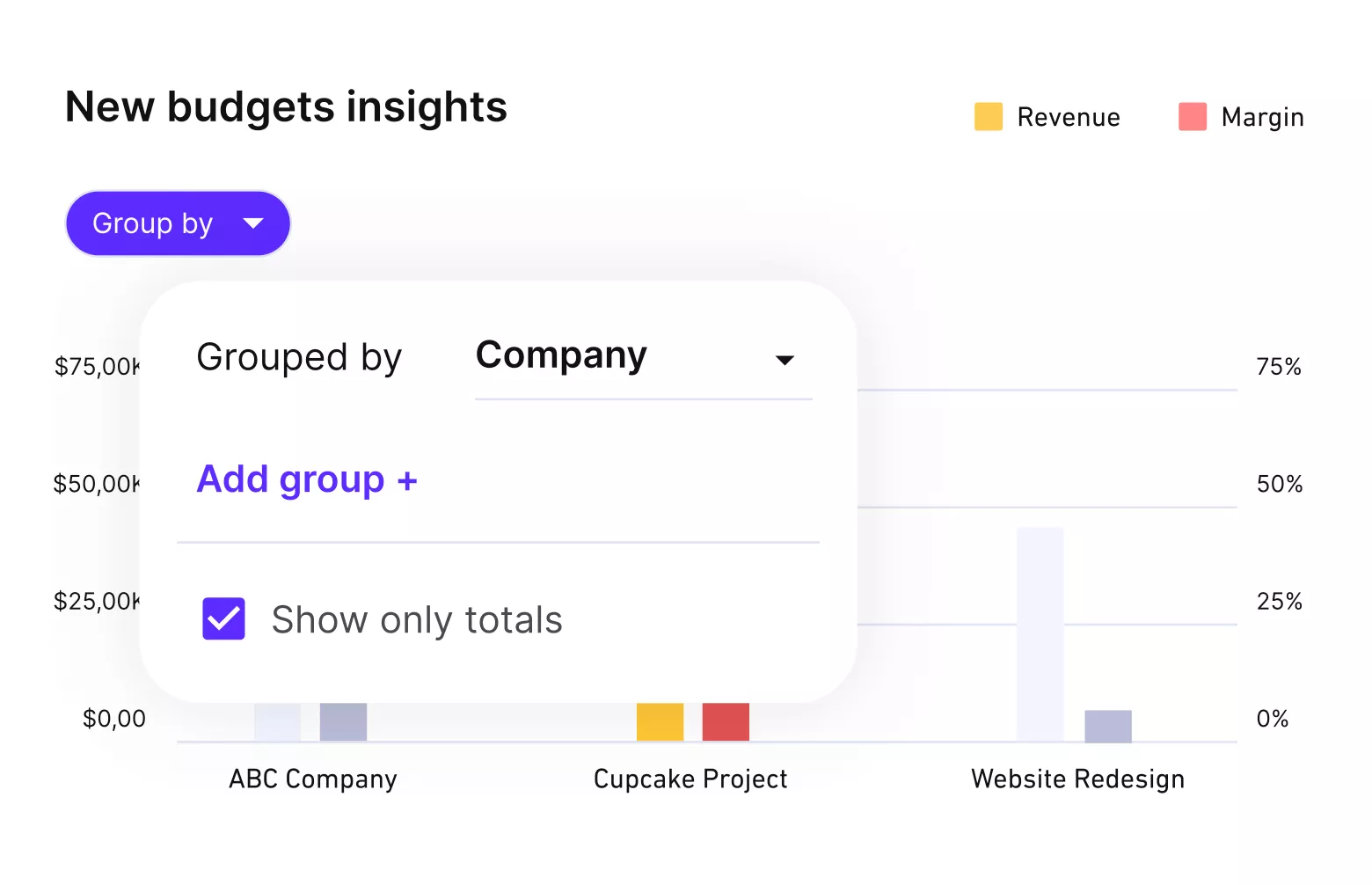
Get real-time budget updates and profitability metrics.
What Resource Allocation Methods Are Used in Project Management?
The common methods of resource allocation are resource leveling, resource smoothing, capacity planning, and priority or skills-based assignment. Each method offers a different way to balance workloads and schedules, and you can use them in combination to keep delivery reliable.

Method 1: Resource Leveling
Resource leveling means adjusting start and end dates to remove overallocation. For example, if a designer is double-booked, their work on a less urgent campaign can be shifted by a few days. This keeps workloads realistic even if it moves project dates slightly.
How to implement:
Map current assignments on a timeline and flag where a person is booked on two tasks at once. Shift non-critical tasks by a few days to balance the load. Use a tool like Productive to visualize workload conflicts across projects.
