What Is a Project Management Plan? (Step-by-Step Guide in 2026)
Projects often fail because of unclear objectives, scattered updates, and limited visibility into costs or resources.
A project management plan brings order by setting clear goals, establishing accountability, and centralizing project details in one place.
By the end of this guide, you’ll know how to build a project plan step by step, follow best practices, avoid common mistakes, and choose the right tools for the job.
Key Takeaways
- A project management plan serves as a single source of truth that organizes scope, objectives, timelines, budgets, and communication in one place.
- Clear project plans prevent scope creep and missed expectations by setting firm boundaries and aligning stakeholders from the start.
- Linking budgets, resources, and schedules to deliverables helps you track financial health and team capacity in real time.
- Using integrated project management tools removes silos, replacing scattered spreadsheets and chats with one connected workflow.
What Is a Project Management Plan?
A project management plan is a formal document that defines a project’s scope, objectives, schedule, resources, and processes. It acts as a roadmap for project execution and guides teams and stakeholders from initiation through closure while keeping everyone aligned.
If you need more context planning, monitoring and executing projects, you might want to check out our big guide on What Is Project Management.
Why Do You Need a Project Management Plan?
A project management plan gives you clarity, accountability, project stakeholder alignment, and risk reduction. This project roadmap also addresses challenges like fragmented systems, manual processes, and a lack of financial visibility.
Project planning creates a single framework that keeps your project on track and decisions transparent. As the PMI’s Pulse of the Profession report states:
Inaccurate requirements gathering remained a primary cause of project failure – 37 percent in 2014, and poor communication negatively impacted requirements management in 75 percent of organizations, more than any other issue including schedule, stakeholders, or budget.
What Are the Key Components of a Project Plan?
A project plan includes eight key components: project scope statement, work breakdown structure, project schedule, project budget, resource planning, risk management, communication strategy, and stakeholder engagement.
These elements work together to define boundaries, allocate resources, and keep teams aligned.
Below, we break down each component along with actionable advice on how to make it fit your plan.
1. Project Scope Statement
The statement lists objectives, deliverables, and a exclusion schedule. Be specific so stakeholders know exactly what you will deliver.
Use past project data to estimate how much effort each part of the scope will require. In Productive, you can store and share the scope in one place and compare it with historical project outcomes to prevent scope creep.
2. Work Breakdown Structure
Create a work breakdown structure (WBS) by splitting deliverables into smaller, manageable tasks. Start with the main phases, then break them down into subtasks until each item can be estimated for time and resources.
For example, “Website Development > Frontend > Homepage Layout.”
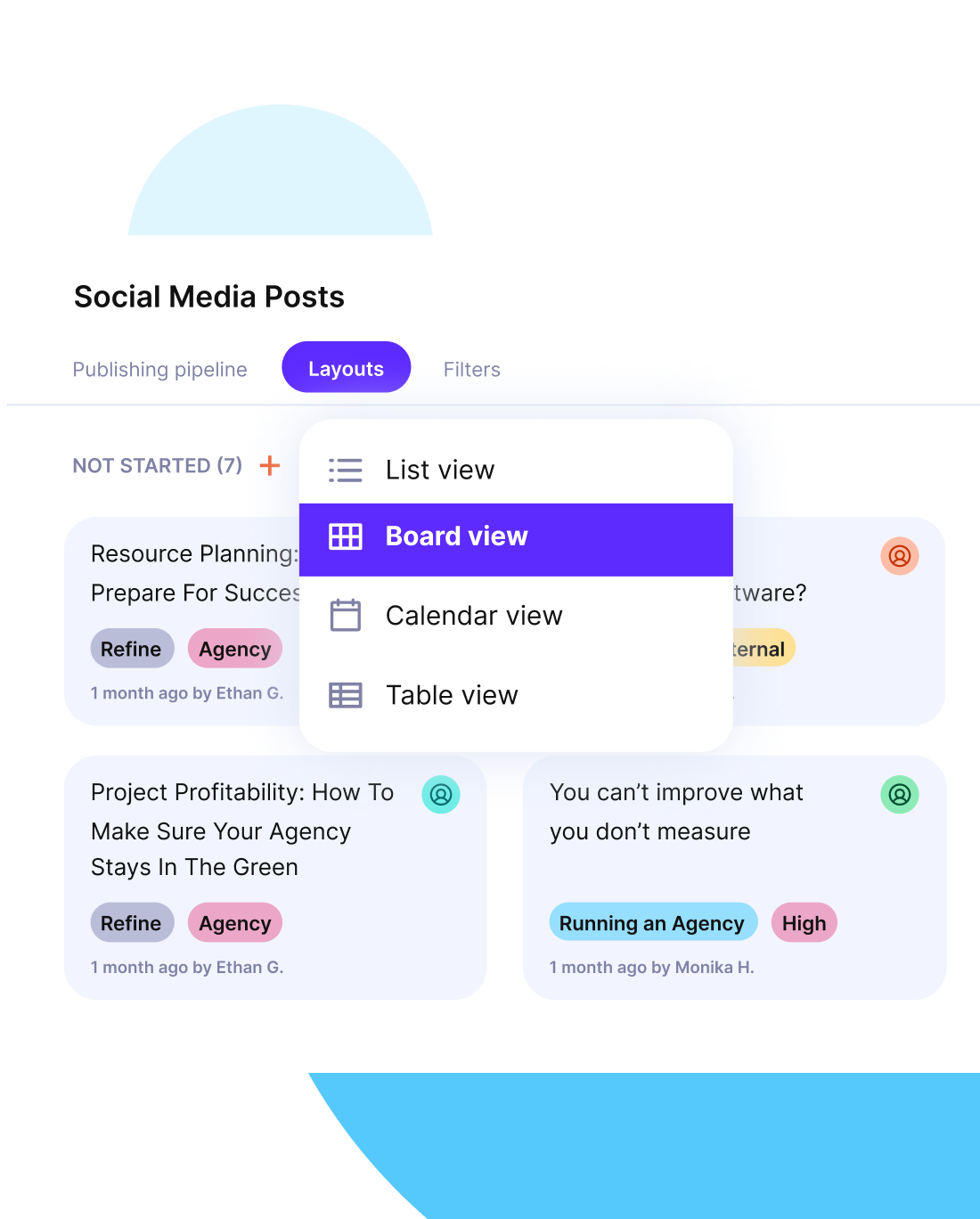
Build this visually with Gantt charts or Kanban boards. In Productive, you can create task hierarchies and link them to milestones for full visibility.
