What Is a Feasibility Study and How To Make One?
A feasibility study is an in-depth analysis that tells you whether or not you should start a project.
The idea is to find out if the project is realistic and worth pursuing before it starts. By the end of this article, you’ll learn all about this report, its components, challenges, types, benefits for project management, and how to create one.
Key Takeaways
- A feasibility study is a report used to assess the viability, practicality, and potential success of a proposed project before it begins.
- Its key components are preliminary analysis, project scope definition, market research, financial analysis, and technical evaluation.
- Conducting a feasibility report involves assessing viability, defining scope, doing a market analysis, analyzing finances, and evaluating technology.
- Operational assessment analyzes an organization’s capacity to execute the project, while risk assessment identifies and prioritizes potential risks.
What Is a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is a detailed analysis that evaluates the practicality, viability, and potential success of a proposed project or business venture. In large-scale projects, the feasibility report has to be done in the project planning phase, usually along with the SWOT analysis.
It assesses every major aspect, including technical, economic, legal, and operational factors, to determine whether the project is realistic and worth pursuing. Project managers use them to make informed decisions and minimize risks before investing resources.
Why Conduct a Feasibility Study?
Conducting a feasibility study tells you whether or not you should start a project. It includes detailed insights and an analysis of the practicality, risks, and economic benefits that the project brings to the table.
Keep in mind that the report is more than just a do or do not analysis. You need it way before the green light of a project kickoff.
In the next part of the article, we’ll talk about how an effective project feasibility study makes your projects healthier and impacts their delivery.
What Are the Benefits of Feasibility Studies?
The biggest benefits of a feasibility study are that it increases the likelihood of successful project delivery, helps you avoid costly mistakes, and improves overall project efficiency.
As we said, this analysis is one of the most valuable steps you can take before launching a project.
It’s not just about determining whether an idea is possible—it’s about making sure your project plan has a strong foundation, realistic expectations, and the best chance of successful delivery.
For starters, the report helps you identify potential obstacles early before they turn into costly problems. It allows you to properly assess risks and create mitigation plans, ensuring that your team is prepared for challenges rather than reacting to them under pressure.
This means fewer surprises, better decision-making, and a smoother execution process.
A well-written feasibility analysis also saves time and money by preventing investment in projects that are unlikely to succeed.
Instead of committing resources blindly, you gain clarity on whether the project is technically, financially, and operationally viable.
If major roadblocks appear, you can adjust the scope, explore alternative solutions, or decide to pivot before costs spiral out of control.
Impact on Project Management
From a project management perspective, this analysis aligns key stakeholders by setting clear expectations and defining the project’s goals, budget, and timeline upfront.
When leadership, investors, and team members all have a shared understanding of what’s feasible, projects move forward with greater confidence and fewer disputes.
All of the mentioned benefits translate to reduced project failure rates because project managers get data-driven insights. Instead of relying on assumptions, you’re making informed decisions based on market research, technical assessments, and financial analysis.
This makes it easier to secure buy-in from key stakeholders and ensures that projects are built on a solid, well-researched plan. Skipping this step means taking unnecessary risks, which often leads to wasted resources, unrealistic timelines, or project failures.
When to Use a Feasibility Analysis?
A feasibility analysis is used during the project planning phase. To be more specific, you should use it in the project initiation phase – when you’re evaluating a project’s viability (before investing significant resources), when identifying potential obstacles (or risks), to determine the best execution approach, and to assess whether a project aligns with business plans and objectives.
Let’s expand on that and give you more context.
1. Before Investing Significant Resources
The study is here so that you don’t waste valuable resources like budget, staff, or time on something that isn’t practical, scalable, or aligned with business objectives. The report helps you to analyze costs, market demand, technical challenges, and operational feasibility before committing.
2. When Identifying Potential Obstacles and Risks
The difference between a successful and a failed project comes down to how well risks were anticipated and managed. This analysis helps you identify potential roadblocks early so you can develop strategies to mitigate them. This could include anything from regulatory issues to technical limitations or unforeseen costs.
Adding them to the risk register early on can save your team from unexpected delays and budget overruns.
3. To Determine the Best Approach
The analysis evaluates different strategies and approaches to determine the most efficient and cost-effective path forward. Whether it’s choosing the right technology stack, project methodology, or team structure, this process helps ensure you make strategic decisions that support long-term success.
4. When Ensuring Project Alignment with Business Goals
The study ensures that the project aligns with your company’s strategic objectives, available resources, and operational capacity.
If a project is going to stretch your team too thin or doesn’t contribute to long-term business objectives, this early assessment will highlight those misalignments before you get too far in.
Get accurate project data and forecasts with Productive
What Are the Types of Feasibility Studies?