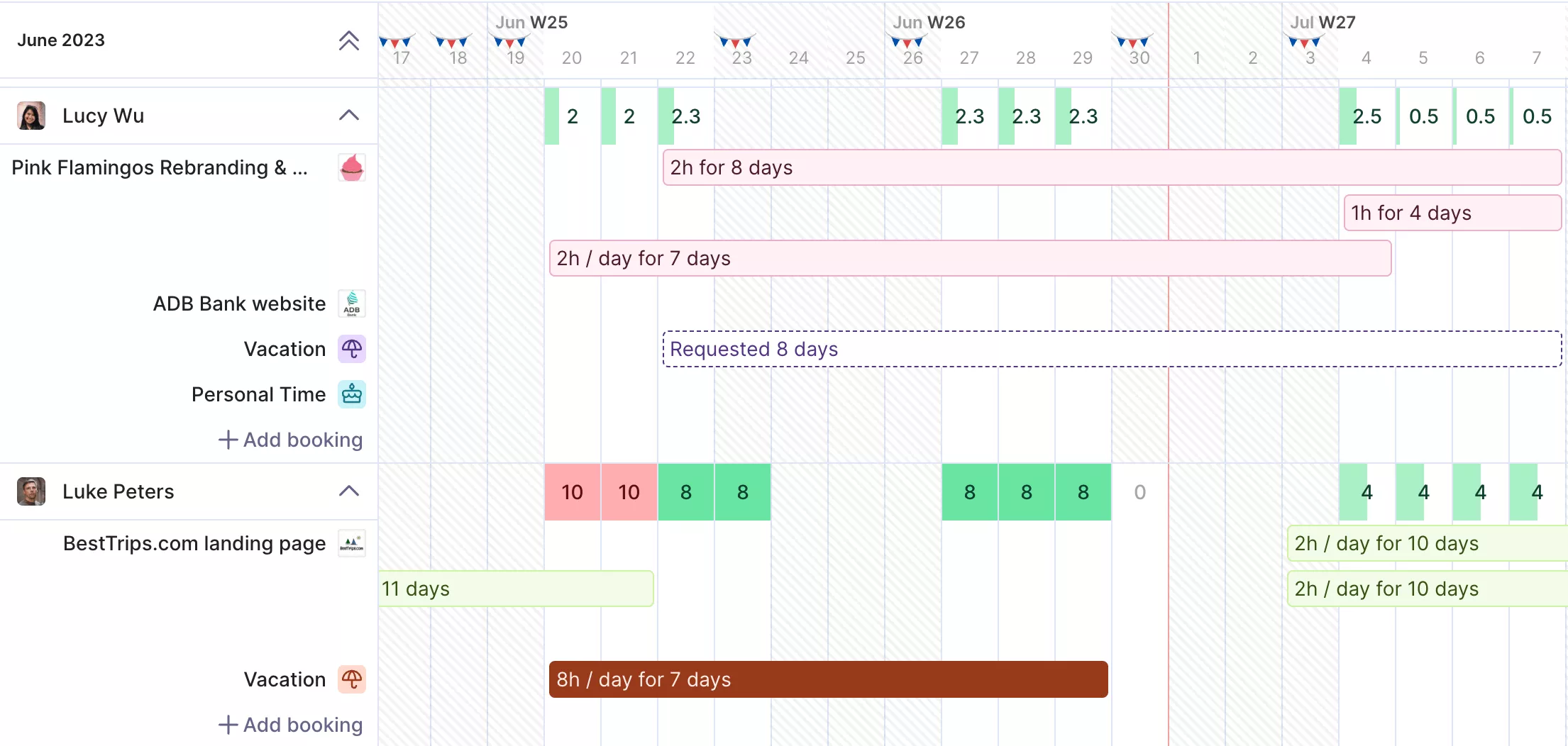
Get a real-time overview of your available resources.
Method 2: Resource Smoothing
Resource smoothing spreads work evenly without changing end dates. If demand spikes in one week, tasks are rescheduled within the project to avoid overload. This protects team well-being while still meeting deadlines.
How to implement:
Review weekly workloads and reassign smaller tasks to lighter days without moving the project’s completion date. Use calendar or Gantt views in software like Productive to keep end dates intact while balancing peaks.
Use Productive to get real-time utilization reports.
Method 3: Capacity Planning
Capacity planning compares upcoming demand with available supply. Agencies use this to forecast hiring needs or shift workloads across project teams. For example, knowing that two campaigns will overlap helps project managers plan hours for copywriters weeks in advance.
How to implement:
Build a rolling forecast of project demand against available hours for each role. Adjust workloads or plan for temporary hires before crunch time hits. In Productive, managers can review utilization dashboards to see capacity weeks ahead.
Method 4: Priority- and Skills-Based Assignment
Sometimes allocation comes down to setting priorities. Agencies may assign senior staff to high-value clients while junior staff cover smaller projects. Skills-based assignment ensures the right expertise is applied where it matters most.
