Top 12 Project Management Methodologies (2026) Overview
Project management methodologies are structured frameworks that guide projects from initiation to completion.
Each method offers unique advantages, so we’ve created a detailed overview with pros, cons, use cases, and implementation tips for every approach. By the end, you’ll know exactly when and how to use each project management method.
Key Takeaways on PM Methods
- Popular PM methodologies include Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, Kanban, Lean, PRINCE2, and Critical Path Method, each with unique approaches.
- You should choose which PM methods to use based on project complexity, structure, industry requirements, organizational goals, and stakeholder involvement levels.
- The Waterfall approach follows sequential phases with extensive planning, while Agile emphasizes iterative cycles, flexibility, and continuous adaptation to changing requirements.
- Implementing standardized methodologies ensures timely delivery, budget adherence, quality standards, efficient resource allocation, and improved collaboration.
What Are Project Management Methodologies?
Project management methodologies are frameworks that combine principles, tools, and practices to guide your projects from inception through completion.
This systematic and structured approach is your roadmap for delivering projects on time and within budget while maintaining quality standards through standardized workflows and enhanced communication.
Definition and Core Purpose
As defined by the Project Management Institute’s (PMI) PMBOK Guide (6th Edition), a project management methodology is:
A project management methodology is a system of practices, techniques, procedures, and rules used by those who work in a discipline.
The PMBOK Guide typically uses “methodology” in this way — referring to the organized set of methods applied to manage a project.
The core purpose of this framework is to guide teams through the all the way to a successful project delivery. We talk more about what is project management in our other comprehensive guide.
Importance in Project Success
Implementing a structured approach greatly enhances your project’s likelihood of achieving its objectives. The right method will make a huge impact in:
- Resource Optimization – Your methodology guarantees efficient allocation of time, budget, and personnel.
- Risk Mitigation – Whether using predictive or Agile project management frameworks, you’ll identify and address potential issues proactively and minimize their effect.
- Stakeholder Alignment – Clear project planning protocols help project managers enhance communication and maintain expectations throughout execution.
What Are the Types of PM Methods?
The types of project management methods are traditional, Agile, advanced, and hybrid. Each of the covered project management approaches has its core principles, frameworks, and best use cases.
Project managers should keep in mind that choosing the right method isn’t a rule-of-thumb thing. Also, there’s another massive list of methods and tools for managing projects on our blog, you might want to check that out as well.
Now that you know everything you should about the importance of using the right PM method, we’ll first give you a detailed overview and then teach you how to choose and implement the best-structured approach for your project.
Let’s start with the classics.
| PM Method Type | What It Is | Best Used For | Key Methods | Best If You Need |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Linear, structured approaches with strict phases and detailed upfront planning. | Projects with fixed requirements, strict timelines, and budgets. | Waterfall Method, Critical Path Method, PRINCE2 | Predictability, strong control, clear scope. |
| Agile Approaches | Iterative, flexible methods focused on rapid delivery, collaboration, and adaptation to change. | Projects with evolving requirements and frequent client feedback. | Agile, Scrum Method, Kanban, Extreme Programming (XP) | Flexibility, speed, and client collaboration. |
| Advanced | Data-driven, efficiency-focused frameworks for complex process optimization and precision. | High-complexity or quality-critical projects, often large scale. | Lean, Six Sigma, Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) | Precision, waste reduction, resource optimization. |
| Hybrid | Combines elements of traditional and Agile to balance structure with flexibility. | Projects needing both controlled planning and adaptive execution. | Scrumban, Adaptive Project Framework (APF) | Flexibility with a layer of structure. |
Detailed Overview of the Most Used Project Management Methodologies
The most used project management methods are Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, and Kanban. Since there isn’t a rule of thumb as to which one to choose, we’ll give you a detailed overview of each one, along with its pros, cons, best tool recommendations, and use cases.
No worries, we’ll get to the more advanced and hybrid approaches later.
Deliver projects with Productive
Waterfall Methodology
What is Waterfall methodology?
Waterfall is a linear project management method where each phase must be fully completed before the next begins.
The sequential approach requires you to:
- Complete each phase before advancing.
- Document well-defined requirements thoroughly
- Use Gantt charts for timeline visualization.
When should you use this method?
You should use Waterfall when you’re managing projects with clearly defined requirements and minimal expected changes. This method has a structured, sequential approach where each phase—from requirements gathering through maintenance—must be completed before progressing to the next.