The basic types of feasibility studies are technical, financial, market, operational, and legal feasibility. All of these inspect the project from different aspects and drill down on specific metrics.
Below, we’ll cover each one’s fundamentals.
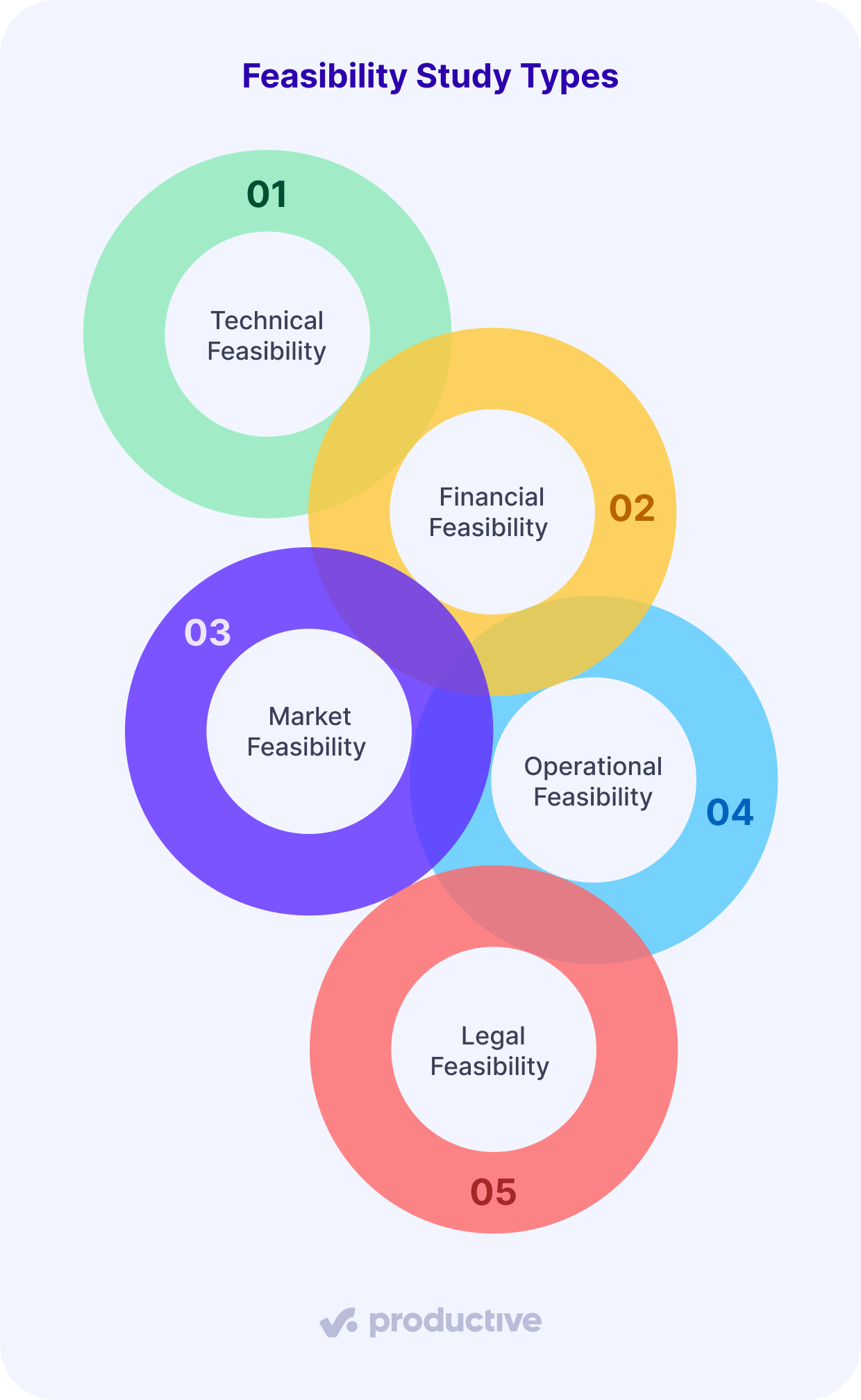
1. Technical Feasibility
Technical feasibility evaluates whether the proposed project can be successfully implemented using existing technologies, assets, and expertise.
The goal here is to help decision-makers understand the technical viability and potential risks associated with the project.
Understanding technical limitations upfront allows for better planning, realistic timelines, and smarter resource allocation.
It involves:
- Evaluating the technical requirements.
- Identifying potential technological challenges.
- Evaluating the availability of necessary assets.
- Determining the likelihood of achieving the desired outcomes.
