What Is Project Monitoring: Guide, Best Practices, Tools
Too much project monitoring creates overhead, while too little leaves blind spots that put delivery at risk.
Effective monitoring in project management means tracking only the metrics that guide real decisions, such as budget vs actuals, hours against estimates, and open risks.
This article will show the best practices, how to avoid common challenges, keep monitoring lean, and build real-time dashboards for an effort-free performance overview.
Key Takeaways
- Monitoring only works when overhead is controlled. Tracking a handful of actionable project metrics prevents wasted time and keeps reporting lean.
- Project management software with real-time dashboards replaces static reports and helps teams with cost control and risk management.
- Linking performance monitoring to ROI proves its value: fewer delays, controlled budgets, and healthier profit margins.
- Making a structured monitoring plan involves setting baselines, aligning KPIs with client goals, and automating reporting.
What Is Project Monitoring?
Project monitoring is the ongoing process of tracking a project’s progress to ensure work stays on schedule, within scope, and within budget. It is different from control, which involves taking corrective action, and from project evaluation, which reviews project results after completion.
A project manager is responsible for setting up and running monitoring so that information flows consistently. A quick weekly check on hours vs estimates, upcoming milestones, and open risks gives clarity to act before problems snowball.
Unlike one-off performance assessments, monitoring is continuous because it feeds day-to-day decisions and helps you steer projects in real time. Clear monitoring also connects directly to project objectives by showing whether the work being delivered aligns with the agreed goals.
What Does Project Monitoring Involve?
In practice, monitoring keeps leaders and teams aligned on the status of tasks, resources, and budgets.
Done well, it prevents missed deadlines, flags risks before they escalate, and keeps budgets from drifting out of control. Extra attention to resource constraints helps you see where capacity is stretched and where underused skills could be reallocated.
Core monitoring activities include:
- Tracking tasks and project deliverables against the project plan while checking how resources are distributed.
- Recording time and resources used compared to the defined project schedule and resource allocation estimates.
- Reviewing risks, issues, and dependencies as they appear.
- Producing clear reports that inform decisions and manage stakeholder expectations.
Why Is Project Monitoring Important?
Project monitoring is very important because it gives you a clear view of how resources are used, how stakeholders stay informed, and how risks are spotted early.
When you track project performance against your plan, you know exactly where budgets and timelines stand. This helps you adjust resources before they get stretched too thin. Monitoring also builds trust and transparency in stakeholder communication.
Instead of just reacting, you can share timely updates that show where things are on track and where decisions are needed.
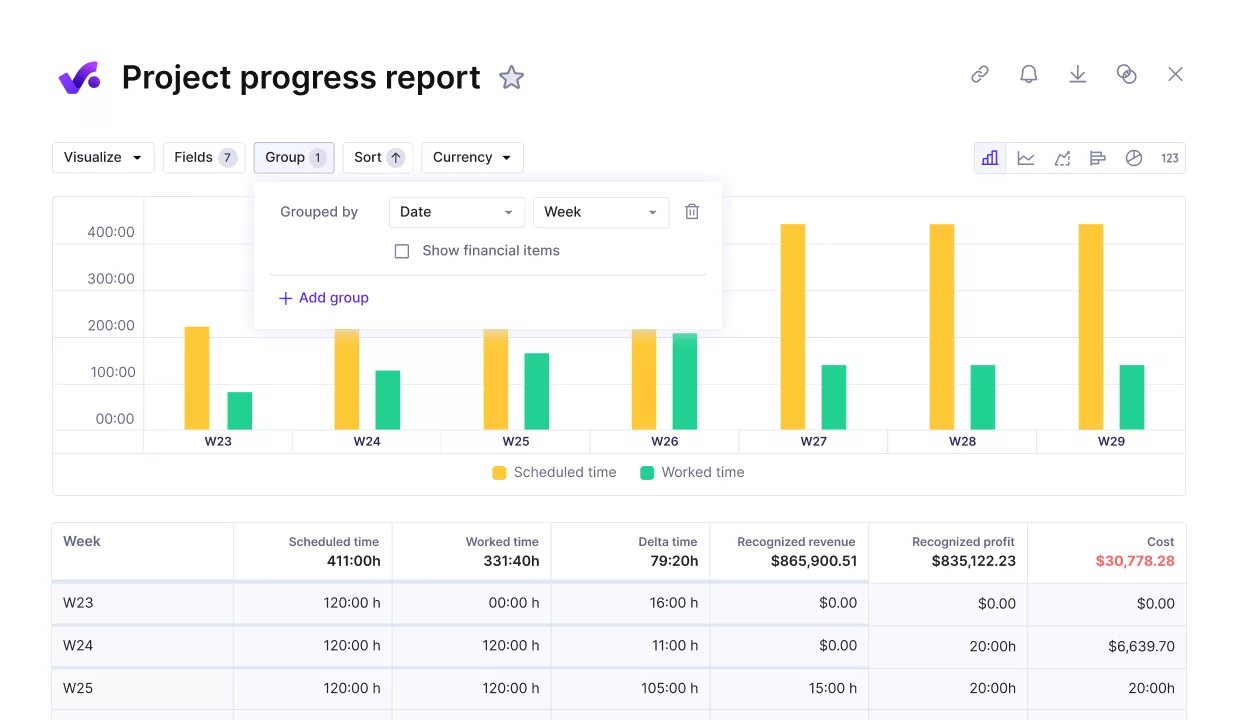
Use productive for real-time monitoring and controlling project progress.