The linear framework of this traditional method is the best fit for maintaining strict budgets and deadlines through extensive upfront planning. It’s important to understand that this same rigidity can become a limitation when your project demands flexibility or iterative adjustments.
We talk more about this in our Waterfall PM guide.
When you shouldn’t use it?
Avoid Waterfall if your project needs flexibility, frequent updates, or if requirements are likely to evolve after work begins. Since it’s so fixed and strict, you can’t make last-minute adjustments; if you do, you’ll end up derailing the project.
What are the best tools for implementing the Waterfall methodology?
Tools like Productive, Microsoft Project, and GanttPRO are the best fit for managing Waterfall’s structured, phase-by-phase workflow.
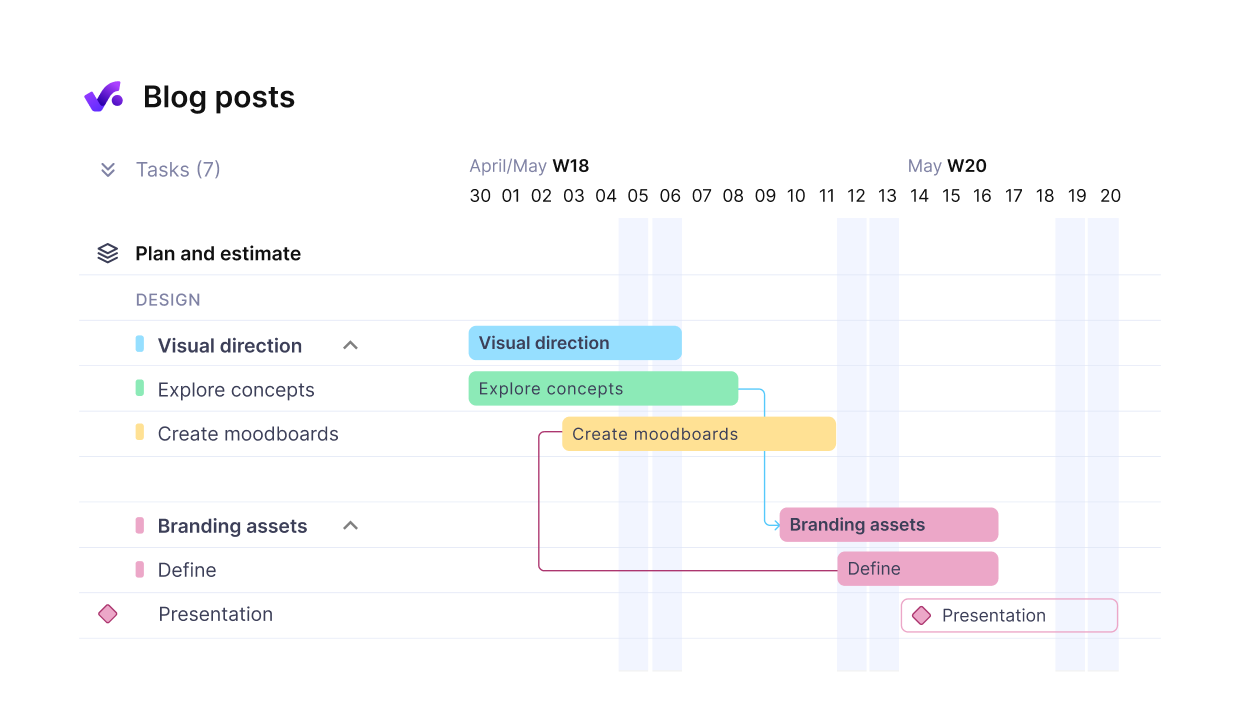
Use Productive to map out and sequence your project phases.
Agile Methodology
What is Agile methodology?
Agile is a flexible project management method based on iterative cycles, where work is divided into short sprints. This project management framework focuses on continuous improvement and adapting to changing requirements.
This approach breaks your project into short sprints—typically lasting two to four weeks—where teams develop, test, and refine deliverables based on ongoing stakeholder feedback.
At its core, Agile’s values and principles prioritize collaboration over contracts, working solutions over documentation, and embracing change rather than following rigid plans.
The “iterative development” part means that you’ll:
- Adapt quickly to changing requirements
- Enhance customer collaboration throughout sprints
- Choose between Scrum’s structured ceremonies or Kanban’s visual workflow
When should you use this method?
You should use it when you’re managing projects with evolving requirements or uncertain outcomes.
When you shouldn’t use it?
Avoid this approach if your project demands strict structure, fixed deliverables, or regulatory requirements that don’t allow for frequent changes.