Set up Gantt charts or WBS with dependencies and timelines.
3. Project Schedule
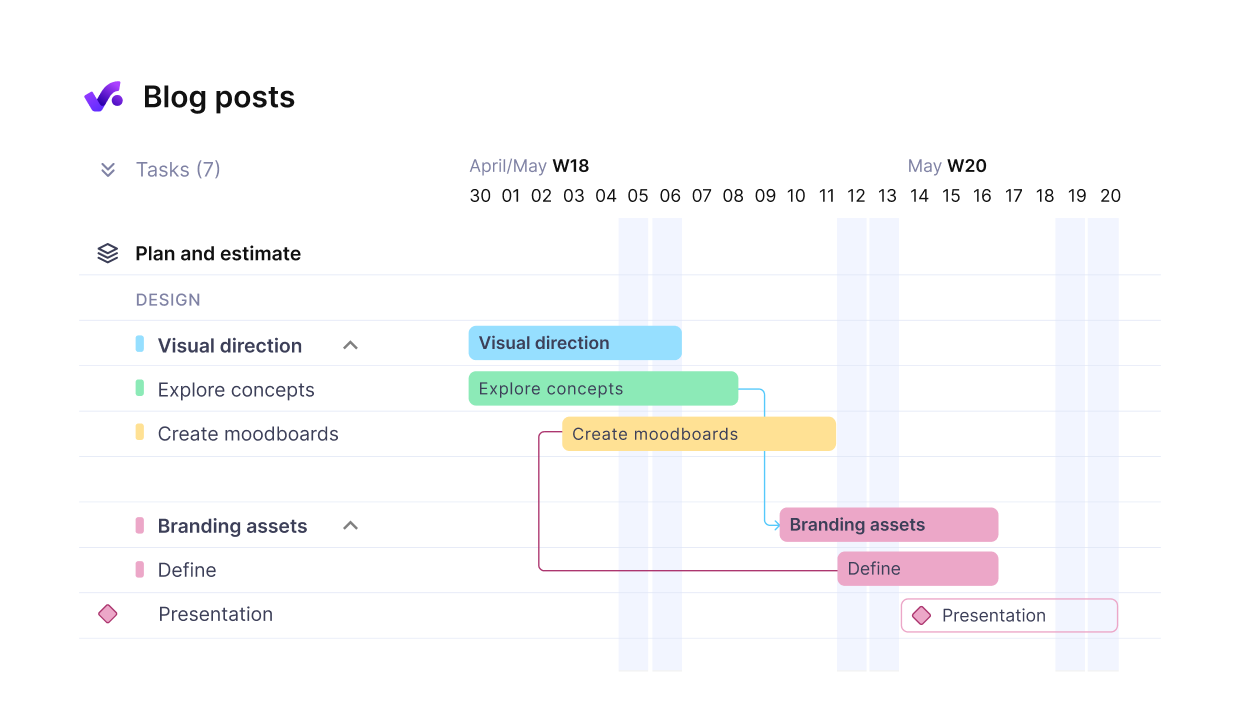
Build a project schedule by sequencing tasks and setting dependencies. Place milestones at key delivery points. A clear project timeline prevents delays and helps with project scheduling across teams.
In Productive, you can drag-and-drop tasks, adjust dependencies, and view the whole schedule of your project plans in a timeline view.
4. Project Budget
Develop a project budget that accounts for labor, tools, and materials. Use past cost data to establish a cost baseline and avoid underestimating expenses. Link budget items to deliverables so you can see what each part of the plan will cost. It’s also important to consider value-based pricing, ensuring your pricing reflects the outcomes and impact delivered to the client—not just the hours or resources used.
Productive ties time tracking and expenses directly to budgets, giving you real-time financial visibility and early warnings when project costs rise.
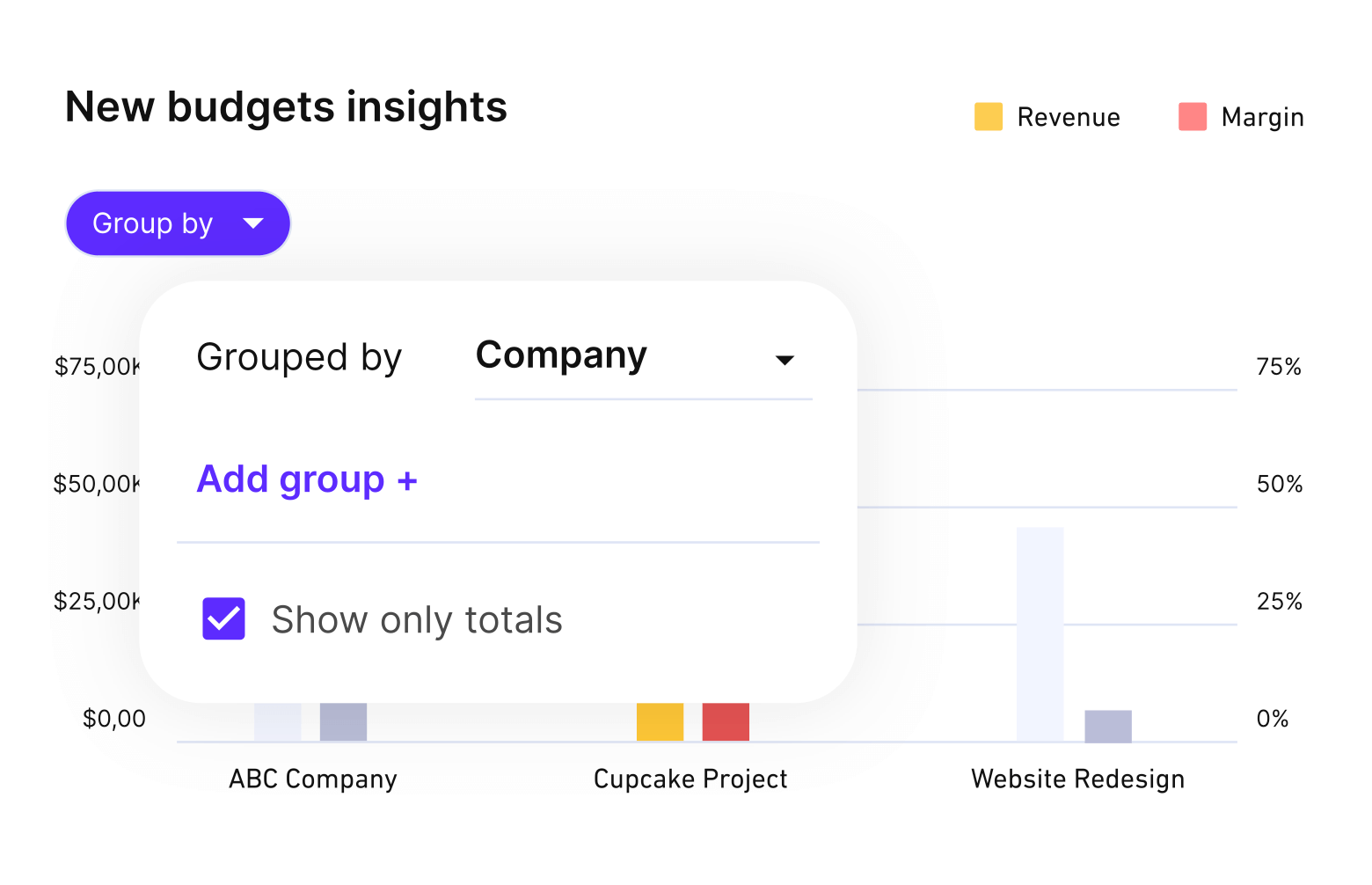
Tie tasks directly to budgets and monitor them in real-time.
