How To Make and Use Gantt Charts in Project Management?
A Gantt chart is a visual project roadmap for a successful delivery. The chart’s structure helps you identify critical paths, manage team workload, and communicate project status to stakeholders.
This article will teach you all you need to know about Gantt charts, their components, best practices, and how to apply them to track projects.
Key Takeaways
- Gantt charts are a must-know project management tool that displays activities as horizontal task bars along a timeline, showing duration and dependencies.
- Project managers use these bar charts to track progress, allocate resources, and manage deadlines through an easy-to-understand graphical interface.
- In a Gantt chart, tasks are listed vertically with start/end dates, while horizontal chart bars represent each activity’s duration and completion status.
- Four main dependency types (Finish-to-Start, Start-to-Start, Finish-to-Finish, and Start-to-Finish) help establish logical task relationships and critical paths.
What Is a Gantt Chart?
A Gantt chart is a project management tool for mapping out project schedules and displaying tasks along a timeline where parallel bars represent the duration of each activity.
Gantt charts were originally drawn by hand on paper. However, modern Gantt timeline versions have evolved into dynamic digital visuals that users can easily modify using specialized project management software like Productive.
They are a key tool for making and managing project plans.
The timeline chart shows connections between tasks and their relationships with other activities through connecting lines moving from left to right (start to finish dates), allowing project managers to visualize workflow sequences.
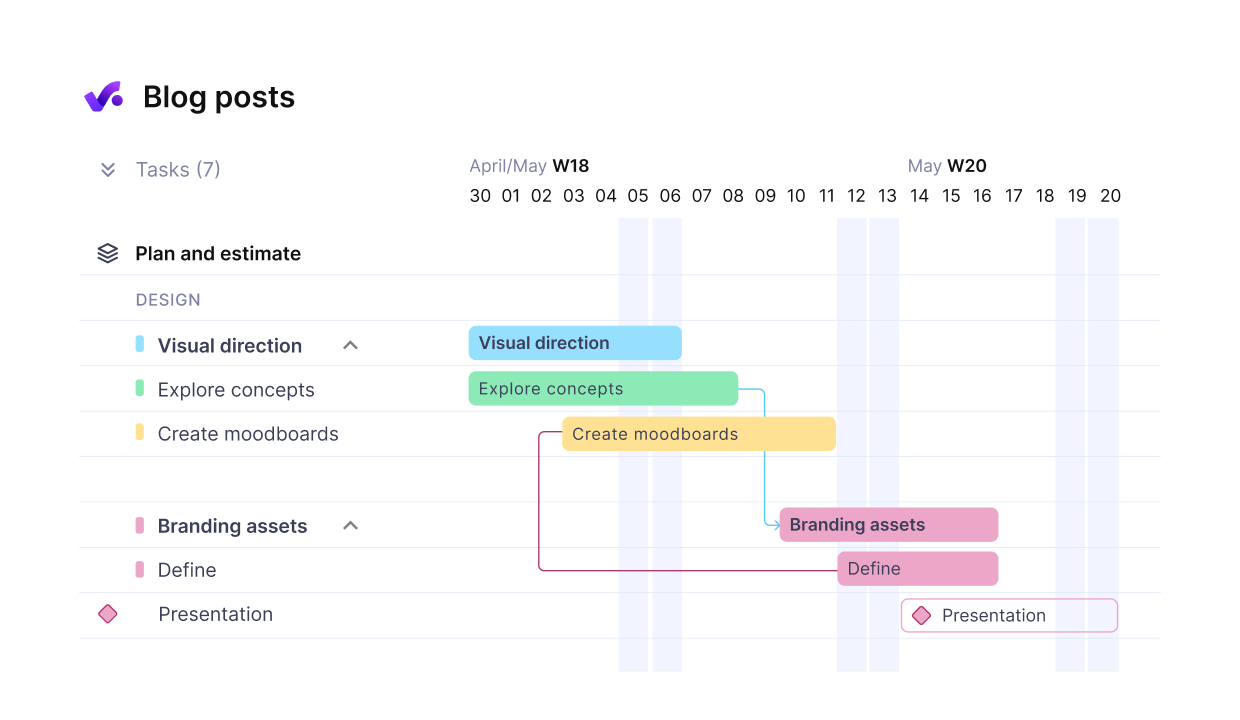
Use Productive’s Gantt charts to visualize timelines and task dependencies.