What are the best tools for implementing Agile methodology?
The best for this approach tools are Jira, Trello, and Productive since all of them support Agile workflows (like Scrum sprints and Kanban boards).
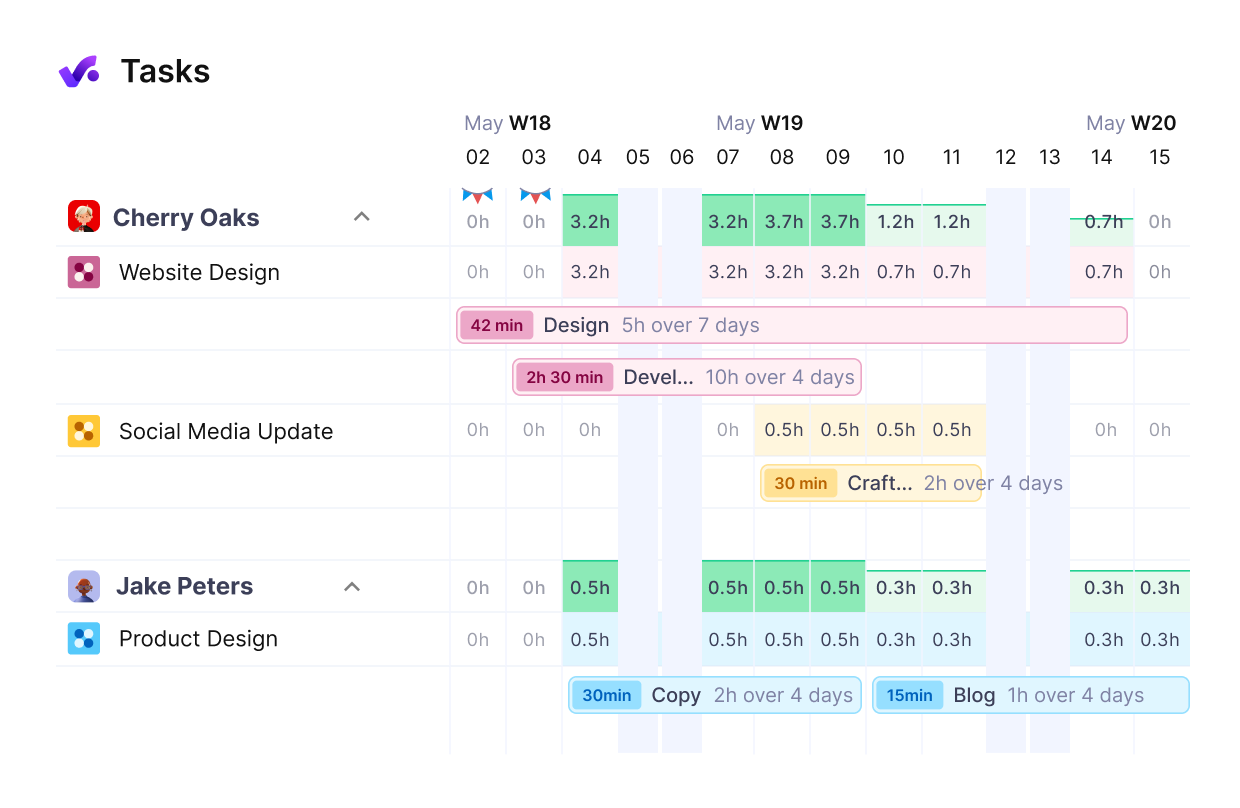
With Productive you can schedule your team ahead PLUS get an exact overview of who’s doing what, and what’s next.
Scrum Methodology
What is Scrum methodology?
Scrum is a subset of Agile that organizes work into short sprints with defined roles like Scrum Master and Product Owner. It uses structured ceremonies to drive collaboration and deliver incremental value.
The idea behind this approach is to transform abstract Agile principles into a concrete, sprint-based framework where work progresses through fixed time periods of one to two weeks. This method has clear roles like:
- Scrum Master who helps the team implement and adhere to the Scrum framework
- Product Owner who manages overall priorities and hosts daily stand-up meetings
These elements work together to create transparency, cultivate collaboration, and enable your colleagues to deliver value piece-by-piece while adapting to changing requirements throughout the project lifecycle.
This methodology transforms project delivery through:
- Sprints – 1-2 week iterations enabling rapid customer feedback
- Cross-functional teams – 10 or fewer members collaborating flexibly
- Transparency tools – Sprint backlogs and burndown charts
- The Scrum Master facilitates daily meetings, while performance reviews enhance continuous improvement.