2. Financial Feasibility
The financial feasibility study determines whether the project is economically viable. Even if an idea is technically possible, it has to make financial sense – otherwise, it’s a risky investment.
Here, you should do the cost-benefit analysis of the project’s potential revenue, expenses, potential cost overrun and profitability to determine if it’s financially sound.
This involves creating detailed financial projections and ROI calculations, which help you make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the project.
To be more specific, here you should:
- Analyze potential costs, revenue, and profitability.
- Conduct break-even and cost-benefit analyses to see when the project will start generating a return.
- Estimate the cash flow projections and long-term financial sustainability forecasts.
- Assess funding sources and whether an additional investment is required.
3. Market Feasibility
Market feasibility evaluates the potential demand for your proposed product or service within the target market. This preliminary study focuses on assessing the economic conditions for the project and its long-term growth potential.
Here’s what you should focus on here:
- Analyze market size and economic growth potential.
- Identify target customers and their needs.
- Assess competition and market trends.
- Determine pricing and distribution strategies.
Conducting thorough market research will help you make informed decisions about your venture’s viability.
Productive’s centralized documentation makes it easier to define scope and requirements.
4. Operational Feasibility
The operational feasibility analysis looks at the internal processes, resources, and logistics required to execute the project effectively. It focuses on whether your team and infrastructure can handle the project’s operational demands.
This involves:
- Evaluating production capacity and resource availability and utilization.
- Assessing logistics and supply chain requirements.
- Identifying potential bottlenecks in operations.
- Ensuring internal workflows align with project needs.
You’ll also need to take into account factors such as production capacity, logistics, and the overall complexity of your operations.
5. Legal Feasibility
Conducting a legal feasibility study is essential to guarantee your venture complies with all relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. Overlooking legal requirements can result in costly penalties, delays, or even forced shutdowns.
This process involves:
- Identifying applicable legal requirements.
- Evaluating potential legal risks and liabilities.
- Developing strategies to mitigate legal challenges.
- Ensuring your project aligns with the current legal framework.
Thorough legal due diligence can prevent costly mistakes and safeguard your project’s long-term viability.
How To Conduct a Feasibility Study?
To conduct a feasibility study, you’ll need to first perform a preliminary analysis to assess the project’s viability and identify potential roadblocks. Next, define the project scope and then conduct thorough market research.
After that, perform a financial analysis and finally, conduct a technical evaluation to determine the feasibility of the proposed solutions and technologies.
The idea here is to ask the right questions before the project kickoff. To make things easier, we’ve divided the process into simple steps.

STEP 1: Conduct a Preliminary Analysis
The preliminary analysis lays the groundwork for the project. This step allows you to quickly identify red flags that might indicate the project isn’t viable.
This initial assessment involves:
- Define the project’s objectives and expected outcomes.
- Identify potential obstacles that could derail delivery.
- Estimate project requirements in terms of time, budget, and expertise.
- Assess whether the project aligns with business objectives and overall feasibility.
STEP 2: Define Project Scope
Clearly defining the project scope helps set expectations and prevents scope creep later on. Here, you must determine the specific objectives, deliverables, and constraints of the proposed venture.
The goal of this step is also to keep all stakeholders on the same page regarding what the project will and won’t cover. Having clear expectations and boundaries prevents scope creep.
STEP 3: Perform a Market Research
Market research ensures that your project is backed by data, not assumptions. Skipping market research can lead to investing in a product or service with little demand, which spells disaster early on.
During market research, you should be:
- Identifying your target market and analyzing their needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Evaluating the competitive landscape to determine market saturation and potential opportunities.
- Examining industry trends, growth projections, and regulatory factors.
- Collecting qualitative and quantitative data through surveys, focus groups, and secondary research sources.
STEP 4: Financial Analysis
The financial analysis determines the economic viability of your proposed project. While analyzing, you’ll need to estimate startup costs and project cash flow, as well as calculate key financial metrics like break-even point and ROI.
This analysis will give you a clear picture of the potential profitability and risks associated with pursuing your business idea. Without getting into finances, you risk launching a project that doesn’t generate enough revenue to sustain itself.
STEP 5: Technical Evaluation
This step evaluates whether you have the necessary technical resources to execute the project. Without this evaluation, you risk setting unrealistic project timelines and unexpected technical roadblocks.
In this step, you should:
- Assess technology requirements and their availability.
- Identify potential technical challenges that could slow development.
- Determine if your team has the necessary expertise or if additional hiring/training is required.
- Develop contingency plans for technical risks.
STEP 6: Operational Assessment
After evaluating the technical feasibility, you’ll need to conduct an operational assessment to determine if your proposed project can be successfully implemented and sustained.