5. Resource Planning
Plan resources by listing who will work on each task and what tools they need. Check workloads against past data to make sure assignments are realistic. Spread work evenly to avoid bottlenecks and burnout.
In case you need more actionable, how-to advice, head over to our huge guide on resource planning. In Productive, resource management tools let you see team capacity, forecast availability, and reassign tasks before issues build up.
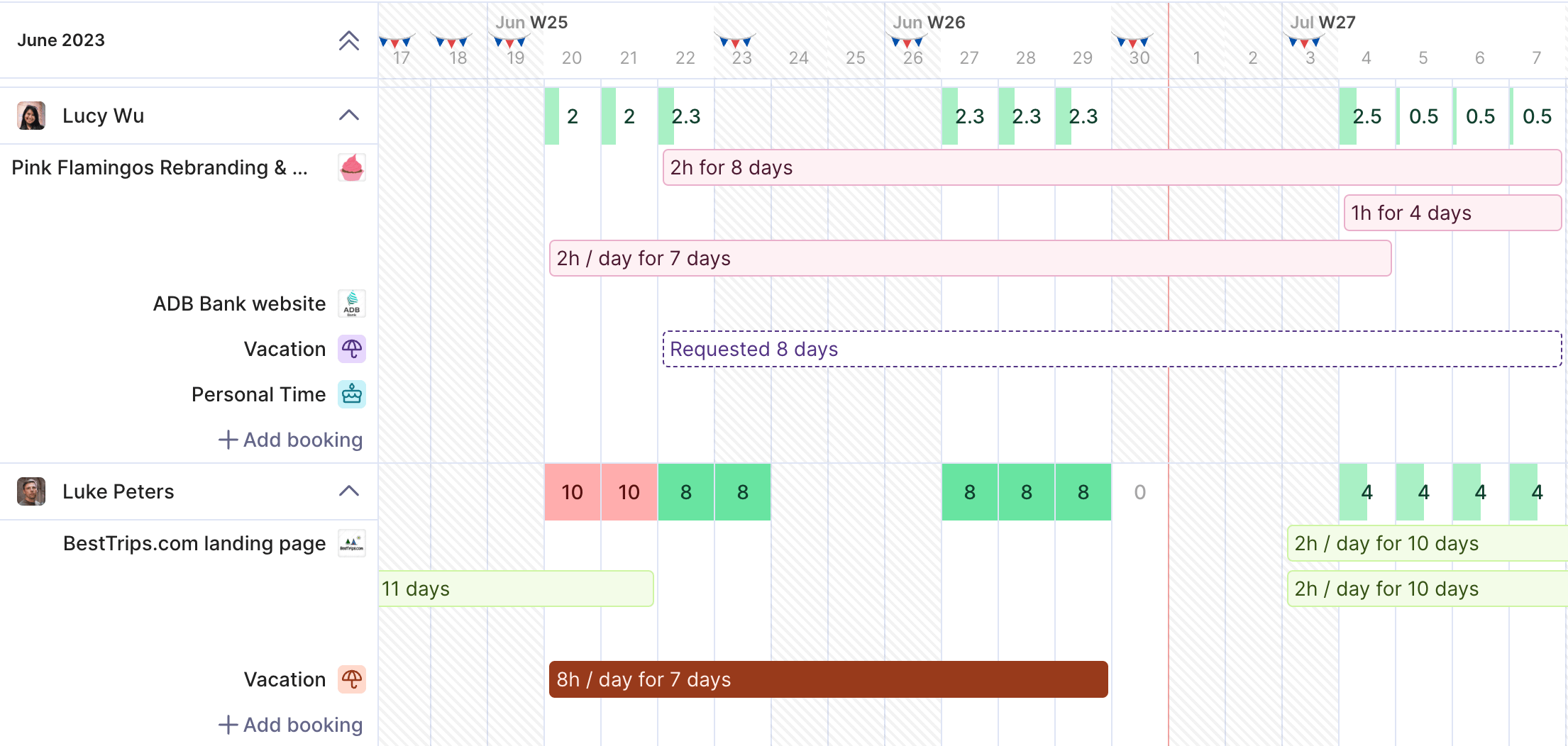
Make realistic resource plans with full visibility.
6. Risk Management
Develop a risk register with risks, likelihood, and impact ratings. Add mitigation strategies and assign each risk to an owner (or risk manager). Look back at previous projects to identify recurring risks (like as vendor delays or unrealistic timelines).
In Productive, you can log risks as tasks, track progress, and get notified if update deadlines slip.
For example, you could create a task called “Development Costs Risk,” assign it to a risk manager, attach documents detailing potential cost overruns, and add comments with mitigation strategies. This way, the entire team sees the risk in context and knows who owns the next steps.
7. Communication Strategy
Design a communication plan that specifies who needs updates, how often, and in what format. Use real examples, such as “Daily 15-minute stand-ups” or “Weekly stakeholder summaries.”
Review past projects to identify where communication broke down and adjust. Productive integrates project communication with tasks, so updates, comments, and files stay in context.