When should you use this method?
You should use Scrum on projects that require fast, iterative progress, close collaboration, and regular feedback in a project with shifting priorities.
When you shouldn’t use it?
Avoid using this approach if your colleagues lack experience with Agile practices or if the project scope and requirements won’t change and everything is fixed.
What are the best tools for implementing Scrum methodology?
Jira, ClickUp, and Productive are top tools for managing Scrum workflows, sprint planning, and task management.
Kanban Methodology
What is Kanban methodology?
Kanban is a visual project management method that organizes project tasks on a board to show their status and focuses on continuous workflow improvement by limiting work-in-progress and refining processes based on real-time data.
The method’s visual workflow management transforms how teams track and complete tasks by displaying work items on boards that clearly show each task’s current status and progression.
The idea here is to regularly evaluate workflow metrics, identify bottlenecks, and systematically refine daily processes based on real-time data rather than predetermined schedules.
These boards consist of:
- Columns representing workflow stages
- Cards tracking individual tasks
- WIP (work in progress) limits prevent bottlenecks
When should you use this method?
Use Kanban when you need to visualize work, manage ongoing tasks without strict deadlines, and improve efficiency through gradual, data-driven changes.
When you shouldn’t use it?
Don’t use this method if your project requires fixed timelines, rigid schedules, or structured phases rather than a continuous flow.
What are the best tools for implementing Kanban methodology?
Trello, Kanbanize, and Jira are leading specialized tools for setting up and managing Kanban boards and workflows. Productive can also be an amazing Trello alternative.
If you want to learn more about this approach, have a look at our detailed Kanban guide.
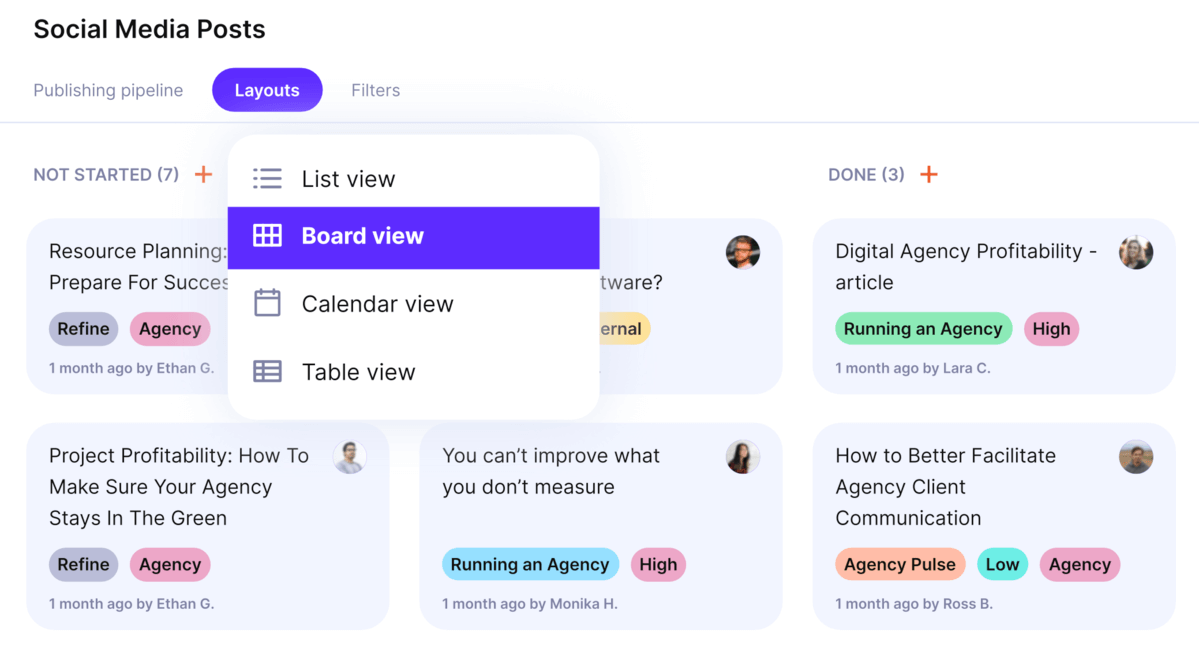
Productive’s Kanban boards are simple to set-up and easy to use.
Overview of the Advanced Project Management Frameworks
The more advanced PM frameworks are Lean Methodology, Six Sigma, PRINCE2, Critical Path Method, and Critical Chain Project Management. They go beyond the traditional approaches and are a better fit for more complex organizational challenges.