This involves analyzing your organization’s capacity to execute the project, including workforce planning, management capabilities, and operational processes.
You’ll also need to assess potential risks and develop contingency plans to mitigate them, ensuring smooth operations and long-term viability.
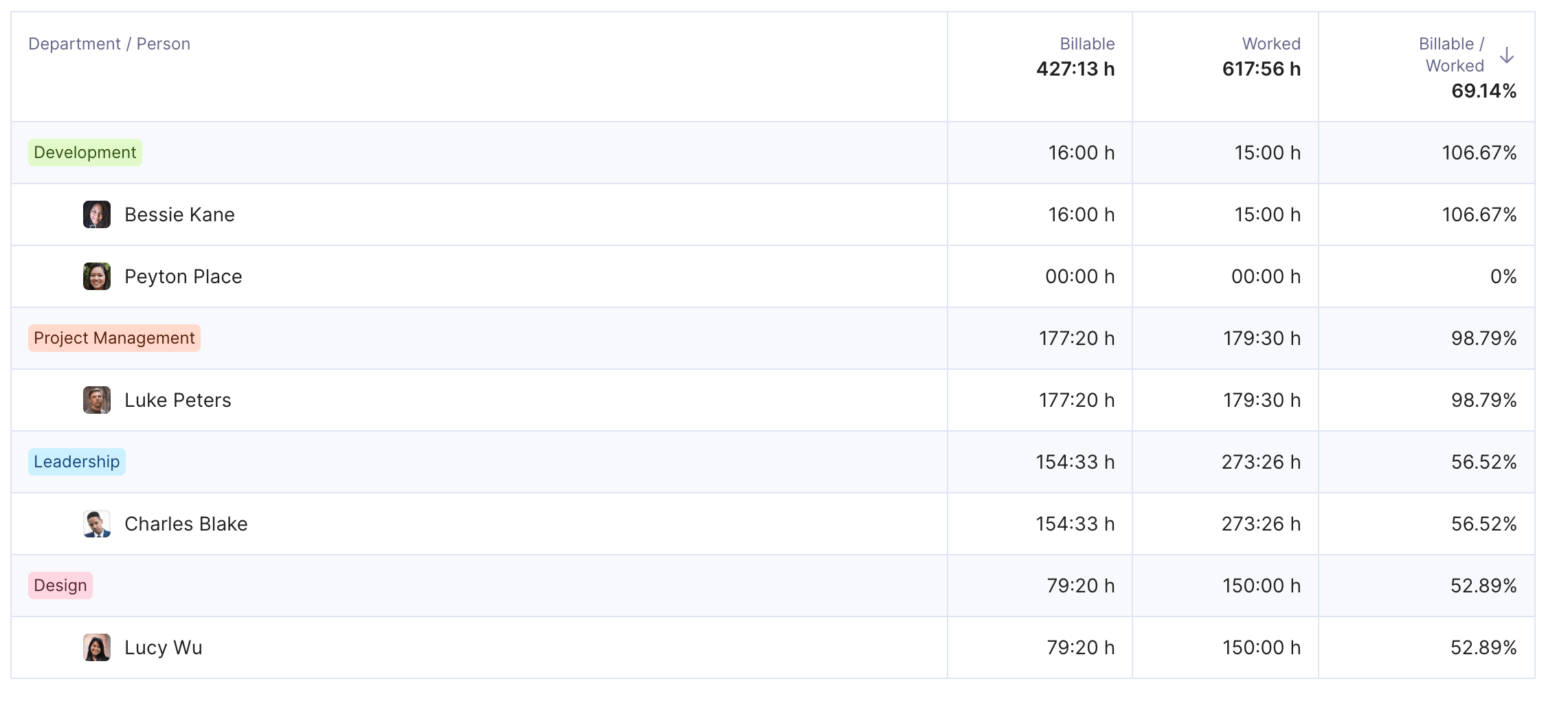
Productive gives you better insight into cost-efficiency across teams for more accurate feasibility studies.
STEP 7: Risk Assessment
A risk assessment identifies potential risks, assesses their likelihood and impact, and develops mitigation strategies.
Here, you’ll need to:
- Identify risks in various categories, such as financial, technical, and legal.
- Evaluate the probability and potential impact of each risk.
- Prioritize risks based on their severity and likelihood.
- Develop contingency plans to mitigate high-priority risks.
STEP 8: Final Decision Making
Here, you need to summarize all the previous findings and decide if the project is a go or no-go. Evaluate the project’s viability by considering the financial, technical, operational, and market aspects.
Weigh the potential risks and benefits and determine if the project aligns with your organization’s strategic objectives. Make a confident go/no-go decision that positions your venture for success.
What Are the Components of a Feasibility Study?