8. Stakeholder Engagement
Create a stakeholder management plan that lists all project stakeholders, their level of influence, and preferred communication channels. Engage them early by sharing the project outline and getting input on deliverables. Schedule regular check-ins to stay aligned and prevent conflicts.
We talk more about this (and share actionable advice) in our stakeholder engagement article.
In Productive, you can track project stakeholders, log feedback, and ensure every update reaches the right audience.
How Do You Create a Project Plan Step by Step?
You create a project plan by following eight clear steps: define the scope, set goals and objectives, develop deliverables, assign roles and responsibilities, plan budget and resources, identify risks, build a project schedule, and establish communication workflows.
These steps give structure to your project planning process and keep stakeholders on the same page. Below, we break them down into practical actions for making project plans.
Step 1: Define Scope
Write a project statement that spells out what you will deliver and what you will not. Use lessons learned from past projects to estimate realistically how long each type of activity might take. Share the document with stakeholders early to avoid scope creep ensure contract alignment with the project plan.
In Productive, you can document the scope directly in the project so everyone works from the same version, and you can compare against historical project data.
Centralize all documentation, so that team members can edit, share and collaborate on project plans.
Step 2: Set Goals and Objectives
Translate the scope into SMART objectives. For example, “Launch the campaign website by June 30 with five landing pages.” Check past project timelines to confirm your deadlines are realistic.
Productive links objectives with milestones and lets you monitor progress against similar projects, so you know whether you’re on track.
Step 3: Develop Deliverables
Break objectives into tangible outputs such as reports, prototypes, or finished features. Estimate the time and resources each deliverable will require based on past experience. Attach each deliverable to a milestone.
In Productive, you can track deliverables with deadlines, owners, and historical data on similar work to plan more accurately.
Step 4: Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Clarify who owns each task. Use a RACI matrix if the group is large. In Productive, you can assign tasks to people, set watchers, and ensure accountability with built-in roles that are transparent to the whole team.
Step 5: Plan Budget and Resources
List expected costs for people, tools, and materials. Use past project cost data and apply proven effort and cost estimation techniques to refine estimates and avoid underbudgeting.Track planned versus actual spend. Productive connects budgets to time tracking and expenses, so you see profitability in real time and compare with historical trends.
Step 7: Identify Risks
Create a risk register with clear descriptions, likelihood ratings, and mitigation steps. Review past project data to identify recurring risks to project success (like vendor delays or slow client feedback cycles). For example, “Vendor delay could impact delivery. Mitigate by preparing a backup supplier.”
In Productive, you can log risks as tasks, assign them to owners, and monitor them on dashboards.
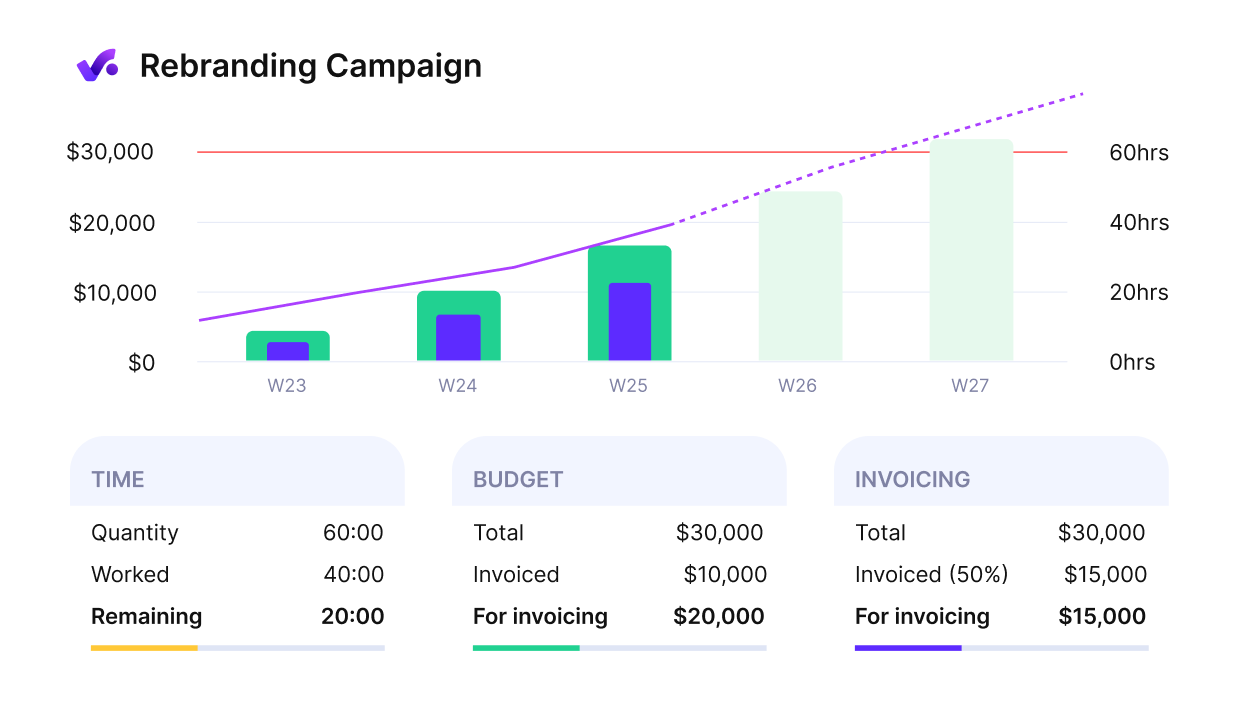
Get an early warning in case of budget overruns.
Step 8: Build a Project Schedule
Sequence activities, set task dependencies, and define milestones. Use lessons from past project schedules to predict bottlenecks.
Apply Gantt charts or timelines to visualize the plan. In Productive, you can drag-and-drop tasks on a timeline and adjust as changes happen while also comparing to historical delivery data.
Step 9: Establish Communication Workflows
Decide how the team will report status, share feedback, and escalate issues. For example, daily check-ins for progress and weekly reports for stakeholders.
Look at communication protocols from before and fine-tune the process. Productive integrates chat, comments, and notifications into each task, keeping updates visible and tied to context.
Make project plans with Productive
What Are the Phases of the Project Planning Process?
The phases of project planning are: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring & controlling, and closure. These phases structure the project lifecycle and provide checkpoints to keep teams aligned.
Below, we break them down into goals, impact, and what you do in each phase.