Again, each framework has its specific pros and cons, but it’s up to you to understand the method and your project to best know how and when to use it. Just like with the previous batch, here’s a detailed overview:
Lean Methodology
What is Lean methodology?
Lean project management methodology focuses on eliminating waste, streamlining workflows, and maximizing value by continuously improving processes. It was originally developed as a part of Toyota’s Production System.
The core principles of this approach are:
- Eliminate the 3Ms – Remove muda (wastefulness), mura (unevenness), and muri (overburden)
- Deploy value stream mapping – Visualize workflows to identify bottlenecks
- Integrate with Agile – Combine frameworks for enhanced flexibility
When should you use this method?
Use Lean when you want to boost efficiency, cut down excess effort or resources that shouldn’t be used, and deliver consistent value in controlled environments that benefit from ongoing process refinement.
You should mostly use it in manufacturing (whether you’re building something on an assembly line or sprint-based code development).
When you shouldn’t use it?
Don’t use the Lean project management methodology if your organization resists continuous change or if short-term deadlines don’t allow for slower improvements.
Six Sigma Method
What is the Six Sigma methodology?
Six Sigma is a data-driven method that uses the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control)framework to reduce defects, control variability, and improve processes to achieve near-perfect quality standards.
This PM method uses statistical analysis and data-driven decision-making to identify root causes and implement sustainable solutions. When you combine this approach with Lean methodologies, you’ll maximize efficiency while maintaining exceptional quality.
Your organization’s trained professionals, designated as Green and Black Belts, will lead transformative projects that reduce variability and enhance customer satisfaction through continuous improvement initiatives.
When should you use this method?
You should use this method when you require high levels of precision, consistency, and measurable improvements to achieve the project goals.
When you shouldn’t use it?
The method isn’t for your project if you lack the time, data, tech, or trained personnel needed for its detailed statistical analysis and structured problem-solving.
What are the best tools for implementing the Six Sigma methodology?
Specialized tools for implementing the method are Minitab, SigmaXL, and JMP. Alternatively, you can use Productive to track every bit of your project data and get advanced analysis on costs, progress, performance, costs, and so much more.
PRINCE2
What is the PRINCE2 methodology?
PRINCE2 is a structured project management method that has seven principles, themes, and processes. It provides clear roles, responsibilities, and a step-by-step approach from project start to finish.
The seven steps of PRINCE2 are:
- Starting up a Project – Define if the project is viable and worth pursuing.
- Directing a Project – Give overall guidance and decision-making authority to the project board.
- Initiating a Project – Plan the project in detail, setting clear baselines for cost, scope, and risk.
- Controlling a Stage – Manage each phase of the project, monitor progress, and deal with issues as they arise.
- Managing Product Delivery – Ensure that project outputs are created and delivered according to specifications.
- Managing Stage Boundaries – Review and plan as you move from one phase to the next, making adjustments if needed.
- Closing a Project – Wrap up the project, confirming completion and capturing lessons learned.