The components of a feasibility study are market research, financial projections, technical requirements, operational plan and risk mitigation strategies.
Market research methodology assesses demand and competition, financial projections determines profitability, technical requirements evaluate the necessary assets, an operational plan to outlines the business processes, and risk mitigation strategies address potential challenges.
Let’s expand on those.
Market Research Methodology
A return on investment starts with understanding the market you’re selling on. The goal here is to assess the market potential of your project. Special effort should be invested in this assessment to determine the targeted market share.
Here’s a market analysis checklist to follow:
- Define your target market and identify potential customers.
- Conduct market surveys and interviews to gather valuable insights.
- Analyze competitor offerings and differentiate your product or service to stand out.
- Assess market demand and potential profitability.
Financial Projections
Financial projections are an essential component of any feasibility study, as they provide a quantitative assessment of the potential profitability and financial viability of your business idea.
You’ll need to develop detailed forecasts of revenue, expenses, cash flow, and break-even points, typically for a three to five-year period.
This will help you determine if your venture is financially sound and sustainable.
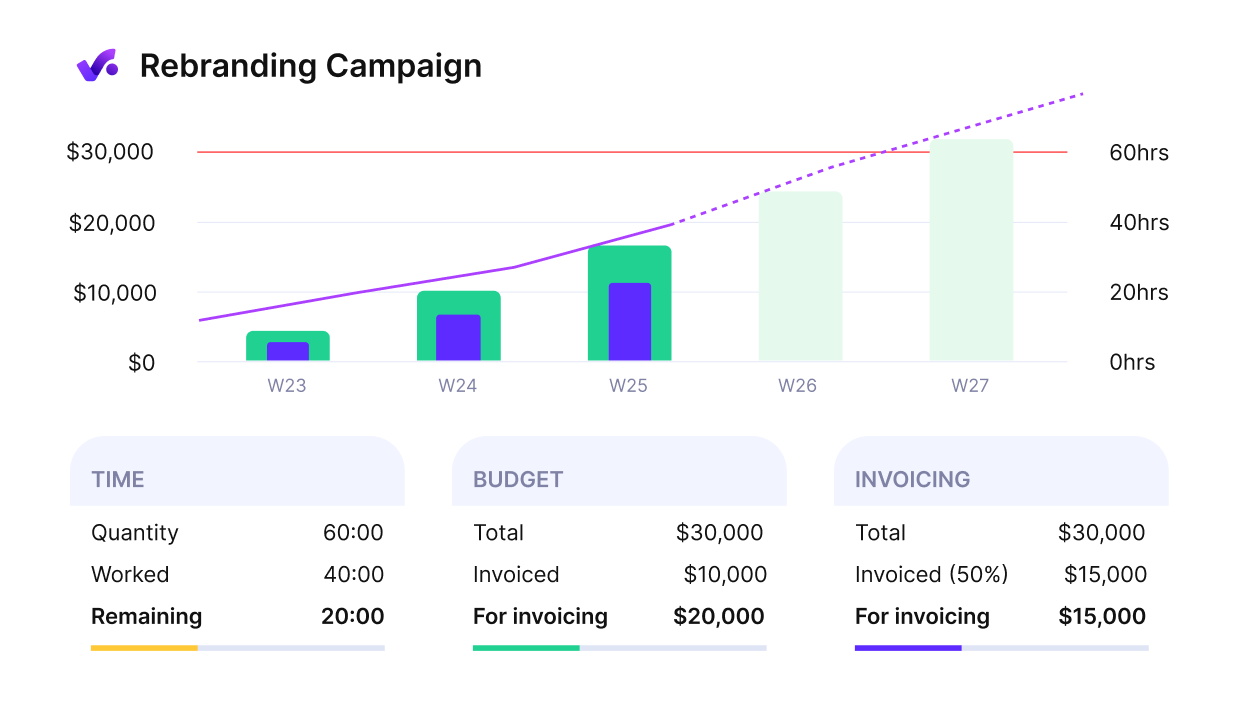
Time and budget visibility is essential in a feasibility study to assess project viability from the start.
Technical Requirements
In addition to the financial projections, you must also evaluate the technical requirements necessary to bring your business idea to life.
This involves analyzing:
- Equipment, machinery, and raw materials (if needed)
- Software and technology
- Production processes
- Staffing and expertise
Operational Plan
An operational plan is an essential component of your feasibility study that outlines the day-to-day processes and procedures required to run your business effectively.
It should detail your organizational structure, staffing requirements, and the systems and processes needed to manage your operations. This plan will be your roadmap, guiding you in executing your business strategy and achieving your objectives.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Despite meticulous planning and preparation, every business venture inevitably faces potential risks that could hinder its execution.