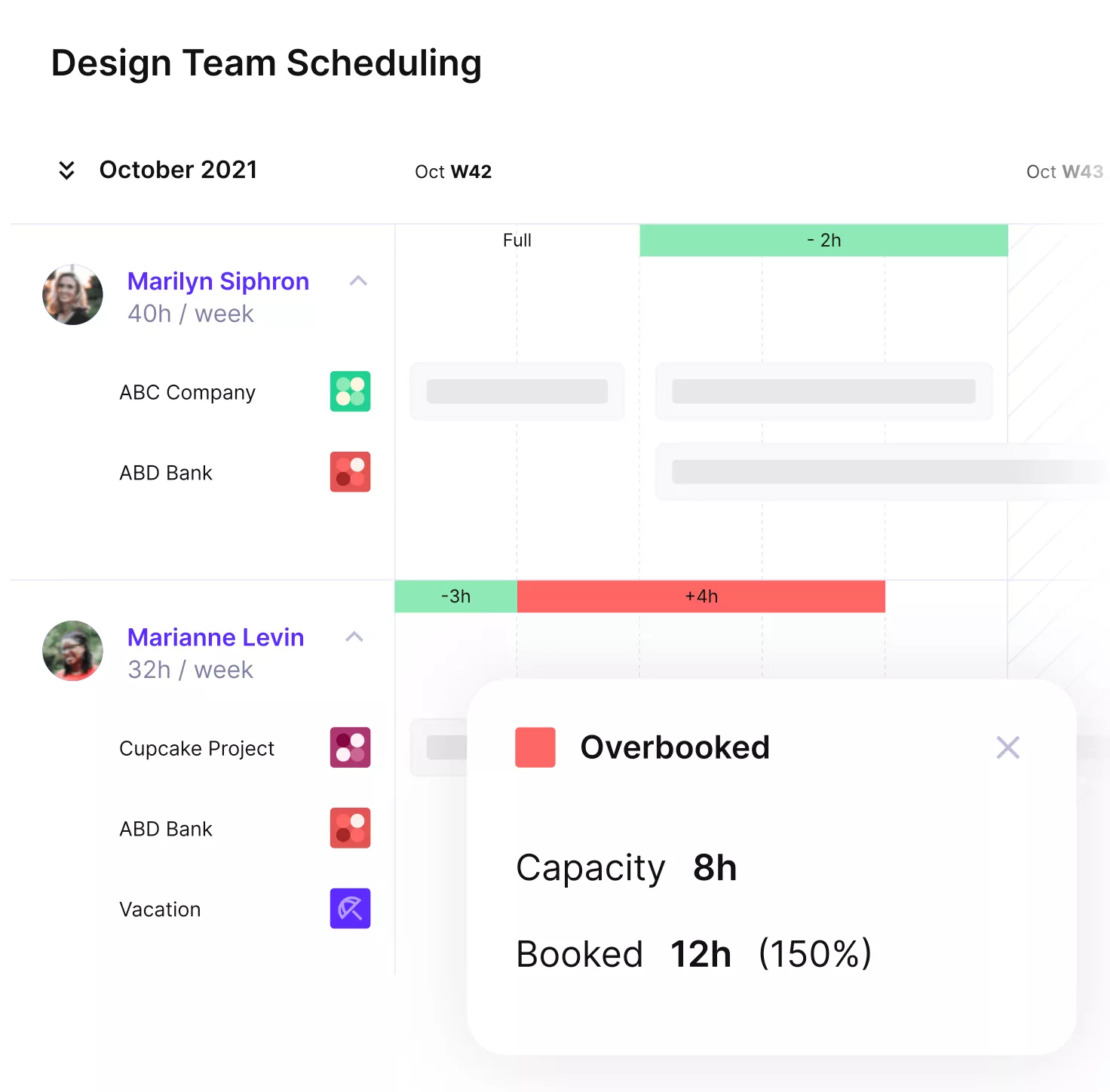
Schedule team members without resource conflicts and overlaps with Productive.
How to implement:
Rank projects by client value, deadline, and complexity. Assign senior roles to strategic work and juniors to support tasks. Track assignments in a shared Gantt chart or resource scheduling tool like Productive so adjustments are visible to everyone.
Manage and plan resources with Productive
What Are the Challenges of Resource Allocation? + How To Solve Them
The challenges of resource allocation are limited visibility, overallocation and burnout, and scope changes and prioritization conflicts. Each of these challenges can be addressed with practical fixes when resource managers have the right process and tools in place.