What Challenges Come With Project Monitoring?
The challenges of project monitoring are reporting fatigue, data overload, lack of real-time insight, and team resistance.
These issues show up in practical ways: reports that no one reads, missed deadlines because risks were spotted too late, issues that remain unresolved, or budgets that creep because resource use wasn’t tracked accurately.
Let’s expand on the challenges below:
- When reports pile up without a clear purpose, they consume hours that could be spent on delivery. These unnecessary reports slow progress and distract from real work.
- Data overload makes it hard to spot the signals that matter, leading to hidden overspend.
- Without real-time insight, decisions are made on stale information, and course corrections come too late. Resistance is another hurdle.
- Teams avoid updating tools or reporting honestly if they see no value, leaving project managers with partial pictures.
How To Solve These Challenges?
1. Simplify reporting:
Replace long PDF updates with short, focused summaries that highlight key risks, issues, and progress. Share them in a consistent format so everyone knows where to look.
2. Automate data collection during project execution:
Use monitoring tools that sync time, tasks, and budgets automatically so updates don’t rely on manual entry. In Productive, this means time tracking flows straight into reports and dashboards, cutting manual work.
3. Focus on critical project metrics:
Agree on 3-5 indicators that matter most to the client and team, such as budget vs actual, hours burned, or open risks. Build these into your reports so they make smarter decisions.
4. Make updates visible:
Share dashboards that refresh in real time and keep them accessible to all stakeholders. This reduces ad‑hoc check‑ins and makes it clear where attention is needed without another meeting.
What Are Project Monitoring Techniques?
Project monitoring techniques are earned value management (EVM), dashboards, variance analysis, KPIs, and reporting cycles. Each technique gives teams a different way to measure status and act on results.
Earned Value Management (EVM)
You should use earned value management (EVM) when you need to measure cost and schedule performance together. It helps you see if you are ahead, on track, or behind by comparing planned vs actual value.
This technique is especially useful in long projects where cost overruns build slowly and deadlines stretch unnoticed.
How to implement:
At project kickoff, document the agreed scope, budget, and schedule in detail. Share these baselines with the whole team so everyone works from the same reference point. Check progress against them at fixed intervals (weekly for short projects, monthly for longer ones).
If you see slippage, decide whether to add resources, change deadlines, or adjust project scope. In Productive, budgets and schedules link directly to dashboards, so you can see variances as they happen instead of after the fact.
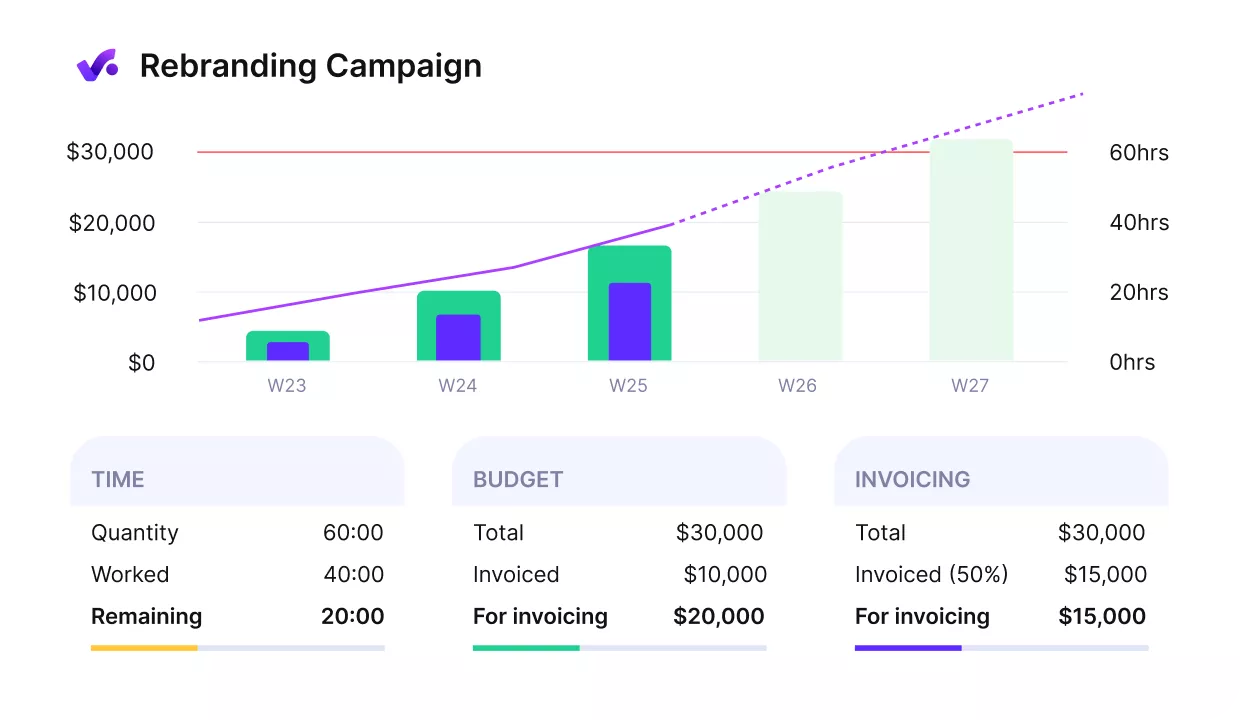
Use Productive to get an early warning of cost overrun.