Definition and Core Concept
These horizontal bar charts display your project’s timeline by organizing tasks vertically while showing their durations horizontally through time-scaled bars. Henry Gantt originally developed them between 1910-1915.
- Individual tasks appear as horizontal bars, with their length indicating duration.
- Dependencies between activities are shown through connecting lines.
- The horizontal axis represents time intervals in your chosen scale.
- The vertical axis is a list of tasks and subtasks.
Gantt charts are particularly useful for tracking project progress, managing dependent tasks, and coordinating team resources.
They provide a visual representation of your project’s structure, making it easier to identify potential roadblocks and adjust schedules accordingly.
Gantt charts are like your bird’s-eye-view of the whole process and its major phases.
How Gantt Charts Work?
Gantt charts work by using bars to represent tasks along a timeline, showing when each task starts and ends, how long it lasts, and how tasks are connected. They work wonders for presenting complex project information in an accessible format.
Here are the basics on how to use this magical project planning chart:
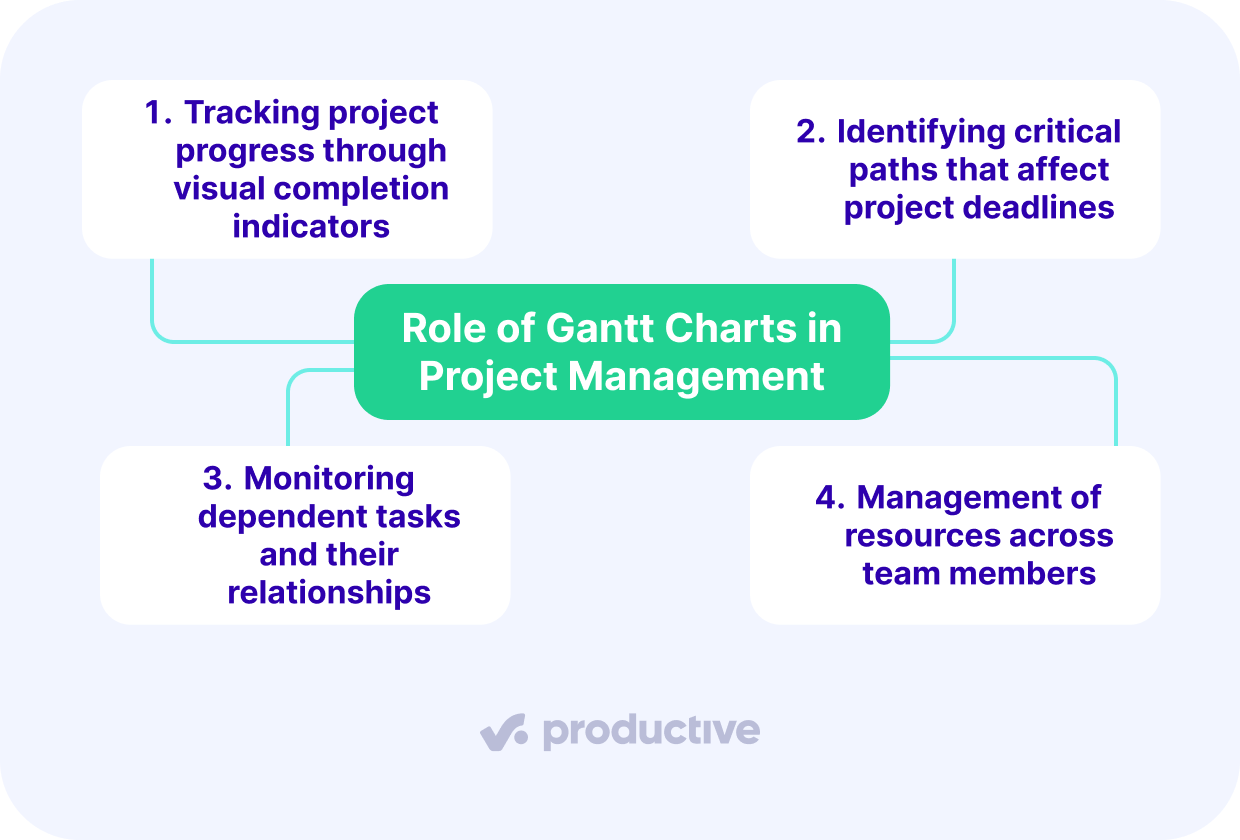
- Track actual progress through visual completion indicators.