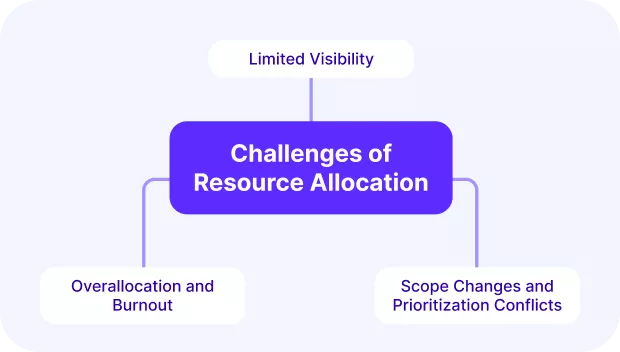
Challenge 1: Limited Visibility
When managers lack a clear overview of who is doing what across projects, conflicts and gaps appear. This leads to double-booking or idle capacity, which hurts both teams and clients.
How to solve:
Centralize scheduling in one platform where availability and assignments are visible to everyone. Use resource management tools to spot conflicts early. Productive, for example, provides real-time capacity views so resource managers can redistribute work before it becomes a problem.
Challenge 2: Overallocation and Burnout
Assigning the same people to multiple projects at once leads to stress, overtime, and eventually missed deadlines. Burnout not only reduces performance but also increases staff turnover, which is costly to replace.
How to solve:
Track each person’s weekly capacity against a baseline, such as 40 hours. Keep in mind that an ideal employee utilization rate is around 80%. If someone is consistently over, redistribute tasks, delay lower-priority projects, or adjust deadlines.
Productive’s workload balancing features highlight these issues in advance so managers can act before burnout takes hold.
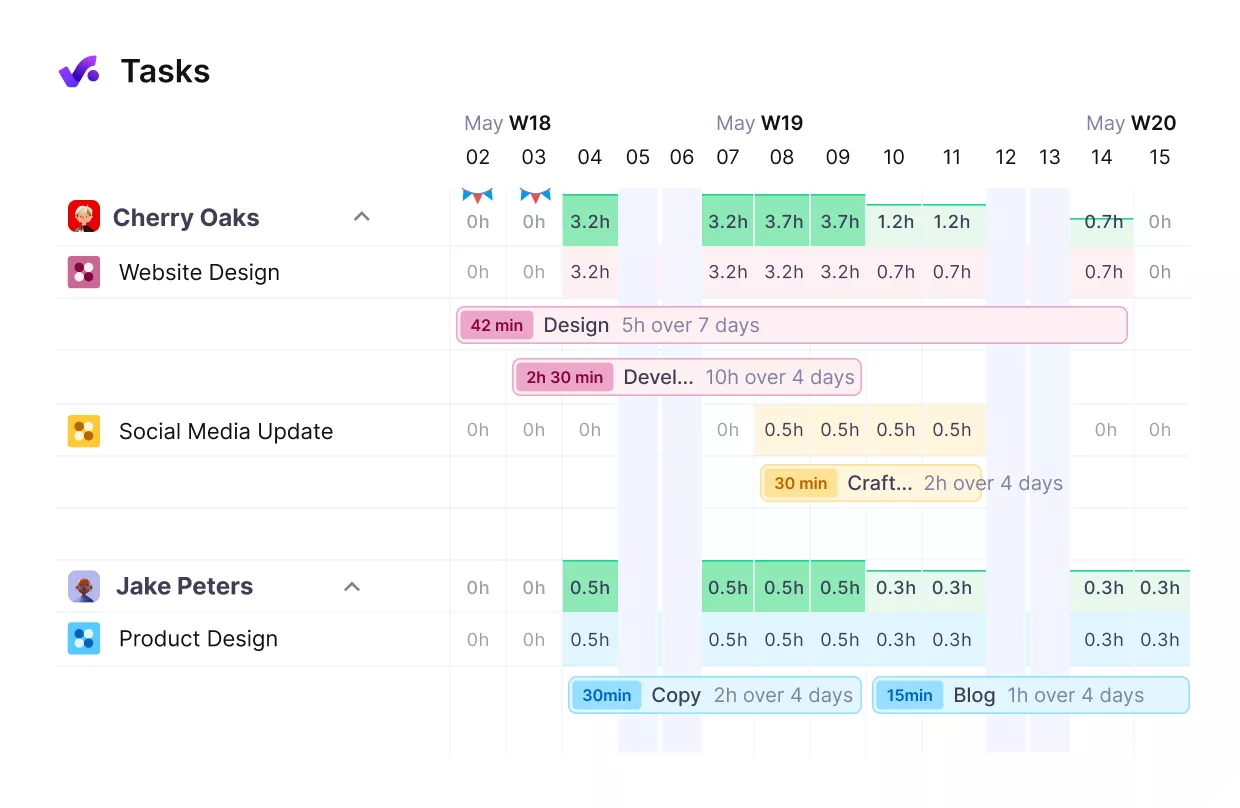
Get a real-time overview of your staff’s workloads.