Aligning KPIs with Clients
KPIs need to match the outcomes your client expects to see. If a client cares about hours burned versus estimates, or delivery speed on key project milestones, tracking other quality metrics won’t help them.
Aligning KPIs with client goals keeps your updates relevant and avoids confusion.
How to implement:
In your project kickoff, agree on 3–5 key performance indicators that matter most to the client. These can be hours vs estimates, deliverables completed, or budget burn. Keep the performance indicators visible in every report or dashboard update so progress is clear and easy to track.
Productive lets you set these performance metrics and automatically track them in dashboards and project execution reports.
Automated Reporting
If every project report requires manual collection, your team loses hours that could be spent managing the project. Automating reporting means updates pull directly from live data, so stakeholders always see the latest status without extra work.
Automated reports also reduce mistakes that happen when numbers are copied across spreadsheets.
How to implement:
Identify the recurring project reports you send (weekly status, budget updates) and automate them. In Productive, you can schedule reports to send directly to stakeholders and build dashboards that refresh automatically with time tracking and task data.
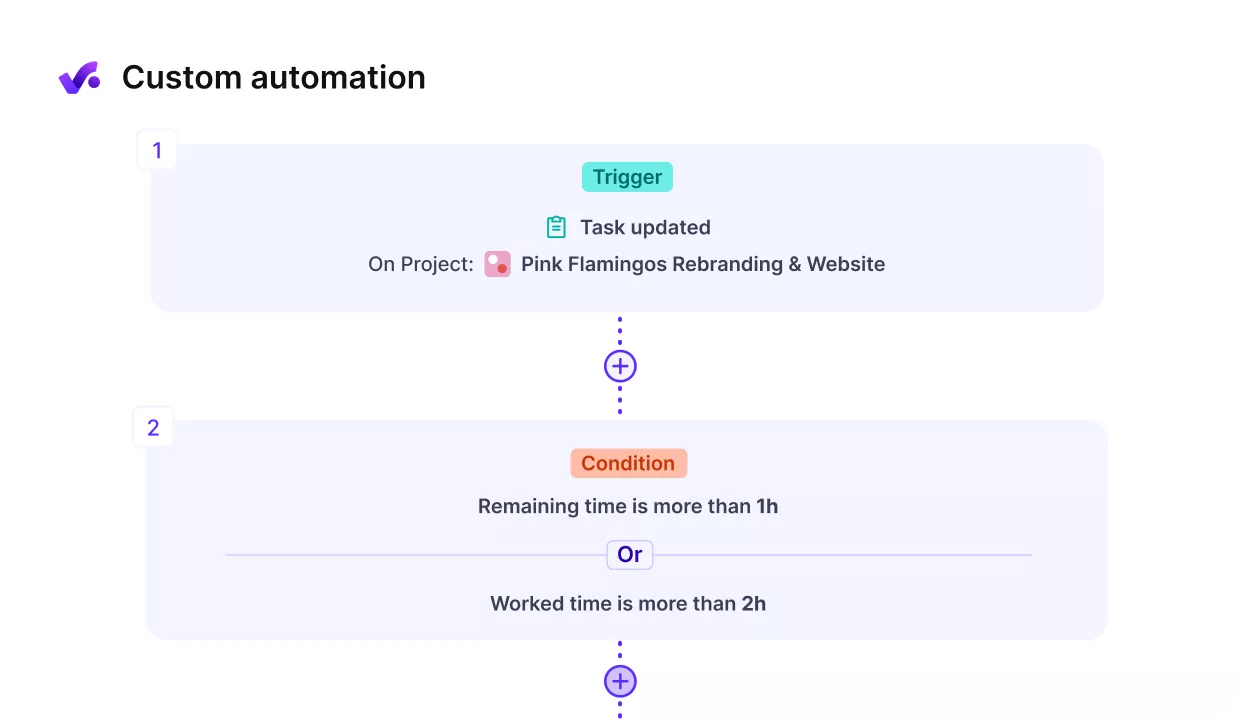
Use Productive to send pulse reports of project execution.