- Identify critical paths that affect project deadlines.
- Manage resources across team members.
- Monitor dependent tasks and their relationships.
What Are the Key Components of a Project Gantt Chart?
The key components of a Gantt chart are tasks, task bars, milestones, and resource allocation within a timeline framework.
Tasks serve as your project’s foundation, listed vertically on the left side with specific start and end dates. You’ll represent these tasks using horizontal timeline bars that visually display their duration and dependencies.
Milestones mark significant achievements or deadlines, while resource allocation helps you track project team members and materials assigned to each task.
The timeline at the chart’s top provides temporal context for your entire project.
Why Use Gantt Charts in Project Management?
You should use Gantt charts in project management because they provide a centralized visual overview of all activities. Since the modern way of managing projects demands modern visualization tools, these charts have become a must-have in the PM toolkit.
These versatile tools enhance your project’s success through:
- Extensive visibility of tasks, their connections, and execution timeframes.
- Improved team communication and stakeholder engagement.
- Efficient resource assignment and time management.
- Enhanced productivity through clear accountability.
They’re particularly valuable for managing remote teams and identifying potential gridlocks before they impact your timeline. With real-time progress tracking and flexible planning capabilities, you can quickly adapt to changes while maintaining project momentum.
When to Use a Gantt Chart?
When to use a Gantt chart mostly depends on your project’s complexity and management requirements. They come in particularly handy when you’re managing multiple tasks with different kinds of connections, coordinating various teams, or allocating resources across different project phases.
They’re especially useful in industries like construction, software development, and manufacturing, where precise production schedules are essential.
You should consider using a Gantt chart diagram when you’re creating a project plan, or when you need to track project progression, monitor key milestones, or do complex resource and work management.
They’re also invaluable for avoiding scheduling conflicts and ensuring your team members understand their responsibilities and deadlines within the project lifecycle.
How To Create a Gantt Chart?
To create an effective Gantt chart, you’ll need to start by breaking down your project into specific, manageable tasks and identifying all dependencies between them.
You should then estimate realistic durations for each task, considering both the complexity of the work and the availability of resources.
With your tasks, dependencies, and durations established, you can sequence and schedule your activities logically, ensuring that your project timeline includes all necessary connections between tasks while maintaining a realistic progression toward your goals.

STEP 1: Identify Project Tasks
Here, you’ll need to break down your project into clear, manageable components while considering their interdependencies and resource requirements.
- Create a thorough task list through brainstorming sessions with stakeholders.
- Break down complex tasks into smaller, actionable subtasks.
- Establish clear task priorities based on dependencies and critical path analysis.
- Determine resource requirements and constraints for each task.
When listing tasks, you’ll want to be specific and measurable, ensuring each component directly contributes to project objectives. Consider both sequential and parallel tasks, but maintain a logical flow that reflects your project’s timeline and deliverables.