Challenge 3: Scope Changes and Prioritization Conflicts
Client requests and shifting priorities mid-project can derail allocations, leaving some tasks under-resourced while others demand too much attention. Without a system, teams end up reacting instead of planning.
How to solve:
Introduce a formal change request process that ties new tasks back to scope, budget, and deadlines. Re-run allocations whenever priorities shift to ensure resources are aligned with the latest plan.
In Productive, resource managers can update allocations dynamically and keep everyone aligned without overloading staff.
What Does the Resource Allocation Process Look Like?
A resource allocation process has four steps: 1. assess availability, 2. match skills to tasks, 3. prioritize and assign, and 4. monitor utilization and adjust. These steps give companies a repeatable way to make sure resources are always aligned with project needs.
In the next sections, we will walk through each step in detail so managers can put the process into practice.
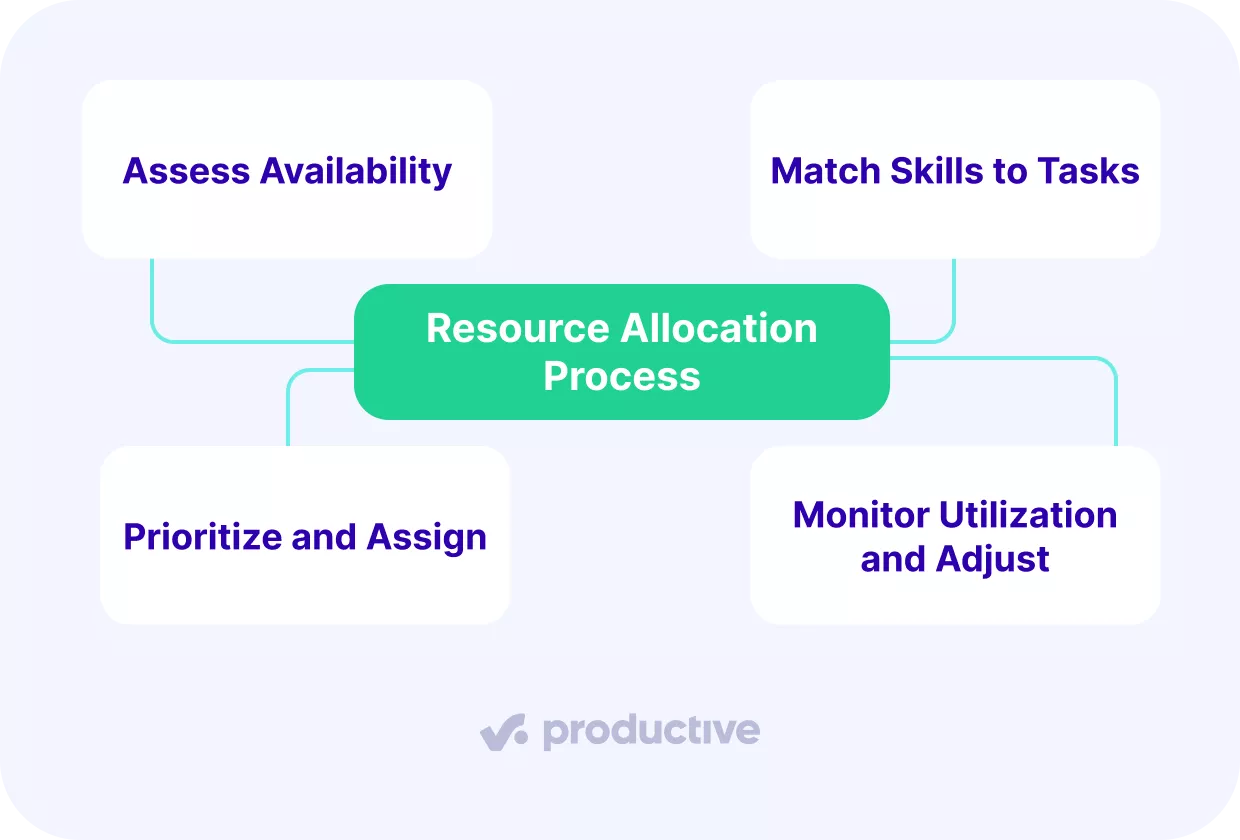
Step 1: Assess Availability
The first step in any allocation process is to understand who is available and when. Companies that skip this step risk overbooking staff or leaving capacity idle. Checking availability includes looking at scheduled project work, internal tasks, and time off.
This ensures managers have a realistic view of resource availability before allocating resources to new projects.
How to implement:
- Review calendars and project schedules for current commitments.
- Subtract planned PTO, holidays, or training time from each person’s hours.
- Use tools like Productive to view real-time availability dashboards across projects.