To mitigate these risks, you should:
- Identify and assess potential risks.
- Develop contingency plans.
- Implement risk management strategies.
- Regularly monitor and review risk mitigation efforts.
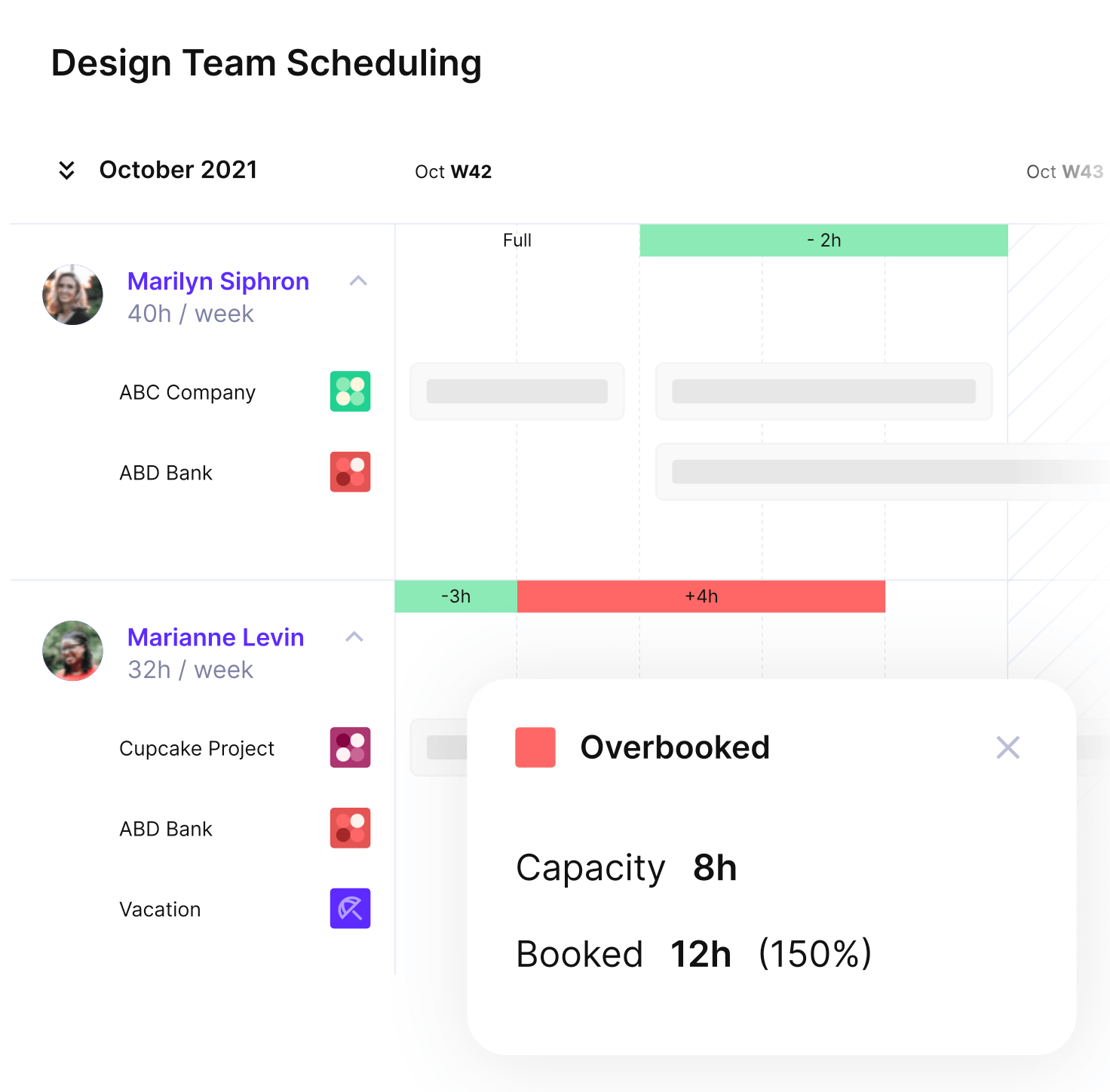
Real-time team capacity tracking helps identify resource constraints early in a feasibility study.
What Is a Feasibility Study Example in Project Management?
An example of a feasibility study in project management would be a software company planning to launch a new AI-powered project management tool.
Before development begins, the team should conduct a technical feasibility study to evaluate whether the necessary AI models can be built with existing assets, whether the infrastructure can support the increased processing demands, and whether integration with third-party tools (like Slack, Jira, or Productive) is possible.
If the study reveals high implementation costs or a lack of skilled engineers, the company may decide to develop a simpler product or delay the project.