How To Optimize Monitoring Overhead?
You can optimize monitoring overhead through effective monitoring that focuses on specific metrics directly influencing project decisions, such as budget, resource load, or risk status.
Effective monitoring means stripping away reports no one reads and concentrating on project metrics that guide real action. If you monitor everything, teams waste hours; if you monitor too little, risks and project costs go unnoticed.
A strong monitoring plan prevents these extremes by limiting updates to what informs resource use, risk management, and budget control. Build the plan around clear metrics so the team knows exactly what to track and how those numbers support decision‑making.
Signs You’re Over-Monitoring
- Status reports that no one opens or reads. If reports sit unread in inboxes, they add overhead without giving anyone clarity.
- The same metrics are tracked in multiple places with no added value. Duplicated spreadsheets and tools confuse teams and waste effort.
- Team members spend more than 15% of their time collecting or preparing data. When monitoring takes up this much capacity, delivery slows down.
- Meetings are dominated by reviewing numbers instead of making decisions. If time is spent reading reports instead of acting on them, monitoring has gone too far.
How To Set Up a Lean Monitoring Plan? (Step-by-Step Process)
You can easily set up a lean monitoring plan using project management software in three steps: pick your most important KPIs, automate project data collections, and share the dashboard with your stakeholders.

Step 1: Pick critical KPIs
Choose 3-5 metrics tied to real decisions, such as budget burn, resource load, or open risks. Build these into your monitoring plan so the team has a clear reference for what to track and why.
For example, tracking budget burn shows when to re‑forecast costs, while monitoring resource utilization rates highlights if one team is overloaded.
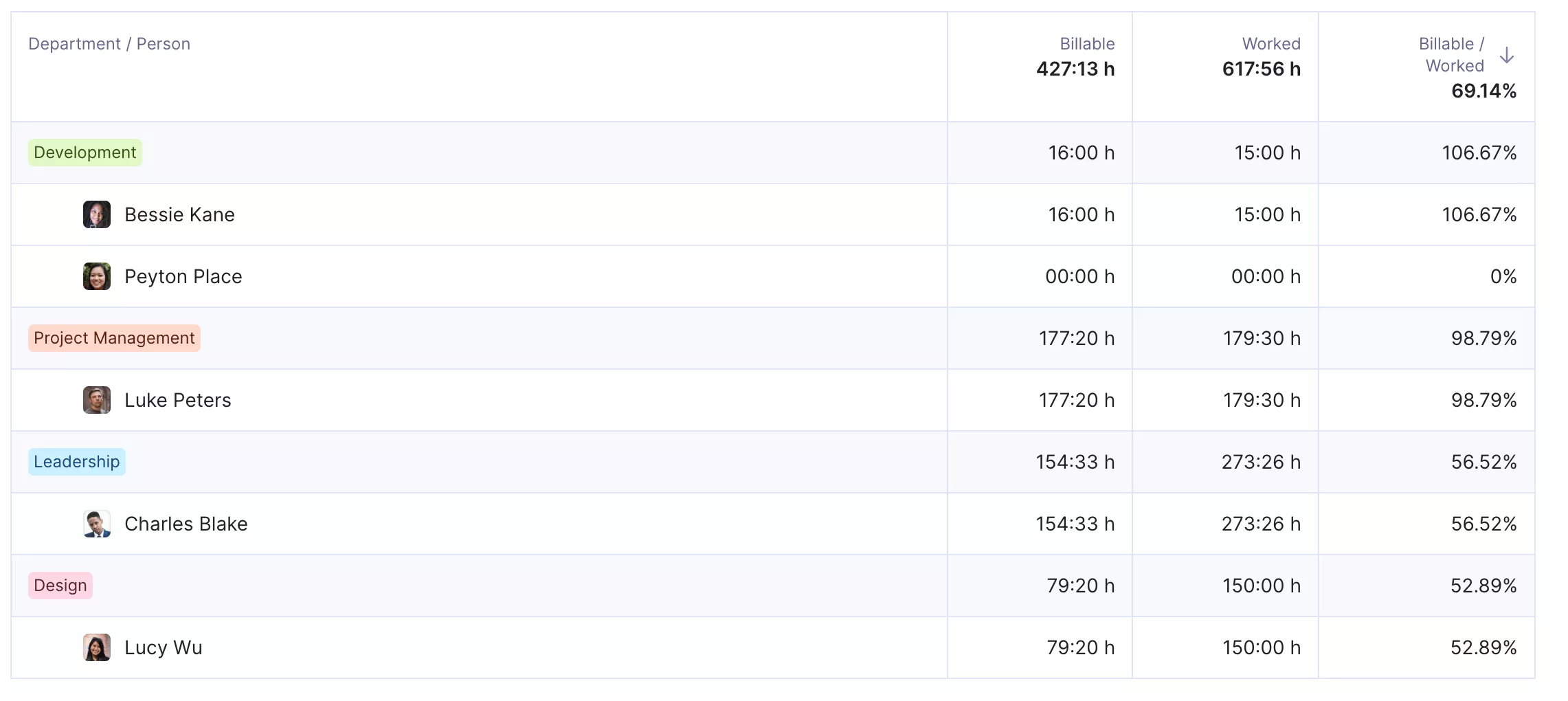
Productive gives you real-time resource utilization rates of your staff.