Step 2: Match Skills to Tasks
The second step in the allocation process is to align the right skills with the right tasks. Simply filling hours is not enough; the quality of delivery depends on matching expertise to project requirements. If a junior developer is given a complex feature without oversight, the project may slow down or require rework.
By assigning tasks based on skill levels, managers improve both efficiency and client satisfaction.
How to implement:
- Review each project’s requirements and list the core skills needed.
- Match staff to tasks according to their skill set and experience.
- Use task assignment features in tools like Productive to ensure everyone knows their responsibilities and gaps are easy to spot.
Step 3: Prioritize and Assign
The third step in the allocation process is to prioritize projects and assign resources accordingly. Agencies often juggle multiple clients with overlapping project deadlines, which means not every task can be treated equally.
Clear prioritization ensures that critical projects get the focus they need while less urgent work is scheduled realistically. This step helps prevent resource allocation conflicts and keeps projects aligned with business goals.
How to implement:
- Rank projects by client value, deadlines, and strategic importance.
- Assign senior staff to high-priority tasks and distribute support work to junior staff.
- Use allocation process rules in Productive to visualize assignments across projects and quickly adjust when priorities shift.
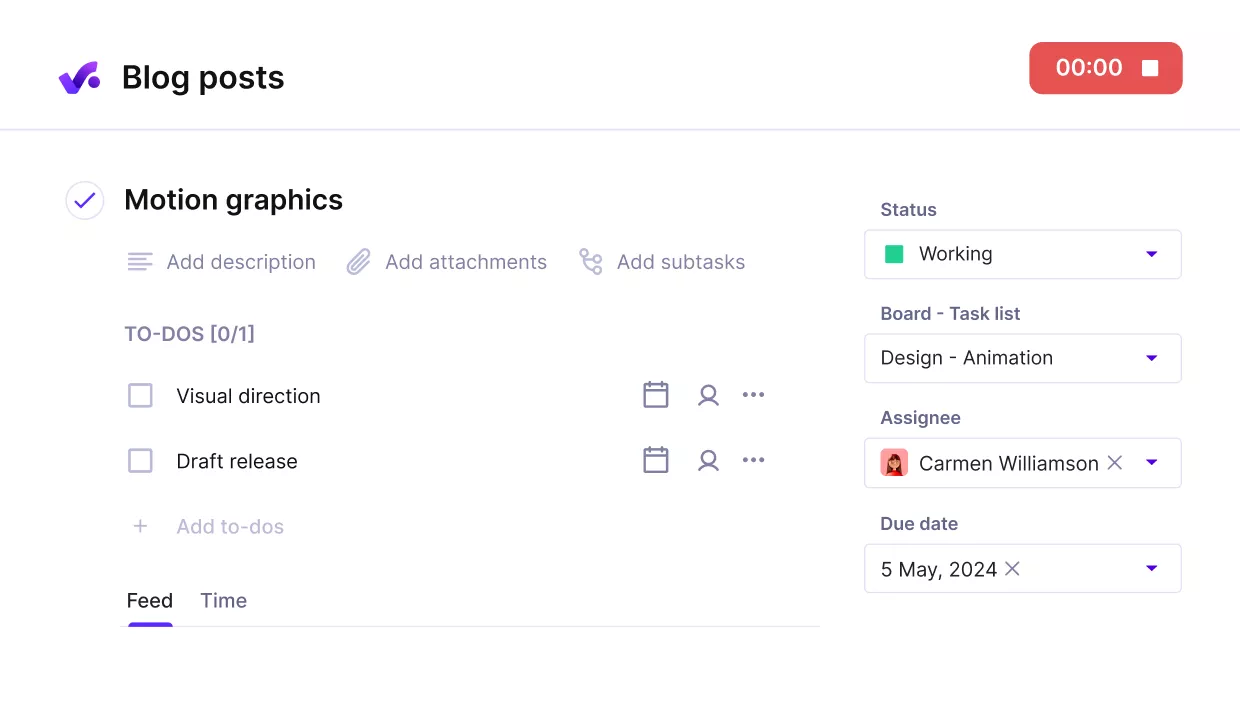
Assign dependent tasks with clear owners, descriptions, and to-do lists.
Step 4: Monitor Utilization and Adjust
The final step in the allocation process is to monitor utilization and make adjustments as projects evolve. Even with careful planning, workloads change as new requests come in or tasks take longer than expected.
Regularly tracking resource utilization helps managers catch issues early and redistribute work before deadlines slip.
How to implement:
- Review utilization reports weekly to see how close each person is to their target workload.
- Adjust assignments when someone is consistently under or over their planned capacity.
- Use Productive’s real-time reporting to compare actual utilization with forecasts and make proactive changes to allocations.
What Are the Best Practices for Resource Allocation? + How To Implement Them
The best practices of resource allocation are keeping a live capacity plan, protecting focus time, standardizing change requests, using role-based placeholders, tracking utilization and billable mix, and closing the loop with reviews.