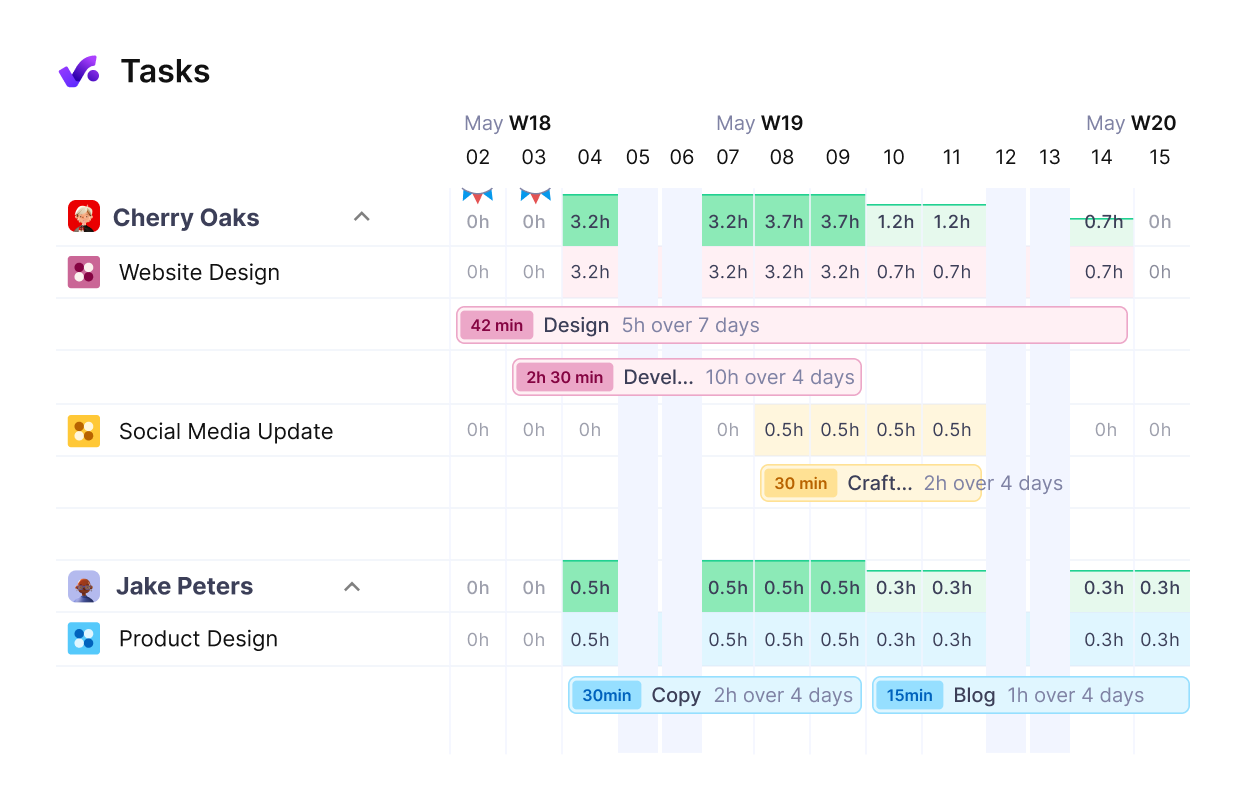
Use Productive to coordinate task progress and team output in real-time.
STEP 2: Determine Task Dependencies
Before committing to this step, you should analyze the relationship between tasks. The idea here is to have a comprehensive overview of how project activities interconnect and influence one another.
You’ll need to identify predecessor and successor tasks.
Establish the relationships between tasks through four main dependency types: Finish-to-Start, Start-to-Start, Finish-to-Finish, and Start-to-Finish. Using Gantt chart software is super helpful for visualizing these connections with linking lines or dependency arrows between tasks.
As you map out dependencies, remember that changes to any predecessor task will affect its successors, potentially impacting your entire project timeline.
STEP 3: Estimate Task Duration
After identifying task dependencies, focus on making accurate duration estimates of each activity. For this step, you should employ various estimation techniques while considering multiple factors that can impact task completion times.
The best practices for this step are:
- Break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable components using bottom-up estimation.
- Analyze historical data from similar projects to establish realistic timeframes.
- Include buffer time to accommodate potential delays and external factors.
- Consult industry experts to validate your estimates.
- When estimating durations, you’ll might want to read our guide on how to choose a project management tool like Productive or Jira.