Step 2: Automate data collection
Connect tasks and time entries directly to your monitoring system. This removes manual updates and ensures numbers stay accurate. In Productive, dashboards update automatically as budgets and hours are logged, which means reports are always current and reliable.
Step 3: Share dashboards
Replace bulky reports with shared dashboards so stakeholders see progress in real time. Keep them simple and role‑specific: project managers can focus on workload and budgets, while executives only see overall status.
A shared dashboard makes monitoring and controlling much easier.
Monitor and manage projects with Productive
How To Build Real-Time Dashboards for Monitoring Reports?
You can build a project dashboard for project monitoring by combining the right metrics, clear visuals, and automated updates. A good dashboard gives you and your stakeholders an instant view of project health without digging through reports.
Instead of waiting for a weekly summary, you can see real-time progress, risks, and resource use as they happen.
A project dashboard works best when it pulls in live data from tasks, time tracking, and budgets. That way, it becomes a project monitoring system rather than just another static report.
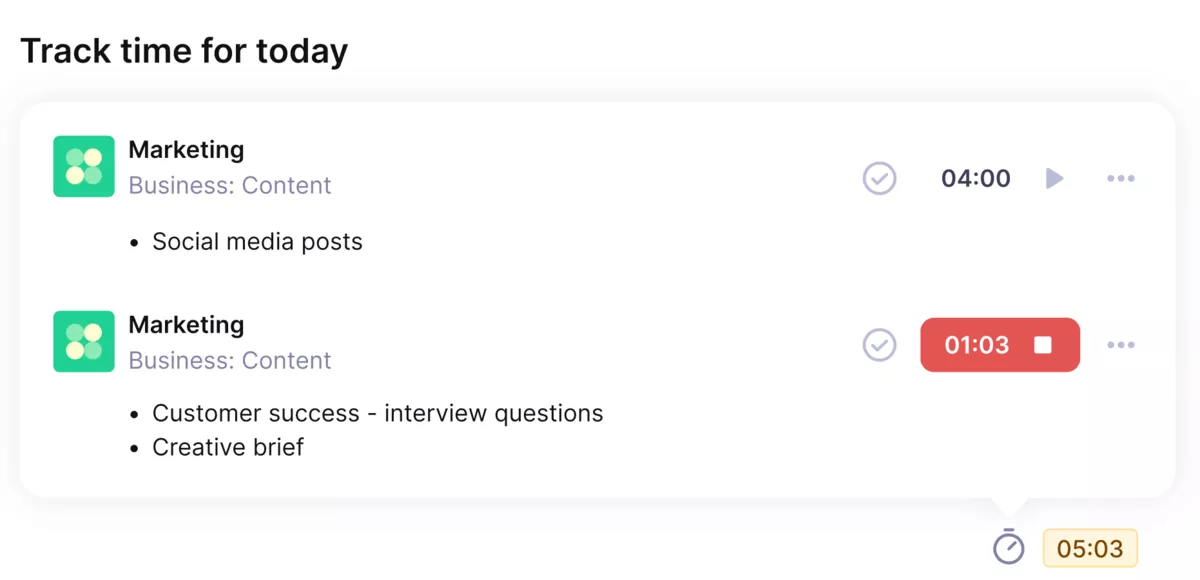
Use Productive’s automated time tracking.
Using monitoring tools that update automatically reduces reporting fatigue and keeps everyone aligned. In Productive, dashboards show budgets, hours, and tasks in one place so project managers and teams can act quickly when something drifts off plan.
What Data Should Go on a Project Dashboard?
- Budget vs actuals: A core metric that shows cost control in real time and highlights when spending starts to drift.
- Time tracking data: Another essential metric that links logged hours to estimates, so you know when a project is drifting and can act early.
- Task progress: Percent complete against milestones to flag delivery risks and keep the project plan realistic.
- Earned Value Management (EVM): Combines cost and schedule into one performance monitoring view, giving you a metric that shows both efficiency and progress at the same time.
- Open issues and risks: Keep attention on what might delay or derail the project so teams can prioritize fixes.
In Productive, time tracking flows directly into reports and dashboards, so budget and effort metrics always reflect reality. Earned value management can also be reviewed here alongside other metrics for a full picture of project health.