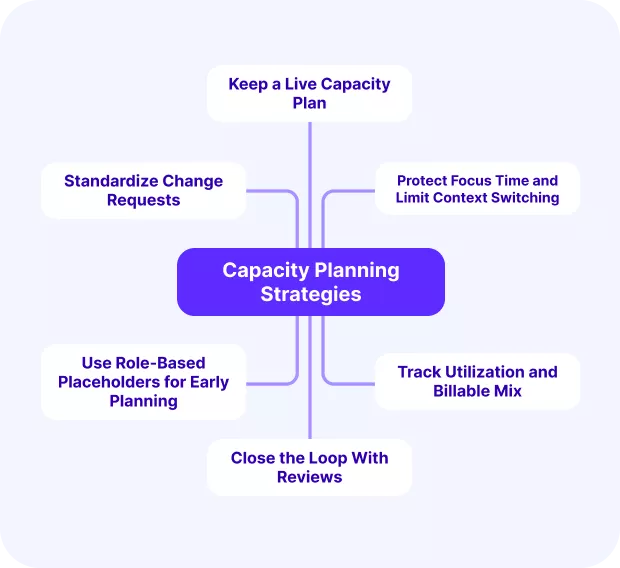
These practices ensure that resource allocation is not just reactive but proactive, making teams more resilient to changes.
In the next sections, we will explore each practice in detail, explain how it works, and show the impact it can have on projects and profitability.
1. Keep a Live Capacity Plan
A live capacity plan shows you exactly who has hours free and who is fully booked. It helps you avoid overbooking and ensures resource availability is always clear. With an accurate view, you can plan projects with confidence and prevent last‑minute reshuffles that disrupt teams and clients.
How to implement:
- Track available hours for each role or person in a spreadsheet or tool like Productive.
- Update it weekly with PTO, training, and internal commitments so the plan reflects reality.
- Review the plan with your team at the start of each week and adjust workloads together so deadlines stay realistic.
2. Protect Focus Time and Limit Context Switching
Protecting focus time means giving people blocks of uninterrupted hours so they can finish meaningful work without constant resets. This leads to higher quality output and less wasted energy.
How to implement:
- Limit the number of active projects each role is assigned to at one time.
- Schedule blocks of at least two to three hours for deep work and communicate these blocks to the team.
- Agree with clients on reasonable response times so your team is not pressured into constant context switching.
3. Standardize Change Requests
A clear, standardized process for handling change requests protects your team from constant disruption and helps you keep delivery predictable. By documenting and reviewing each change, you make sure new work is balanced against current capacity instead of simply added on top.
How to implement:
- Create a simple template for change requests that captures impact on scope, budget, and deadlines.
- Require approval from both the client and an internal project lead before reallocating resources.
- Re-run your resource allocation plan after approval so the workload stays balanced. Productive can log change requests and show how new work affects existing allocations.
4. Use Role-Based Placeholders for Early Planning
When projects are still being scoped, you might not know exactly which person will take on a task. Using role-based placeholders allows you to plan realistically without waiting for every detail. This keeps your allocation process moving and prevents projects from stalling while names are confirmed.
How to implement:
- Set up roles such as Designer, Developer, or Account Manager during initial planning.
- Assign hours to these roles based on the estimated workload.
- Once project dates and budgets are confirmed, replace placeholders with specific people.
- In Productive, you can plan with roles first and then swap in actual team members when decisions are final.
5. Track Utilization and Billable Mix
Keeping an eye on utilization and the balance of billable versus non‑billable hours shows you if your team’s time is being used effectively. If too many hours are non‑billable, profitability drops even when people are busy.
Tracking these numbers regularly helps you make better staffing and pricing decisions.
How to implement:
- Review the utilization rate weekly and compare it against your target (many agencies aim for around 80 percent).
- Break down billable and non‑billable hours by role so you can see where time is going.
- Use reports in Productive to monitor trends and make adjustments, such as shifting internal work to slower weeks or reallocating staff to higher‑value projects.