Similarly, a construction firm looking to build a high-rise office complex in a major city must perform an extensive feasibility study before breaking ground.
This includes conducting:
- Financial feasibility to determine if the project will generate enough return on investment based on rental demand and projected costs.
- Legal feasibility to ensure compliance with zoning laws, safety regulations, and building codes.
- Environmental feasibility to assess the impact on local wildlife, traffic congestion, and energy consumption.
Without these assessments, the company would risk lawsuits, regulatory fines, or financial losses from unforeseen issues.
What Are Feasibility Study Best Practices?
Conducting a feasibility study is more than just doing the research; it’s about utilizing proven practices to maximize the study’s effectiveness.
Here are some best practices that will enhance the study’s accuracy and credibility:
- Clearly define the project’s scope and objectives.
- Assemble a diverse, experienced team.
- Gather extensive data from reliable sources.
- Analyze findings objectively and present a detailed report.
Tools and Resources
Leveraging the right tools will make your research process a whole lotta smoother. Here, you should definitely use project management software to organize tasks, assign responsibilities, and track progress.
- Analyze similar past project insights to help make accurate assessments of key tasks and milestones.
- Employ financial modeling tools to analyze actual costs, revenues, and risks.
- Collaborate with subject matter experts who can provide valuable insights.
- Access industry reports, market research, and case studies to inform your analysis and support decision-making.
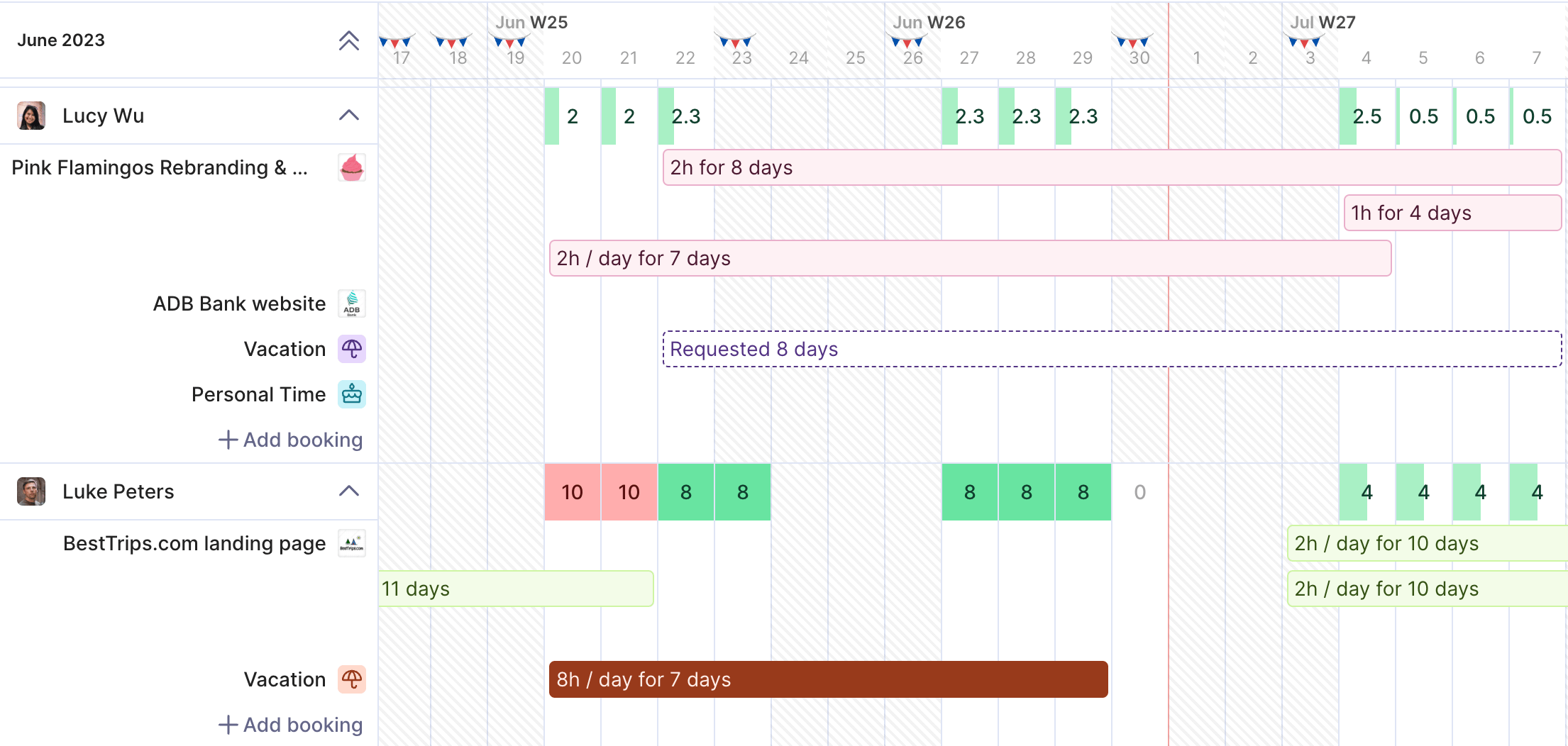
Productive allows you to view resource availability across timelines.