Remember to maintain flexibility in your estimates while documenting your assumptions for future reference.
STEP 4: Sequence Tasks and Schedule Milestones
In the last step, you’ll need to identify all activities within your project’s scope and arrange them in a logical order based on their dependencies.
Once you’ve established the sequence of tasks, you’ll determine realistic timeframes for each task, considering resource availability and potential constraints.
Again, use chart tools to visualize these elements by placing relevant tasks along a timeline, clearly marking dependencies, and setting milestones. And that’s it. You get a high-level overview of the project timeline.
Remember to maintain flexibility in your task scheduling and regularly update the chart as your project progresses.
Create smarter Gantt charts in Productive
Practical Applications Across Different Roles
Every team member can actively engage with the chart by updating their task progress, identifying potential roadblocks, and coordinating their work that affects other team members.
Whether you’re overseeing a construction project or managing a software development team, you’ll use these charts to maintain transparency and accountability while cultivating collaborative problem-solving among team members.
Project Manager Perspective
From a project manager’s perspective, Gantt charts are very powerful tools that streamline the complex process of planning project resources or timeline management.
An up-to-date project Gantt chart is your essential go-to tool for tracking connected tasks and identifying critical paths while maintaining precise control over project schedules.
- You can effectively balance team workloads through real-time resource monitoring.
- You’ll easily identify tight spots and adjust resource assignments accordingly.
- You’re able to track actual versus planned project completion for better timeline management.
- You can proactively manage risks by visualizing dependent tasks and milestones.
These capabilities enable you to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource utilization, and guarantee project success through thorough timeline visualization and strategic planning.
Team Member Engagement
These visual tools help teams collaborate better because they provide a shared platform where you can track dependent tasks, monitor progress, and maintain clear communication channels with your colleagues.
Real-time updates and centralized task management help coordinate team members across different departments (e.g., product marketing, design, and copywriting teams) while maintaining accountability for assigned responsibilities or each task owner.
The charts’ adaptable nature allows you to respond quickly to changes, ensuring you’re always aligned with project objectives and timelines.
What Are Real-life Gantt Chart Examples?
Gantt charts are used in almost any industry that requires serious project management. The most common examples are in software development projects, marketing campaign planning, event planning, construction, and project development lifecycles.
Let’s add more context to each example so you get a better idea of their role and when to use them.
1. Marketing Campaign Planning
A marketing team launching a new product often deals with multiple moving parts—content creation, social media scheduling, email campaigns, video production, and event planning.
A Gantt chart helps the team visualize deadlines, coordinate tasks across departments, and ensure everything is launched on time. For example, it can show that social media assets must be approved before the campaign goes live and that the press release must be completed two days before launch.
When to use it: When you need to align cross-functional tasks and ensure campaign timing is flawless.
2. Software Development Projects
Software teams use Gantt charts to map out sprints, development cycles, testing phases, and deployment timelines. By visualizing dependent tasks (like completing backend development before frontend integration) the team can manage workloads better and avoid bottlenecks.
When to use it: When your project includes phased work, multiple teams, and critical dependent tasks.