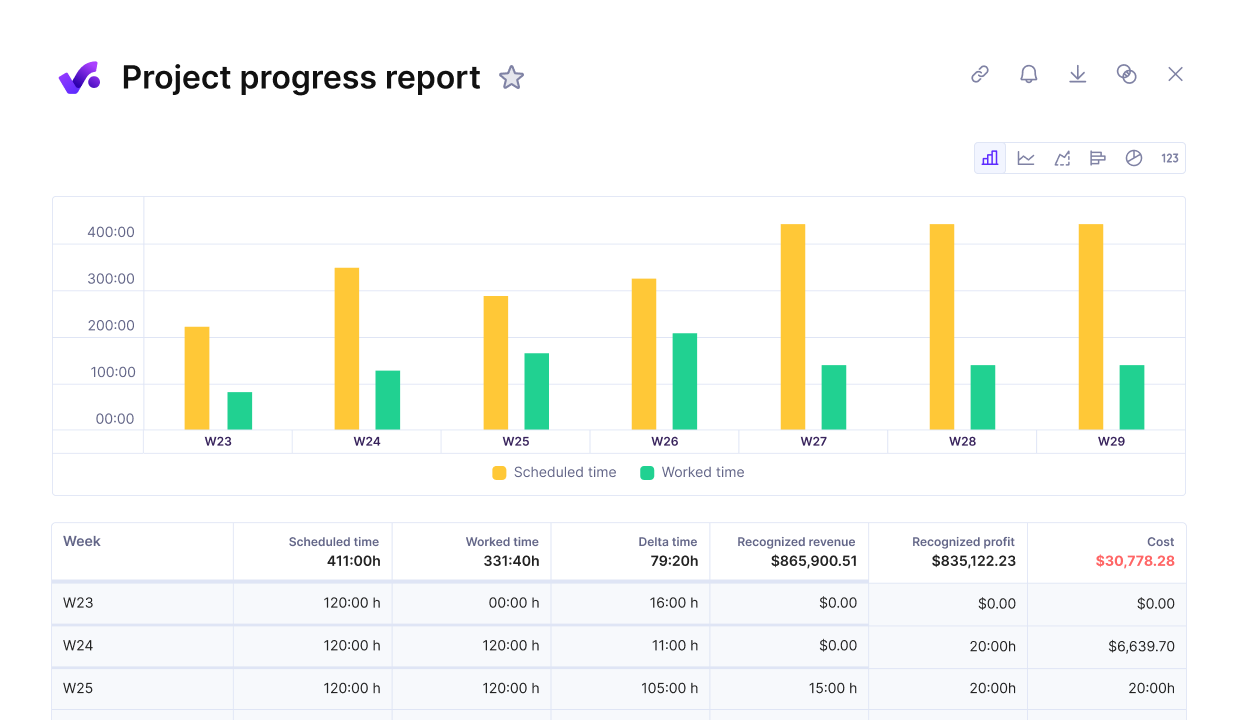
In Productive, you can monitor project progress in a single view.
When should you use this method?
You should use PRINCE 2 in complex project environments, where you need strong project control, well-defined processes, and clear accountability.
When you shouldn’t use it?
Don’t use PRINCE2 if your project needs flexibility or rapid changes that don’t align with its formal, process-heavy structure.
What are the best tools for implementing the PRINCE2 methodology?
Tools like PRINCE2 templates, Microsoft Project, and Sciforma help support PRINCE2’s structured project planning and control needs.
Critical Path Method
What is the Critical Path Method?
Critical Path Method (CPM) is a PM technique that maps out task dependencies to identify the longest sequence of activities, showing the shortest possible time to complete a project. This technique uses Gantt charts to visualize task schedules and dependencies, making it easier to spot bottlenecks and track progress.
When should you use this method?
You should use CPM when you’re managing projects with multiple interconnected project tasks that require clear critical task prioritization and where it’s super important to stay on schedule with the development cycle.
When you shouldn’t use it?
Project managers should avoid using CPM if their projects are small, simple, or lack clearly defined task dependencies.
What are the best tools for implementing the Critical Path Method?
Productive, Microsoft Project and Primavera P6 are widely used for creating Gantt charts and managing CPM schedules.
Critical Chain Method
What is Critical Chain Project Management?
Critical Chain Project Management is a PM method that builds schedules (chains of critical tasks) based on resource availability and protects timelines with strategically placed buffers, emphasizing resource flow over strict task order.
It focuses on resource optimization rather than just task sequences.
To be more specific, this approach focuses on:
- Strategic buffer management – You’ll place protective buffers at critical points rather than padding individual tasks.
- Resource-focused scheduling – You’ll prioritize resource availability over arbitrary deadlines.
- Dynamic monitoring – You’ll track buffer consumption to identify potential delays early.
When should you use this method?
Project managers should stick with CCPM if they manage projects that have limited resources and tight timelines.
When you shouldn’t use it?
Don’t use this approach if your project priorities shift frequently or if your project team doesn’t work well with disciplined buffer and resource management.
What are the best tools for implementing Critical Chain Project Management?
Again, use a tool like Productive that can help you keep track of strict timelines and tight buffers. Alternatively, you could go with specialized CCPM tools like ProChain, Sciforma, and CCPM+.
Hybrid and Specialized Methodologies
Hybrid and specialized methodologies offer tailored solutions for unique project challenges. The most popular approaches are:
- Scrumban – Scrum’s sprint structure + Kanban’s continuous flow.
- Extreme Programming (XP) – emphasizes technical excellence through practices like pair programming and continuous integration.
- The Adaptive Project Framework – provides a structured approach that leaves space for uncertainty, has iterative cycles, and encourages stakeholder collaboration.
Below is a breakdown of each hybrid approach.
Scrumban
What is Scrumban?
Scrumban is a hybrid methodology that combines Scrum’s structured sprint planning with Kanban’s continuous flow and visual task management to create a workflow that’s flexible and adaptive to change.