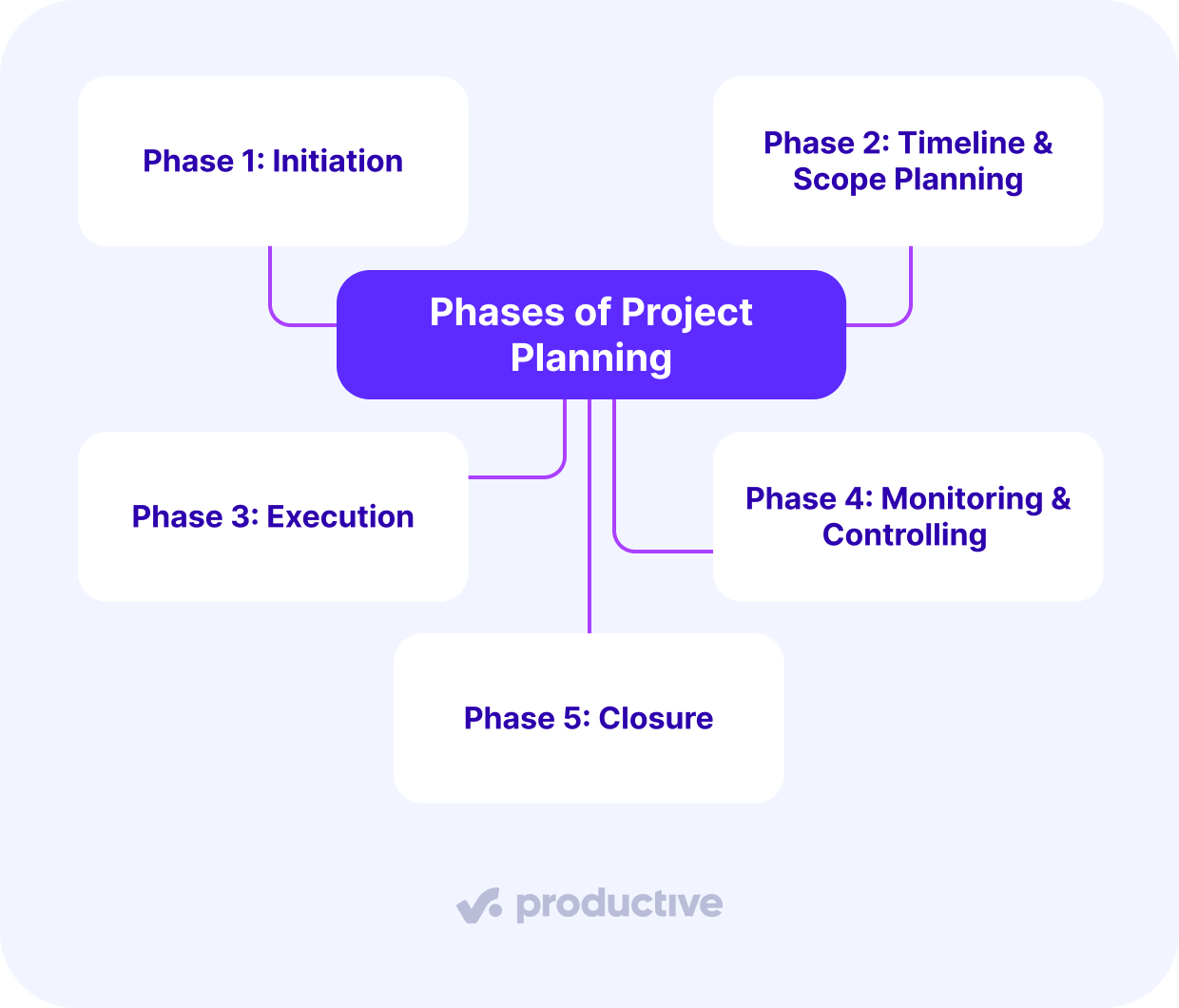
Phase 1: Initiation
Define the project’s purpose, objectives, and feasibility. The goal is to secure approval and stakeholder buy-in before committing resources. Strong initiation ensures a clear direction and business justification.
Required input: business case, stakeholder needs, high-level project outline.
Output: approved project charter with clear objectives and decision to proceed.
Phase 2: Timeline & Scope Planning
The project planning phase creates the detailed roadmap for execution throughout the project lifecycle. Teams define scope, objectives, budget, schedule, and risks. A solid plan reduces surprises and provides clarity for every person on your stakeholder list.
Required input: project charter, stakeholder requirements, past project data.
Output: complete project plan with scope statement, scope management plan, WBS, budget, schedule, risk register, and communications management plan.
Phase 3: Execution
During execution, teams deliver the agreed tasks and outputs. The goal is to complete deliverables while managing resources effectively. Execution has the biggest impact on timelines and quality management.
Required input: approved project plan, team assignments, tools, and resources.
Output: project deliverables completed according to the plan.
Phase 4: Monitoring & Controlling
Run monitoring and controlling alongside execution. Track progress, compare results with the plan, and adjust where needed. The goal is to keep the project aligned with objectives and budget. Productive dashboards help you track performance in real time.
Required input: live project data (progress reports, time tracking, budget use).
Output: status updates, issue logs, and corrective actions that keep the project aligned with objectives.
Phase 5: Closure
Finalize the project. Deliver final outputs, release resources, and document lessons learned. The goal is to confirm stakeholder satisfaction and record insights for future projects. Strong closure improves trust and future planning.
Required input: completed deliverables, client acceptance, and team feedback.
Output: formal project closure report, released resources, and a lessons learned document.
How Do Project Plans Help Avoid Common Mistakes in Execution?
A project management plan helps avoid common mistakes by preventing scope creep, improving team alignment, providing financial visibility, and ensuring resource planning is realistic.
These benefits keep projects on track and address common issues that cause delays, overspending, or missed expectations.
| How It Helps? | Context | Impact | How It Prevents Mistakes? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prevents scope creep | Defines clear deliverables and exclusions | Keeps work focused and avoids wasted effort | Provides documented boundaries so out-of-scope requests can be rejected with evidence |
| Improves team alignment | Makes roles, responsibilities, and objectives visible | Teams understand their tasks and dependencies | Reduces duplicated work and missed hand-offs by clarifying accountability |
| Provides financial visibility | Links budgets with tracked time and expenses | Shows profitability and burn rate in real time | Prevents overspending by comparing planned vs. actual costs with early alerts |
| Ensures resource planning is realistic | Forecasts team capacity and workloads | Keeps assignments balanced and achievable | Avoids burnout and delays by spotting over-allocation or under-utilization early |
What Are the Common Mistakes in Planning Projects + How To Avoid Them?