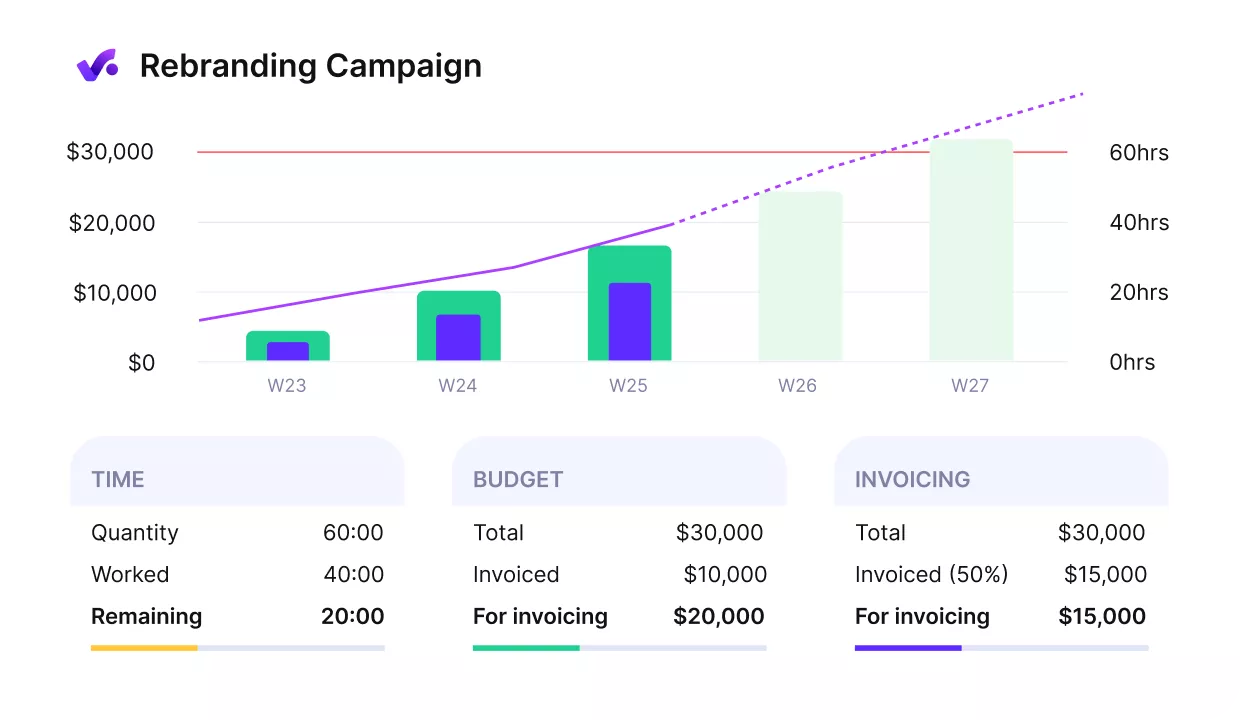
Get an early alert in case of budget overruns.
6. Close the Loop With Reviews
Teams improve allocation when they learn from past projects. A structured review at the end of each engagement captures what worked, what caused bottlenecks, and how resources could have been used better.
These insights give you practical data to refine your next resource allocation plan instead of repeating the same mistakes.
How to implement:
- Schedule a one‑hour retrospective within a week after project delivery.
- Prepare specific data points before the meeting: planned hours vs. actual, utilization by role, and major scope changes.
- Ask each team member to share one under‑allocation and one overallocation they noticed, plus one thing that went smoothly.
- Document the findings in a shared system or in Productive, linking them to the project record.
- Translate the insights into changes you can apply immediately, such as adjusting default estimates for similar project types or updating your allocation templates.
What Are the Best Tools for Resource Allocation?
The best tools for resource allocation are all-in-one project management platforms, dedicated resource management software, and lighter scheduling apps.
Each type has its strengths, but companies that manage multiple projects benefit most from integrated tools that combine planning, budgeting, and reporting in one place.
In the following sections, we will look at the features you should expect and how to evaluate project management tools for your team.
Must-Have Features List
To manage allocation effectively, resource management tools and project management software should include:
- Forecasting: Plan upcoming demand and see where capacity will be stretched.
- Visibility: A shared view of who is available and when across projects.
- Utilization reports: Track how much time is billable vs non-billable and compare against targets.
- Gantt charts: Visualize timelines, dependencies, and workloads in a single view.
- Time tracking: Capture hours accurately so you know where resources are spent.
- Change request management: Log new client requests and see how they affect existing plans.
How To Choose the Right Tool?
When choosing between resource management software, resource management tools, or project management software, consider how well the tool fits a multi-client portfolio.
Project-based companies need to balance competing deadlines and shifting scopes without losing track of profitability.
Look for platforms that connect capacity planning, budgets, and reporting in one system. Test how easily you can adjust allocations when priorities change and whether the tool gives you real-time utilization data.
We cover our top picks in our capacity planning software list.
Productive, for example, brings scheduling, time tracking, and financials together so you can see the impact of resourcing decisions before issues escalate.
Final Thoughts
Getting resource allocation right means your teams work at a steady pace, projects meet deadlines, and profitability is protected.
If you’re still managing allocation with spreadsheets or a patchwork of apps, it may be time to think about other, more centralized options. Productive brings projects, budgets, time tracking, and resource planning into one platform.
Book a demo to get started.
Connect allocation to budgets and time with Productive
Link resource plans to budgets and time tracking. Productive shows the impact on costs and margins in real time.