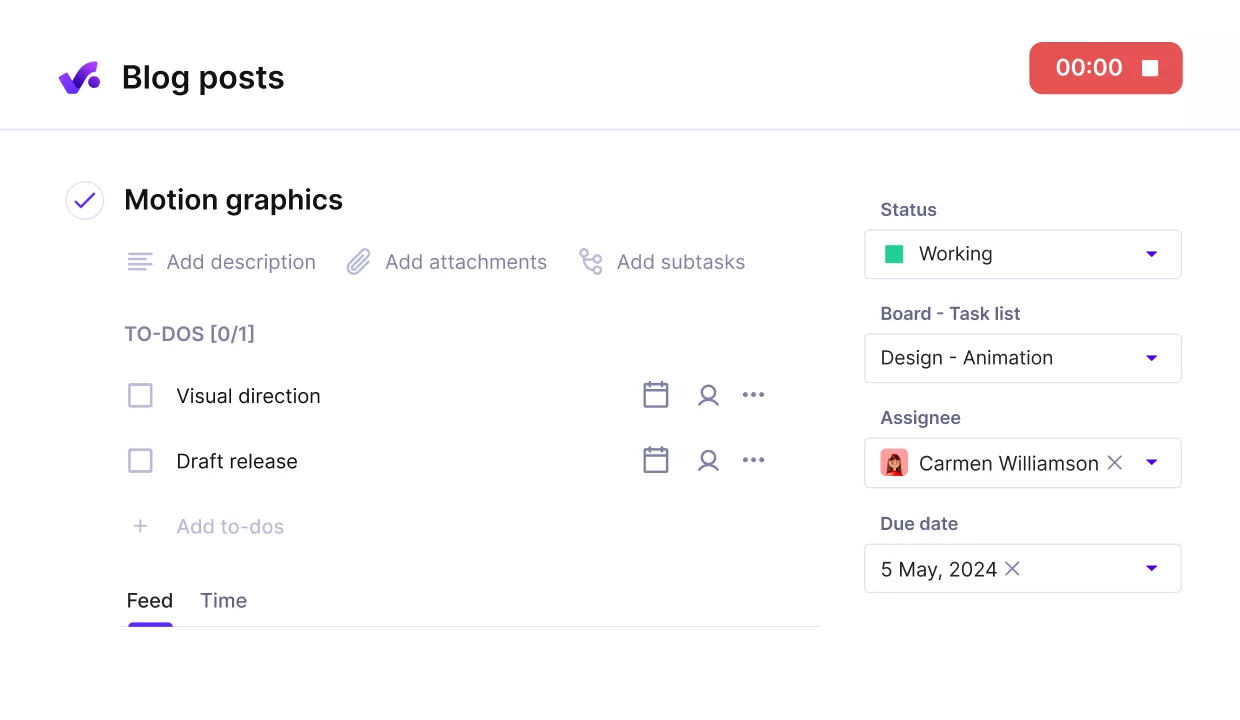
Keep all project data tied and tracked directly on tasks.
Tips for Designing Dashboards
A project management dashboard is useful when it highlights the information people need to make timely decisions. Here are our tips to make it more effective:
- Role-based views: Give executives a high-level overview and project managers more detail.
- Simple layout: Limit each view to a handful of widgets so the signal isn’t lost in noise.
- Automated refresh: Data should update automatically without extra input. In Productive, dashboards act as a single source of truth for budgets, hours, and tasks.
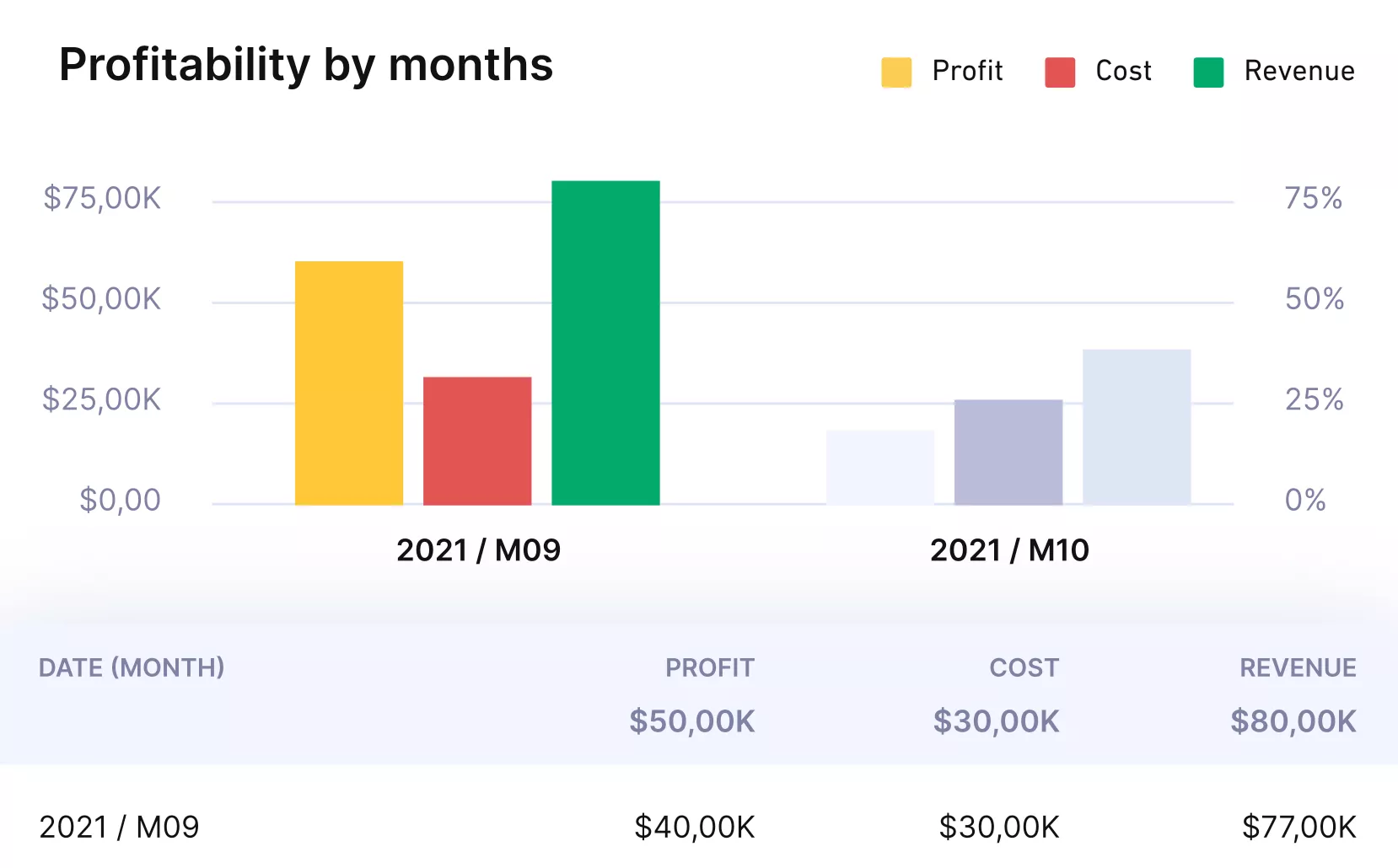
Get real time updates on budgets and profitability.
How To Measure ROI of Project Monitoring?
The ROI of project monitoring is measured in saved costs, improved deadlines, and reduced scope creep. When you treat monitoring as a structured process, you can connect it directly to profitability.
The steps below show how to evaluate whether your monitoring efforts are paying off.
1. Project Audit
A project audit gives you a snapshot of how your monitoring process is working. Instead of being a paperwork exercise, it’s a chance to see if your monitoring setup actually changes outcomes.
For example, did risk reports trigger timely fixes, or did issues still slip through?
How to implement:
Schedule an audit at key milestones, like the halfway point of a large project. Interview the team to check whether reports were clear and actionable. Review if flagged issues were resolved quickly or ignored. Add what you’ve learned to your risk management strategies.
2. Project Review
A project post-mortem review helps you look back at how well the project delivered against the plan. It measures whether deadlines, budgets, and resources are aligned with expectations.
For example, you might find that design tasks took 20% longer than estimated, or that weekly reporting kept the client aligned and reduced project scope disputes.
How to implement:
After delivery, sit down with the project team and client. Compare baseline budgets and project schedules with actuals and capture lessons learned. Note what worked (like automated time tracking) and what caused friction.
In Productive, you can pull side‑by‑side reports showing planned vs actual costs and project timelines to make reviews factual and faster.