The most common mistakes in making project plans are unclear scope, unrealistic schedules, weak budgeting, and poor communication. These issues often come from rushing the planning process or relying on guesses instead of past project data.
Below is a table that shows each mistake, its root cause, the impact it has on the project plans, and how you can fix it.
| Common Mistake | Root Cause | Impact | How to Fix It? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unclear scope | Lack of stakeholder input and vague objectives | Scope creep, missed expectations, wasted effort | Create a detailed scope outline and validate it with stakeholders early. |
| Unrealistic schedule | Guessing task durations without past data | Missed deadlines, overworked teams | Use historical project data to set realistic timelines and add buffers. |
| Weak budgeting | Ignoring hidden costs or underestimating resources | Cost overruns, reduced profitability | Link budgets to deliverables and track planned vs. actual spend continuously. |
| Poor communication | Scattered updates across tools or no clear reporting rhythm | Misalignment, duplicated work, stakeholder frustration | Define communication workflows and centralize updates in one platform. |
What Tools To Use to Create a Project Management Plan?
The best tools for creating a project management plan are project management software with Gantt charts, Kanban boards, and dashboards, collaboration tools for communication, and all-in-one platforms like Productive that combine planning, tracking, and reporting in one place.
These project planning software tools should solve common problems like fragmented systems, manual processes, and a lack of financial visibility. Below, we break down each type of tool and how it helps you create better project management plans.
In case you need extra advice, head over to our article on choosing project management software.
Project Management Software (Gantt, Kanban, Dashboards)
Use project management software to structure tasks, timelines, and dependencies. Create Gantt charts to map schedules, manage tasks on Kanban boards, and track key performance metrics (KPIs) with dashboards in real time.
These tools help you reduce confusion and spot delays early on. In Productive, you can do all of this in one platform without switching between separate apps.
Key features to look for:
- Gantt charts: visualize project timelines and dependencies to avoid bottlenecks.
- Kanban boards: manage tasks in a simple drag-and-drop view that keeps progress clear.
- Dashboards: track KPIs and budgets at a glance so you always see project health.
- Integration options: connect with time tracking, file storage, and communication tools.
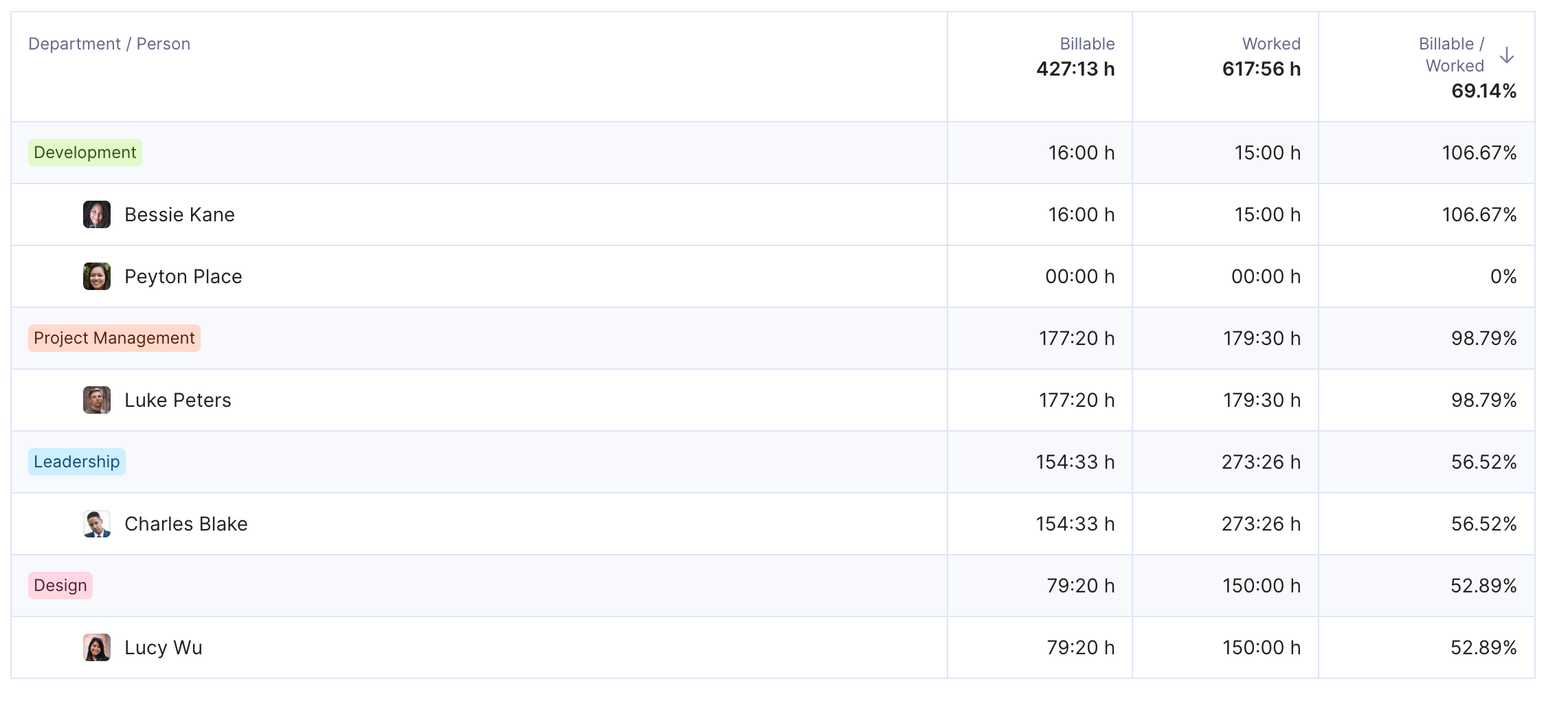
Use Productive’s Kanban boards with tasks and assigned owners.
Collaboration Tools
Choose collaboration tools that make things like updates, discussions, and file sharing easy to access in one place. When you centralize communication, you prevent silos that cause missed information and alignment issues.
If your team is drowning in scattered messages across email, chat apps, and spreadsheets. Productive solves this by tying task discussions directly to project tasks so you always keep context.
Key features to look for:
- Real-time messaging: keep conversations quick and searchable.
- File sharing and version control: ensure the team works with the latest documents.
- Task-linked communication: connect discussions directly to tasks to preserve context.
- Notifications and alerts: keep everyone aware of updates without overwhelming inboxes.