The three biggest benefits of this Agile approach are:
- Continuous Flow – You’ll pull critical tasks based on capacity, eliminating bottlenecks while maintaining sprint structure.
- Adaptive Planning – Your teams conduct regular reviews and sprint retrospectives, ensuring alignment with changing requirements.
- Balanced Workload – Work-in-progress limits prevent overwhelming colleagues. Scrumban’s flexibility makes it ideal for fluctuating demands.
- You’ll also maintain iterative development while adapting priorities dynamically and promoting collaboration throughout your project lifecycle.
When should you use this method?
Project managers should use Scrumban in dynamic environments where disciplined sprints are mandatory, but workloads and priorities change often.
When you shouldn’t use it?
You definitely shouldn’t use Scrumban if your project schedule has strict deadlines or if your project task priorities get changed often.
What are the best tools for implementing Scrumban?
Similar to Scrum and Kanban, you should use tools like Jira, Trello, and ClickUp to manage Scrumban boards and combine sprint and flow-based work.
Extreme Programming (XP)
What is Extreme Programming (XP)?
Extreme Programming is an Agile software development method focused on rapid releases, continuous feedback, and engineering practices like pair programming and test-driven development to deliver high-quality software.
When should you use this method?
XP should be used by software development teams that need maximum responsiveness to changing requirements. It’s best suited when working with small to medium-sized teams that prioritize customer satisfaction through continuous feedback loops.
When you shouldn’t use it?
Avoid XP at all costs if your developers lack experience with Agile frameworks or if your project requires strict documentation and rigid execution schedules.
What are the best tools for implementing Extreme Programming (XP)?
The best software tools for implementing this method are Jira, GitHub (with CI/CD pipelines), and TestRail because they support XP’s fast release cycles and testing-focused workflows.
Adaptive Project Framework
What is an Adaptive Project Framework (APF)?
Adaptive Project Framework (APF) is a change-driven and flexible PM approach that uses iterative planning, continuous stakeholder involvement, and self-organizing teams to handle evolving requirements.
Let’s break that down a little bit:
- Stakeholder collaboration – You’ll engage clients continuously, ensuring alignment with evolving expectations.
- Iterative development – You’ll reassess goals regularly, adapting deliverables based on feedback.
- Self-organizing teams – You’ll empower groups to make rapid decisions autonomously.
When should you use this method?
You should stick with APF when there’s a lot of uncertainty in your projects (like rapidly changing product requirements or innovation-driven goals). It’s mostly used in the software industry.
When you shouldn’t use it?
Don’t go with APF if you’re dealing with fixed outcomes, strict timelines, or a stable scope from the beginning.
What are the best tools for implementing the Adaptive Project Framework?
The best tools for implementing APF are Productive, Jira, and Wrike because they can manage iterative planning and dynamic collaboration.
How To Choose a Methodology for Managing Projects?
To choose the right project management methodology, you’ll need to assess your project’s type and complexity. Factor in your team’s skills and experience to make sure they can work within the chosen framework.
Then, align the methodology with your industry’s compliance needs and your organization’s strategic goals to ensure it supports both day-to-day execution and long-term success.
Keep in mind that choosing and implementing the right PM technique depends on various factors that you genuinely need to understand before you commit to the implementation.

Project Type and Complexity
The top three factors in choosing a PM method are project type, complexity level, and team dynamics. When you’re doing the evaluation, you should take into account that:
- Software development initiatives typically demand Agile’s flexibility to accommodate evolving requirements.
- Construction projects benefit from Waterfall’s structured phases and predictable progression.
- Product launches require methodologies matching their unique complexity levels. Your methodology selection directly correlates with project intricacy.
- Simple initiatives thrive under Waterfall’s linear approach, while complex endeavors necessitate Agile or Scrum’s iterative frameworks.
Team Structure and Skills
Beyond the characteristics of your projects, your team’s composition and capabilities shape which method you’ll use most effectively. Here, you’ll need to assess your team’s skills carefully; Agile demands adaptability and quick learning, while traditional approaches require strong documentation abilities.
You should also consider stakeholder involvement requirements. In case you’re managing complex projects with a lot of dependencies, you might choose the Critical Path Method. Always match your methodology to your team’s strengths for the best results.
Industry and Organizational Goals
Your industry’s unique requirements and organizational objectives serve as critical anchors when selecting a project management methodology. You’ll need to align your choice with:
- Compliance standards – Different sectors demand varying documentation levels and stakeholder involvement.