Project Management Integration
Integrating your feasibility study into the broader project management framework is essential for ensuring a smooth shift from planning to execution. Effective integration facilitates informed decision-making and increases the likelihood of project success.
You should:
- Align the feasibility study with project objectives.
- Communicate findings to stakeholders.
- Incorporate recommendations into the project plan.
- Monitor and adjust as needed throughout the project lifecycle.
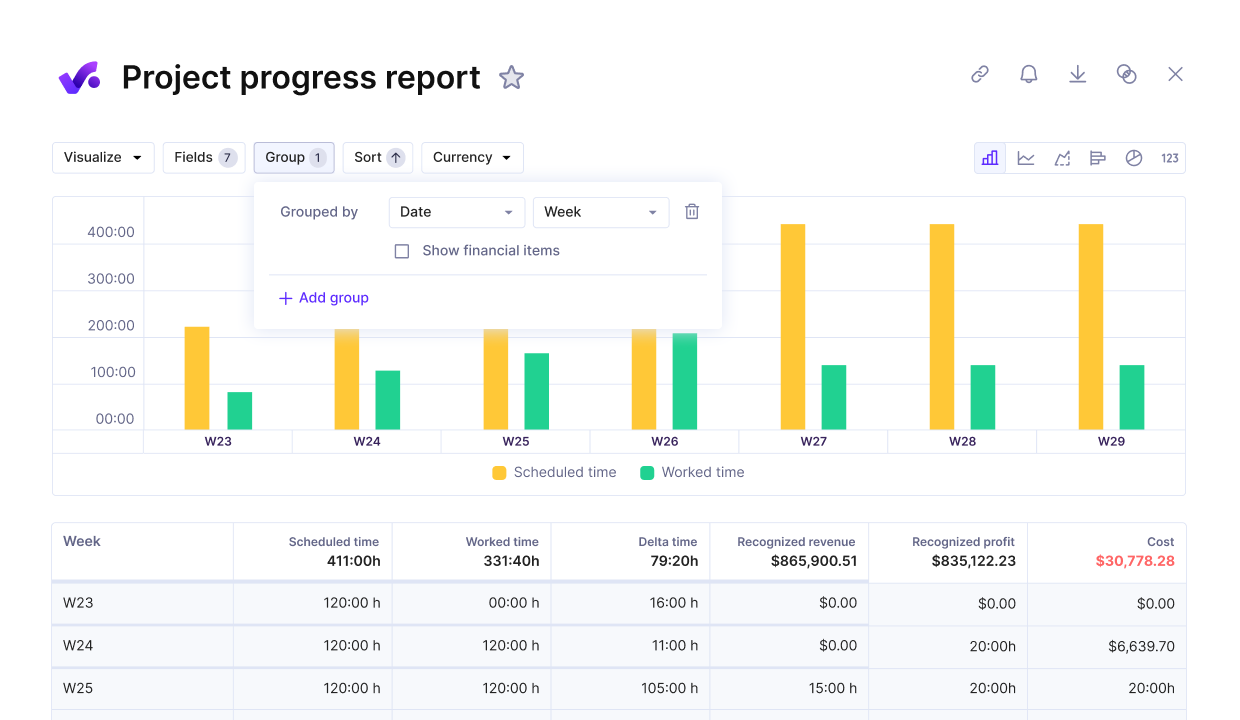
Accurate progress reports support feasibility studies by comparing planned versus actual performance.
Final Thoughts
A feasibility study is an analysis in project management that helps you determine whether a proposed project is viable and worth pursuing.
When you thoroughly analyze the technical, economic, legal, operational, and scheduling factors, you can make an informed decision about whether to move forward with the project.
Investing time and resources in the study upfront can save you significant costs and headaches down the road.
The study also helps identify the biggest roadblocks and challenges as well as the best course of action for executing the project. When conducting the study, it’s always good to use project management tools to analyze similar past projects while keeping all data in one place.
Start today and book a demo or claim a free two-week trial.
Make Smarter Project Plans With Productive
Make smarter go/no-go decisions and set projects up for success with an all-in-one project management platform.