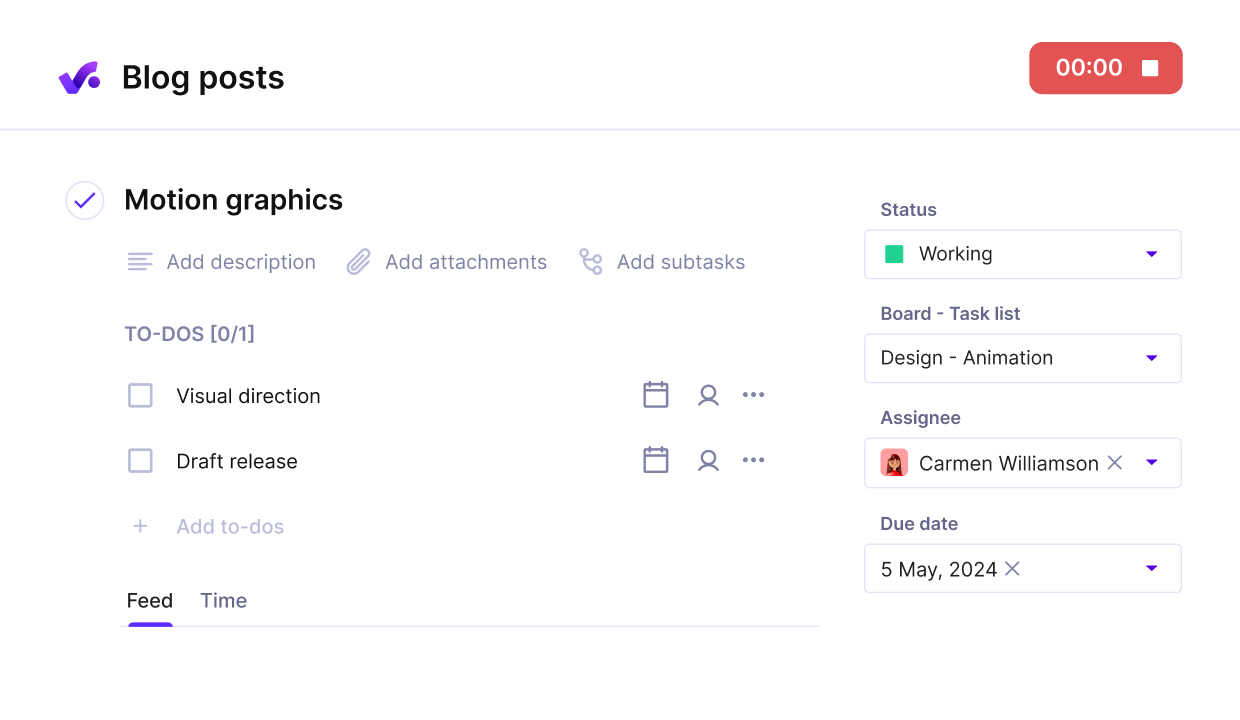
Tie execution and collaboration directly on tasks and easily keep track of statuses and project progress.
All-in-One Tools Like Productive
Work with all-in-one tools to bring planning, budgeting, resource allocation, and reporting together. Instead of juggling multiple systems, manage everything in a single platform. This approach eliminates fragmented systems and manual data transfers.
With Productive, you gain financial visibility, real-time capacity planning, and clear dashboards, helping you deliver projects on time and within budget.
Key features to look for:
- Integrated planning and budgeting: connect financials to tasks for accurate forecasting.
- Resource management: monitor availability and workloads in one dashboard.
- Reporting and analytics: generate real-time insights on progress, costs, and profitability.
- Scalability: support multiple teams and projects without adding disconnected tools.
Work with all-in-one tools to bring planning, budgeting, resource allocation, and reporting together. Instead of juggling multiple systems, manage everything in a single platform.
This approach eliminates fragmented systems and manual data transfers.
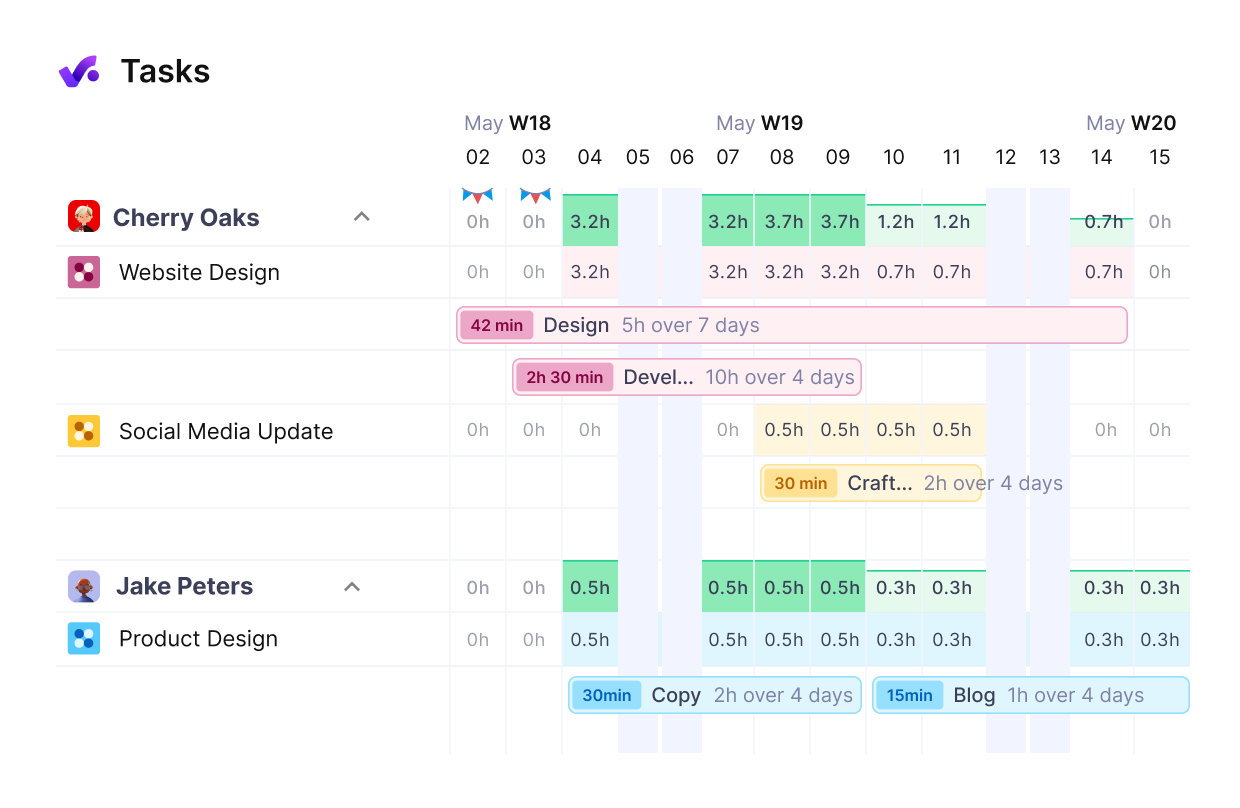
Get a real-time overview of your team’s workload.