- Resource allocation – Your organizational goals determine whether structured methodologies or Agile methodologies fit better.
- Risk tolerance – High-stakes industries often require predictive methodologies for tighter control. Consider how complexity, time, timelines, and deadlines intersect with your sector’s norms.
How To Implement a PM Method?
Project management method implementation starts with matching the methodology to your project’s size and complexity. Before you commit to implementation, you should absolutely set clear roles and responsibilities (this part is super important, especially for structured frameworks).
When the roles are set and the method is decided, you should choose a project management tool that fits the required workflow. That’s also super important because you really need a reliable tool to streamline communication and task tracking.
Use the tool to run regular retrospectives to spot improvements early and document key metrics to track progress and keep your team aligned.
Use Productive to keep all documentation and collaboration in one place.
Here’s a short PM technique implementation checklist:
- Choose the right method – Agile for change, Waterfall approach for clear structure.
- Define clear roles – Make accountability clear from day one.
- Use the right tools – Platforms like ClickUp keep communication and tracking simple.
- Hold regular retrospectives – Catch issues early and improve fast.
- Track key metrics – Measure what matters to stay aligned and on target.
Why Do PM Methodologies Matter?
Project management methodologies matter because implementing them properly enhances your team’s efficiency by establishing clear workflows that eliminate redundant tasks. They bring structure to progress.
When you standardize your project processes through these frameworks, you’re creating repeatable patterns that reduce confusion, minimize errors, and enable team members to focus on creating value rather than figuring out what to do next.
As said before, these methodologies help you identify and mitigate risks early, which can prevent costly delays and budget overruns that threaten project success. Below is a short breakdown of the benefits:
Improved Team Efficiency
Project management methodologies introduce structured frameworks that transform chaos into efficiency. This, in turn, makes coordination smoother and unclear processes more straightforward.
You’ll enhance efficiency through:
- Visual workflow management – PM tools like Kanban boards help you track progress and identify bottlenecks instantly.
- Adaptive frameworks – Agile teams can quickly respond to changes while maintaining productivity.
- Continuous improvement – Lean and Six Sigma eliminate waste through iterative refinement and optimizes your resource allocation with clear roles and responsibilities. In turn, you’ll prioritize tasks effectively, align efforts with deadlines, and reduce confusion.
Standardized Project Processes
When you standardize ongoing project processes (or operations), you create a foundation that transforms individual successes into organizational excellence.
The goal here is to reduce errors and ensure consistency across all initiatives. These PM frameworks clearly define roles and responsibilities so that your team understands what’s expected of each member.
By following structured approaches to project execution, you’ll deliver predictable results that enhance stakeholder satisfaction through on-time, within-budget completions.
Reduced Project Risks
While standardized processes create organizational consistency, they also help identify and eliminate potential threats before they derail your project goals. Popular project management methodologies effectively reduce risks through:
- Early Detection – Frameworks like PRINCE2 evaluate potential roadblocks at each project phase.
- Adaptive Response – Agile methods enable continuous feedback and rapid adjustments
- Enhanced Communication – Collaborative tools minimize misunderstandings and help reduce scope creep
Closing Thoughts: How To Make a PM Method Work
You’ve explored a detailed overview project management methodologies, from traditional frameworks to hybrid approaches. When it’s time to select the best PM approach, your choice depends on project complexity, dynamics, and organizational culture.
Don’t hesitate to adapt methodologies as circumstances evolve. Start with one framework, measure its effectiveness, and refine your approach based on results.
Remember, the best methodology isn’t necessarily the most popular—it’s the one that aligns with your team’s capabilities and project requirements, while delivering consistent and measurable outcomes.
The tools you use play a huge part in the way you execute projects. If you want to keep all execution, communication, collaboration, progress reporting and task tracking under one roof – book a short 30-min demo with Productive.
From Agile to Waterfall, Manage Every Project With Productive
No matter which project management methodology you use, Productive adapts to your workflow. Simplify how you manage projects, teams, and budgets without the mess of multiple apps.
FAQ
What are the three most commonly used project management (PM) methodologies?
The three most commonly used PM methodologies are Waterfall, Agile, and Scrum.
What are the four types of methodology in a project?
The four types are Traditional (Waterfall, PRINCE2), Agile (Scrum, Kanban), Advanced (Lean, Six Sigma, CCPM), and Hybrid (Scrumban, Adaptive Project Framework).
What are the 5 methodologies of project management?
The five widely recognized project management methodologies are Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, Kanban, and Lean.