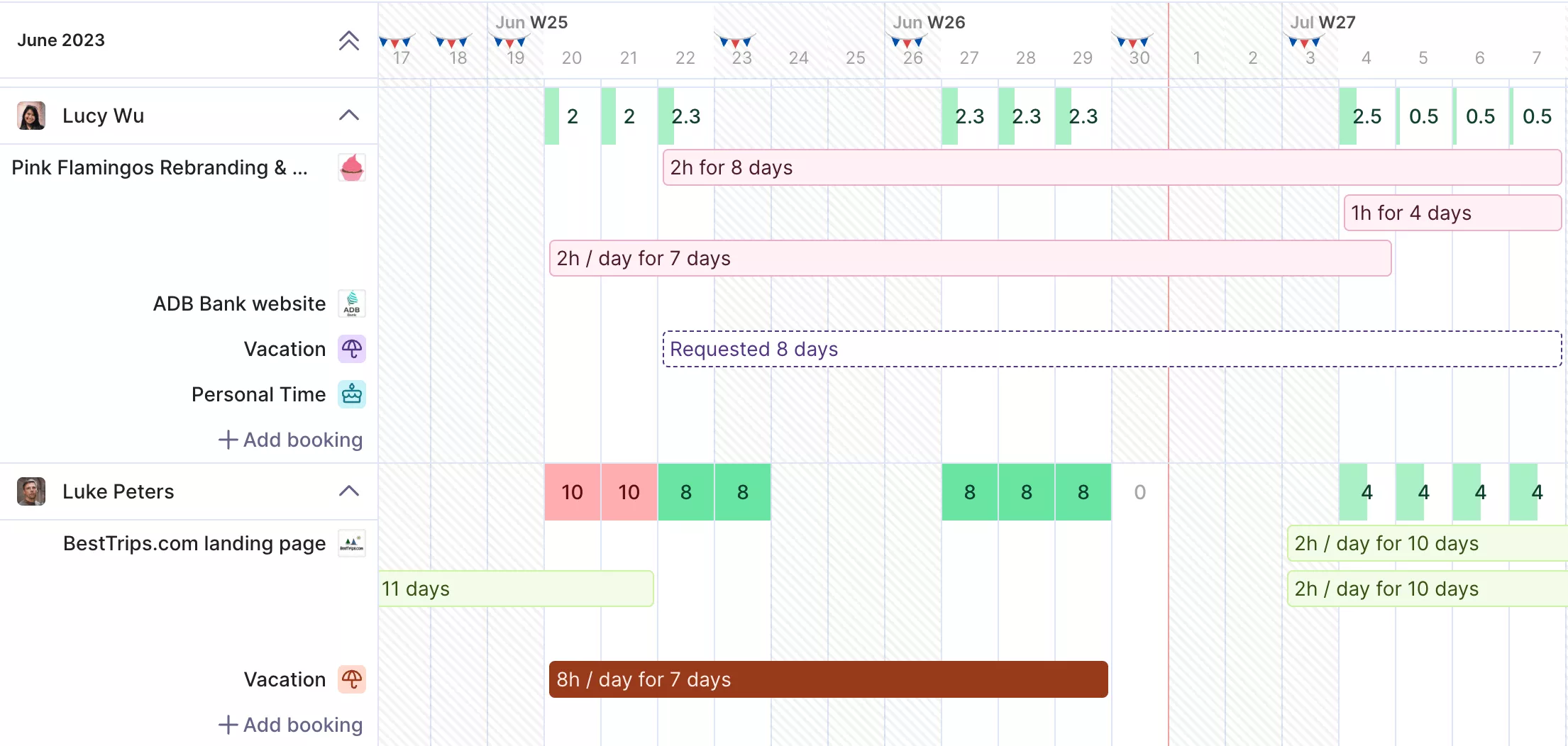
Get a real-time overview of your available resources and capacity.
3. Monitoring Evaluation
Monitoring evaluation ties everything back to business value. The question is simple: did monitoring save money, reduce delays, and protect profit margins?
For example, spotting a budget variance early might have saved $10,000 in overrun, or weekly variance checks might have cut delivery time by two weeks.
How to implement:
Quantify benefits in numbers: hours of rework avoided, costs saved, revenue protected. Compare the profitability of projects with strong monitoring against those with weak or no monitoring.
What Are the Best Tools for Monitoring Projects?
The best tools for project monitoring include all-in-one project management software, specialized project monitoring tools, and time tracking software.
Each type supports monitoring in different ways:
- Project management software centralizes tasks and budgets.
- Reporting systems create dashboards and scheduled updates.
- Time tracking tools show how resources are actually spent.
Productive combines all three (time tracking, resource planning, and dashboards) into one project monitoring system. This reduces tool sprawl and ensures updates flow automatically instead of relying on manual collection.
For example, instead of exporting spreadsheets for a weekly report, you can open a budget monitoring dashboard that already shows budget vs actuals and logged hours. We talk more about the best tools in our in-depth reporting software comparison.
When choosing tools, look at how much reporting effort they eliminate and whether they fit the way your team works. Agencies with multiple projects or clients often get the most value from all-in-one platforms because they reduce context switching and keep monitoring lean.
Must-Have Features in Project Monitoring Tools
- Real-time dashboards with budget vs actuals.
- Integrated time tracking that updates reports automatically.
- Resource management and planning to see workloads and capacity.
- Automated reports (weekly or monthly).
- Risk and issue tracking that surfaces problems early.
- Role-based access so stakeholders see what matters to them.
Closing Thoughts
Project monitoring and controlling are all about high visibility and being proactive.
However, you shouldn’t waste time and effort on numbers that don’t influence decision-making. Pick KPIs that drive decisions, automate updates, and make sure monitoring ties directly to priorities.
If you want to cut reporting effort and keep your team focused on delivery, book a short 30-min demo with Productive and get started today.
Keep monitoring lean and useful with Productive
Monitor budget burn, utilization, milestones, and open risks. Productive turns monitoring into a simple daily habit.