What Are the Best Practices of Managing and Monitoring Project Management Plans?
The best practices for managing and monitoring project management plans are regular progress reporting, maintaining risk registers, applying plan adjustment strategies, and keeping stakeholders updated.
These practices give you visibility, help you react quickly, and build trust with your team and clients. Below, we expand on each practice with actionable instructions and bonus tips.
Regular Progress Reporting
Establish a clear reporting rhythm and compare actual progress against planned milestones to catch deviations early and keep the project on track. Share metrics like tasks completed, budget used, and time logged.
In Productive, you can generate automated reports and dashboards that show this data in real time, saving you from manual spreadsheets.
Bonus tips:
- Set a fixed reporting rhythm (e.g., every Friday) to create consistency for your team and stakeholder list.
- Compare current progress with baselines from past projects to catch delays early.
- Focus reports on outcomes, not just activity, to make updates more meaningful.
- Tailor reports to your audience: leadership wants summaries, while teams need detailed task data.
Risk Registers
Keep a risk register that lists threats, their likelihood, and mitigation actions. Your risk management plan need to be updated weekly.
Each risk should have an assigned owner. Productive lets you track risks as tasks, assign them to team members, and monitor them on project dashboards so nothing slips through the cracks.
Bonus tips:
- Involve the team in risk identification workshops to capture risks you might overlook.
- Categorize risks (financial, technical, client-related) to prioritize actions more effectively.
- Revisit risks after each project milestone to adjust likelihood or impact scores.
- Use visuals such as heatmaps to make risks easier to understand during updates.
Plan Adjustment Strategies
When results deviate from the plan, act fast. Re-sequence tasks, re-allocate resources, or revise deadlines. Productive makes this easier with drag-and-drop scheduling and budget alerts, so you can adjust without losing sight of overall objectives.
Bonus tips:
- Compare current progress with similar past project data to see if deviations are temporary or recurring.
- Adjust priorities based on business value, not just urgency, to keep resources focused where they matter most.
- Document every adjustment and its reason so stakeholders understand trade-offs.
- Use scenario planning to test how different changes (e.g., shifting deadlines or resources) will affect the overall project plan.
Stakeholder Updates
Update stakeholders consistently with clear, concise information. Send weekly summaries, highlight wins, and flag issues early. Productive centralizes all communication in one place, so updates are visible to everyone without digging through email chains.
Bonus tips:
- Segment your stakeholder list by their level of involvement and customize updates for each group.
- Share both positive outcomes and risks so stakeholders see a balanced picture.
- Use visuals like dashboards or milestone charts to make updates easy to digest.
- Schedule feedback sessions, not just one-way updates, to keep stakeholders engaged and aligned.
Example of a Project Management Plan
Here’s a realistic example of a project management plan: A digital marketing agency is launching a client’s e-commerce website.
The plan includes a statement of scope (deliver a fully functional site with integrated checkout), a project schedule (12 weeks with weekly milestones), a budget ($60,000 with line items for design, development, and testing), a risk register (vendor delays, scope changes), and a communication strategy (weekly client calls, daily internal stand-ups).
The team assigns responsibilities through a RACI matrix (or on tasks) and tracks the project execution plan with Gantt charts and Kanban boards in Productive.
What Can You Learn From This Example
- Clear scope keeps client expectations realistic and prevents scope creep by setting firm boundaries for what will and won’t be delivered.
- Defined milestones and budget tracking improve accountability and financial visibility, allowing both the team and client to see exactly how progress compares with investment.
- A risk register prepares the team for challenges before they become problems by assigning owners and mitigation steps, which avoids last-minute surprises.
- Consistent communication builds trust and ensures quick alignment on changes, reducing friction and strengthening relationships with clients and internal stakeholders.
RACI Matrix Example
Here’s a simplified RACI matrix for the e-commerce website launch project.
| Task | Responsible | Accountable | Consulted | Informed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Define scope | Project Manager | Client | Design Lead | All Team Members |
| Website design | Design Lead | Project Manager | Developer | Client |
| Website development | Developer | Project Manager | QA Lead | Client |
| Testing, QA and quality management | QA Lead | Project Manager | Developer | Client |
| Weekly client communication | Project Manager | Client | Account Manager | Team Members |
| Final delivery and handover | Project Manager | Client | All Leads | All Team Members |
Managing a RACI matrix manually can quickly become messy when projects grow. In Productive, roles and responsibilities are built into every task, so accountability and visibility are always clear without the need for extra spreadsheets.
Free Template For Planning
Project Name:
Project Manager:
Start Date:
End Date:
Scope Statement:
Objectives:
Deliverables:
Milestones:
Budget:
Resources:
Risk Register:
Communication Plan:
Stakeholder Management:
How To Use This Project Template?
1. Copy paste the project plan template and fill in project details like name, manager, and dates to set a baseline.
2. Write a statement of project scope with a list of deliverables to lock down expectations.
3. Add SMART project objectives and milestones to measure progress.
4. Outline your budget with cost categories and link them to tasks.
5. Assign resources and responsibilities clearly.
6. Populate the risk register with threats, likelihood, and mitigation actions.
7. Document how and when you’ll communicate with stakeholders.
8. Review the project management plan with your team and update it regularly in a tool like Productive to keep everything visible and actionable.
Final Thoughts
Project management plans bring clarity, structure, and accountability to every stage of a project, helping you deliver results on time and within budget.
With Productive, you can manage planning, financial tracking, and resource allocation all in one place, making the entire process smoother and more reliable.
See how Productive makes project planning easier, more transparent, and more profitable – book a demo today.
Make realistic project plans with Productive
Use real data to estimate budgets, allocate resources, and forecast profitability.
Keep projects transparent, predictable, and profitable from day one.