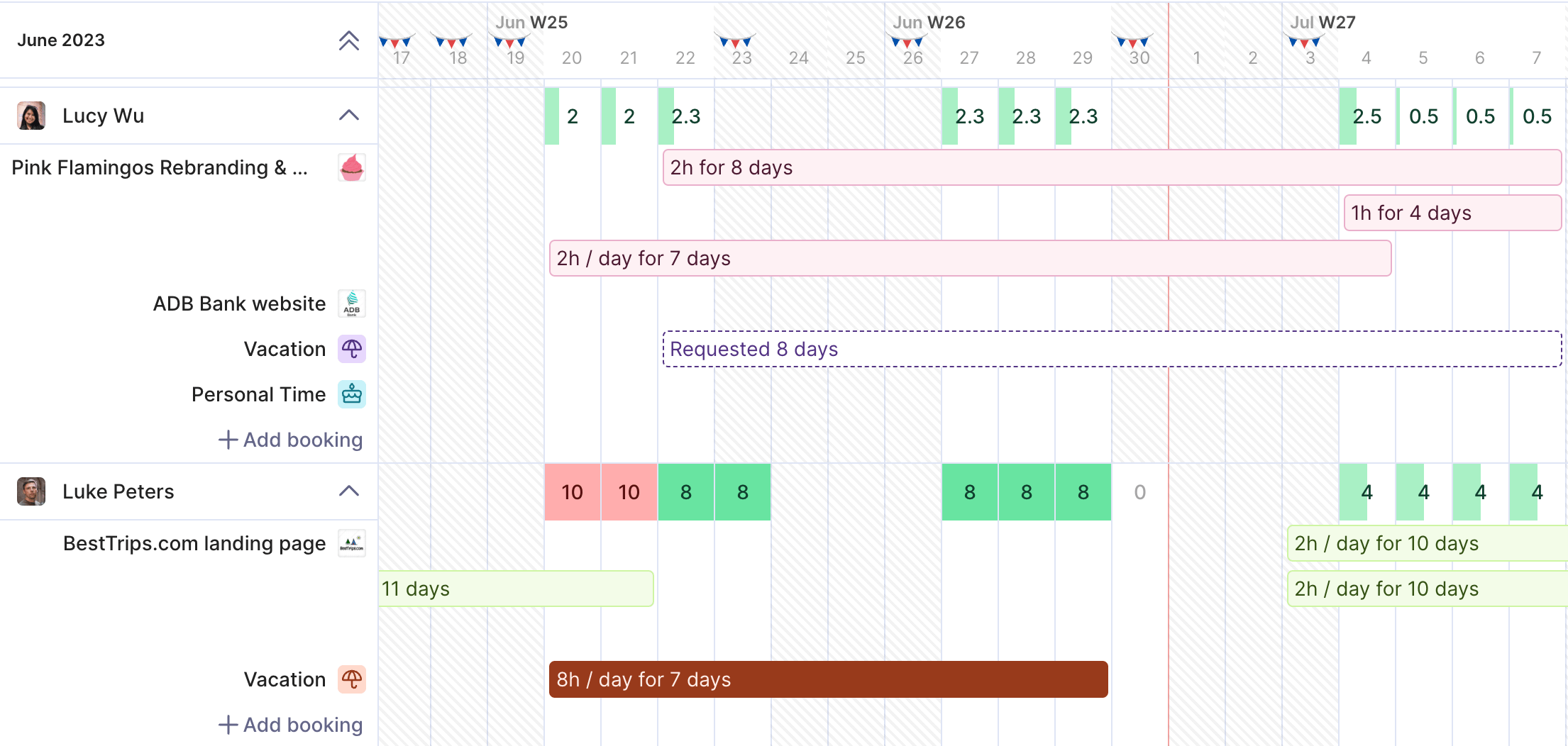
Manage workload allocation and project timelines while easily balancing availability, leave, and task scheduling.
3. Event Planning
Whether you’re organizing a conference, webinar, or corporate retreat, Gantt charts help plan everything from venue booking and catering to speaker confirmations and promotion timelines.
You can see which tasks need to start early—like sending invitations—and which ones are dependent on others, like finalizing the agenda after all speakers confirm.
When to use it: When every step is deadline-sensitive, and tasks are tightly connected.
4. Different Types of Construction Projects
In construction, timelines and task sequencing are everything. A Gantt chart maps out the stages: site preparation, foundation work, structural build, interior work, inspections, and handover.
It also shows which tasks can run in parallel and which depend on the completion of others, helping avoid costly delays.
When to use it: When your project involves strict sequencing and high coordination between contractors.
5. Product Development Lifecycle
From research and design to prototyping, testing, and launch, a Gantt chart helps product managers track each stage of the development process.
It ensures the design phase finishes before manufacturing starts and keeps all stakeholders aligned on deadlines and dependencies.
When to use it: When managing product roadmaps with overlapping activities and fixed launch goals.
How To Present Project Progress With Gantt Charts to Stakeholders?
When you present the Gantt charts to stakeholders, you should simplify complex information and highlight key elements that matter most to them (major events that influence the project goals).
Here are a few handy presentation tips:
- Choose a high-level project view for executive stakeholders, focusing on major project milestone tracking.
- Use strategic color coding to emphasize critical paths and their dependencies.
- Include relevant context, such as current and key dates markers and progress indicators.
- Guide your audience through the chart’s components systematically.
If you can, add animations when presenting digitally. Try to make your presentation dynamic, concise, and to the point.
What Tool To Use for Creating a Gantt Chart?
Modern project managers can choose from different digital solutions to create Gantt charts. These tools are often packed with features for effective planning and execution.
You’ll find different options ranging from Productive’s all-in-one project management platform for professional services to Microsoft Project’s big enterprise solutions.
Here are the main features for making Gantt charts that you should look out for:
- Cloud-based accessibility guarantees you can manage projects from anywhere.
- Real-time collaboration features enhance team communication and productivity.
- Customizable interfaces adapt to your specific project requirements.
- Integration capabilities streamline workflow with existing tools.
Some platforms like Productive offer free trials, allowing you to evaluate their features before committing to a subscription.
What Are Advanced Gantt Chart Techniques?
Advanced Gantt chart techniques are resource leveling, dependency management, task grouping, customizable visualization options, automatic updates, and collaboration features.
Here’s how these advanced approaches make your charts better:
- Resource leveling optimizes workload distribution.
- Dependency management streamlines task sequences.
- Task grouping and customizable visualization options help you create clearer project structures that improve team understanding and bring everyone on the same page.
- Interactive elements and conditional filters let you manipulate data directly on the chart.
- Progress tracking tools help you monitor completion rates effectively.
- Automated updates and collaboration features make it easier to manage complex projects and multi-project scenarios.
What Are the Limitations and Challenges of Gantt Charts?
While Gantt charts will always remain in the mandatory PM toolkit, they come with notable limitations that you’ll need to think about before you start implementing.
- These charts can become overwhelmingly complex when managing large, complex projects with numerous intertwined project tasks.
- They’re also limited in their ability to convey essential information about task priorities, resource requirements, and skill levels needed for completion.
- The visual clarity reduces as your project scope expands, and you’ll likely need additional tools to manage resources effectively.
- Maintaining and updating Gantt charts can be very time-consuming without specialized chart maker software, especially when using very basic tools like Excel.
Final Takeaway
Gantt charts will always remain a must-use tool that works great for visualizing a project timeline and its dependencies.
While you’ll need to evaluate their limits and invest time (and money) in a proper setup, the benefits of improved communication and project visibility far outweigh these challenges.
You should consider project planning software rather than basic spreadsheets or standard project management chart templates. The right tool can really transform your project planning and execution.
You can make amazing Gantt charts; try it out by booking a demo or claiming a free two-week trial.
Plan, Track and Manage Projects in Productive
Switch to Productive’s Gantt chart features and get a high-level overview of tasks, milestones, and resources – all in one platform.
Gantt Chart FAQ
What is a Gantt chart used for?
A Gantt chart is used to plan, schedule, and track tasks throughout a project. The chart is a visual project timeline with start and end dates, task durations, dependencies, and overall progress.
How do I create a Gantt chart in Excel?
To create a Gantt chart in Excel, start by listing your tasks along with their start dates and durations. Then, insert a stacked bar chart and adjust the formatting to reflect the project timeline. You can also use Excel’s built-in Gantt chart templates to simplify the process. There’s a much easier alternative – book a demo with Productive.
What are the 4 components of a Gantt chart?
The four main components of a Gantt chart are tasks, which represent project activities; the timeline, which shows the project schedule; bars, which visualize the start and end of each task; and dependencies, which show how tasks relate to one another.
What are the 7 important elements of a Gantt chart?
The seven key elements of a Gantt chart include the task list, the time scale, task duration bars, milestones, task dependencies, progress indicators, and the resources assigned to each task.
